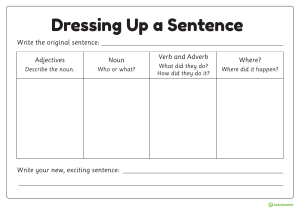
Parts of speech A category to which a word is assigned in accordance with its syntactic functions. In English the main parts of speech are: 1. Noun 2. Pronoun 3. Adjective 4. Determiner 5. Verb 6. Adverb 7. Preposition 8. Conjunction and 9. Interjection. Noun A noun is a word that represents a person, thing, concept, or place. Examples of nouns include names, locations, objects in the physical world, or objects and concepts that do not exist in the physical world Here are some examples: person: man, woman, teacher, John, Rijan. place: home, office, town, countryside, America. thing: table, car, banana, money, music, love, dog, monkey. Pronoun A pronoun is a word that can replace a noun in a sentence. The noun that is replaced by a pronoun is called an antecedent. For example, in the sentence I love my dog because he is a good boy, the word he is a pronoun that replaces the noun dog. Here are some examples: I, he, him, you, we, him, her, yours, theirs, someone, where, when, yourselves, themselves, oneself, is, hers, when, whom, whose, each other, one another, everyone, nobody, none, each, anywhere, anyone, nothing, etc. Adjective An adjective is a word that modifies or describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives can be used to describe the qualities of someone or something independently or in comparison to something else. Here are some examples: 1. good 2. new 3. first 4. last 5. long 6. great 7. little 8. own 9. other o They live in a beautiful house. o Lisa is wearing a sleeveless shirt today. This soup is not edible. o She wore a beautiful dress. o He writes meaningless letters. o This shop is much nicer. Determiner A determiner is a word that is used to modify or introduce the noun in a sentence. It mostly acts like an adjective in that it refers to the noun. Determiners include articles, adjectives of quantity, demonstrative adjectives, possessive adjectives, etc Here are some examples: The man is behaving so strangely. These apples are good. His father is out of the city. Jim is her brother. It's my book. Which is your car? Those mangoes are rotten. This plan will work. Verb A verb is the action or state of being in a sentence. Verbs can be expressed in different tenses, depending on when the action is being performed. Here are some examples: Run. Dance. Slide. Jump. Think. Salman is going home. ... Rijan is writing a novel about the wildlife of america. Kohli is playing cricket at the college tournament. He is riding his new bicycle all-day. Leave me alone! Preposition A preposition is a word or group of words used before a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase to show direction, time, place, location, spatial relationships, or to introduce an object. Some examples of prepositions are words like "in," "at," "on," "of," and "to." Here are some examples: above, across, against, along, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, by, down, from, in, into, near, of, off, on, to, toward, under, upon, with and within. The supermarket will be closed from 9 p.m. to 9 a.m. Can you come after some time? Will you be with Raimy or Mazeeka? I love sitting beside the beach at night. Rachel met Phoebe by the lake. Conjunction A conjunction is a word used to connect words, phrases and clauses. Common examples of conjunctions include and, but and or, although there are many other possibilities (including although). Here are some examples: And, or, so, since, for, because, as, but, yet, still, while, as soon as, therefore, moreover, in case, though, although, even though, etc. He had climbed many mountains when he was a boy. You are very late so that we can not start the lesson. I don’t know whether she’ll be admitted to the university. He had climbed many mountains when he was a boy. You don’t need to go unless you want to. Interjection An interjection is a word or phrase that is grammatically independent from the words around it, and mainly expresses feeling rather than meaning. Here are some examples: Hoorah! We won the match. Congratulations! You have a baby girl. Oh! We lost him. Yeah! I got her number. Jesus! You saved me from those culprits. Good! Now we can start a new beginning. Hey! Get out of the car. Yes! You are right. Adverb An adverb is a word that modifies (describes) a verb (he sings loudly), an adjective (very tall), another adverb (ended too quickly), or even a whole sentence (Fortunately, I had brought an umbrella). Here are some examples: Quickly, slowly, yesterday, last week, here, there, today, daily, never, rarely, extremely, annually John looked around but he couldn't see the monkey. I searched everywhere I could think of. I'm going back to school. Come in! They built a house nearby. She took the child outside.