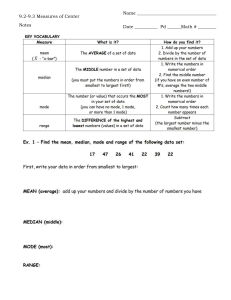
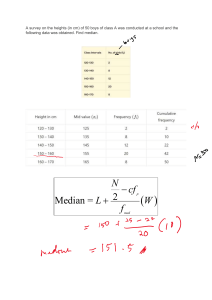
Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, presenting, analyzing, and interpreting numerical data to assist in making more effective decisions. Types of Statistics Descriptive Statistics- method of organizing, summarizing, presenting, data in an informative way. Inferential Statistics- A decision, estimate, prediction or generalization about a population, based on a sample. Population is a collection of all possible individuals, objects or measurement of interest. A sample is the portion, or part, of the population of interest. Types of Variables: the data can have a qualitative or attribute variable and quantitative variable. Quantitative variables can be further classified as discrete variable or continuous variable. Discrete variable- assume certain values where there are gaps between values. Continuous Variable- assume any value within a specified range. Levels of measurement aid on how the data could be summarized and presented and also helps to determine the type of statistical analysis that can be performed on the data. There are four levels of measurement of data: 1. Nominal- classified into categories but cannot be arranged in order. 2. Ordinal- data arranged in order but difference of values are meaningless or cannot be determined. 3. Interval- similar to ordinal but difference of values have meaning that can be determined. Moreover, there is no natural zero point. 4. Ratio- interval level with an inherent zero starting point. Differences and ratios are meaningful for this level of measurement. Arithmetic mean is the widely used measure of location. It requires an interval scale. It is the only measure of central tendency where the sum of the deviations of each value from the mean is zero. For ungrouped data, the population mean is the sum of all the values in the population divided by the total number of population values. For ungrouped data, the sample mean is the sum of all the sample values divided by the number of sample values. The median is the midpoint of values after the data has been arranged from the smallest to the largest. The mode is the value of the observation that appears most frequently. Measure of Shape Skewness the extent of asymmetry in the distribution. If the distribution is symmetric then it is not skewed. Mean=Median=Mode- Symmetric Mean>Median>Mode- Positively Skewed Mean<Median<Mode- Negatively Skewed Dispersion- reasons to study dispersion It is the measure of location of mean or median that is only describing the center of the data. The dispersion in a set of data helps to compare the spread of data in two or more distributions. Measures of Dispersion: Range- the largest value- smallest value