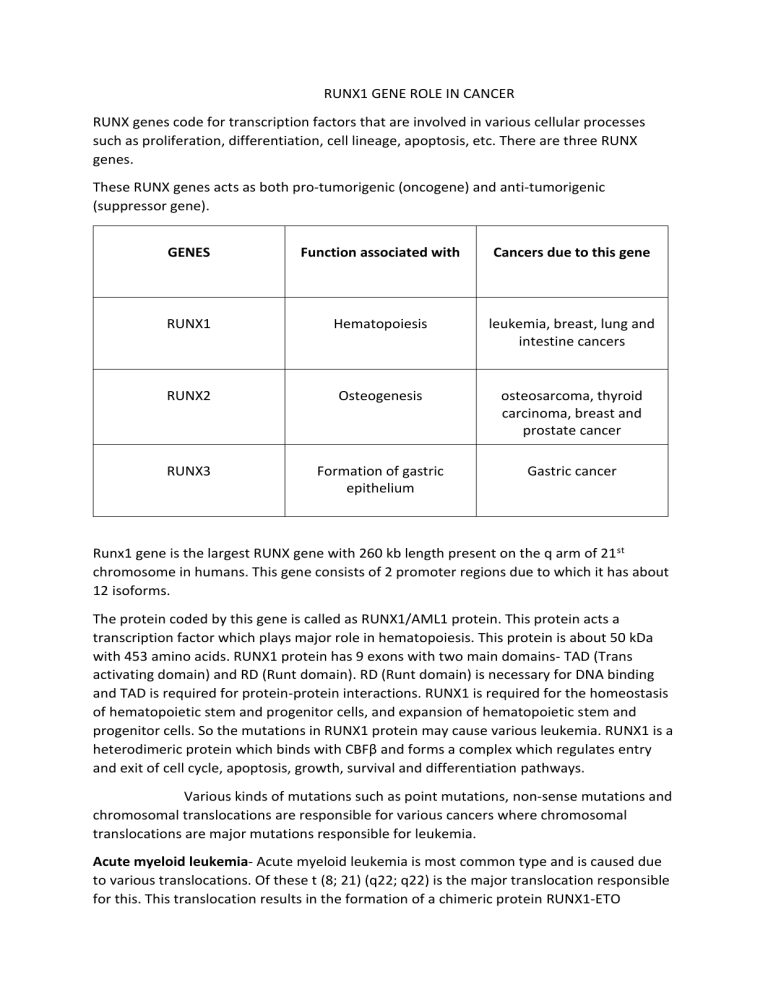
RUNX1 GENE ROLE IN CANCER RUNX genes code for transcription factors that are involved in various cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, cell lineage, apoptosis, etc. There are three RUNX genes. These RUNX genes acts as both pro-tumorigenic (oncogene) and anti-tumorigenic (suppressor gene). GENES Function associated with Cancers due to this gene RUNX1 Hematopoiesis leukemia, breast, lung and intestine cancers RUNX2 Osteogenesis osteosarcoma, thyroid carcinoma, breast and prostate cancer RUNX3 Formation of gastric epithelium Gastric cancer Runx1 gene is the largest RUNX gene with 260 kb length present on the q arm of 21 st chromosome in humans. This gene consists of 2 promoter regions due to which it has about 12 isoforms. The protein coded by this gene is called as RUNX1/AML1 protein. This protein acts a transcription factor which plays major role in hematopoiesis. This protein is about 50 kDa with 453 amino acids. RUNX1 protein has 9 exons with two main domains- TAD (Trans activating domain) and RD (Runt domain). RD (Runt domain) is necessary for DNA binding and TAD is required for protein-protein interactions. RUNX1 is required for the homeostasis of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells, and expansion of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. So the mutations in RUNX1 protein may cause various leukemia. RUNX1 is a heterodimeric protein which binds with CBFβ and forms a complex which regulates entry and exit of cell cycle, apoptosis, growth, survival and differentiation pathways. Various kinds of mutations such as point mutations, non-sense mutations and chromosomal translocations are responsible for various cancers where chromosomal translocations are major mutations responsible for leukemia. Acute myeloid leukemia- Acute myeloid leukemia is most common type and is caused due to various translocations. Of these t (8; 21) (q22; q22) is the major translocation responsible for this. This translocation results in the formation of a chimeric protein RUNX1-ETO (CBFA2T1 protein). This chimeric protein consists of RD domain of RUNX1 and NHR1, NHR2, NHR3, NHR4 of ETO protein. The RD domain helps in binding with target genes of RUNX1 but because of lack of TAD domain instead of transcriptional activator it acts as transcriptional repressor. This protein also downregulates the DNA repair enzyme OGG1 which leads to additional abnormalities required for development of AML. This chimeric protein represses CEBPα which is necessary for differentiation of myeloid progenitors and activates AP-1 subunit which promotes leukemic self-renewal and expansion.




