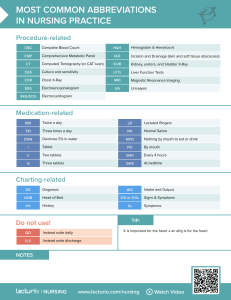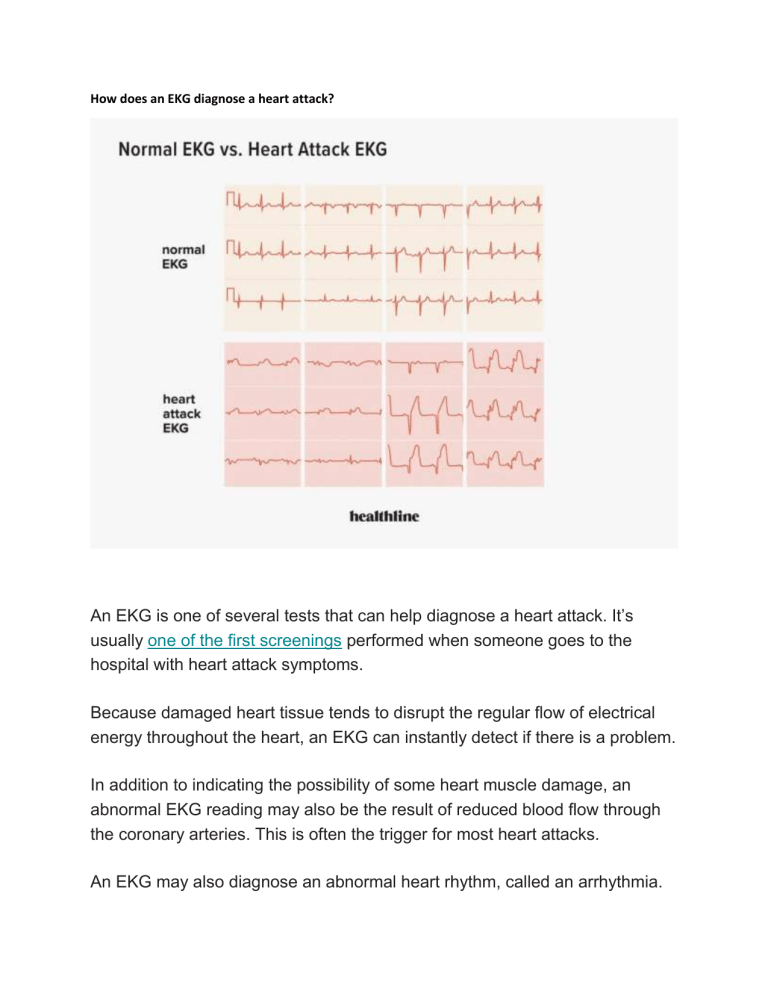
How does an EKG diagnose a heart attack? An EKG is one of several tests that can help diagnose a heart attack. It’s usually one of the first screenings performed when someone goes to the hospital with heart attack symptoms. Because damaged heart tissue tends to disrupt the regular flow of electrical energy throughout the heart, an EKG can instantly detect if there is a problem. In addition to indicating the possibility of some heart muscle damage, an abnormal EKG reading may also be the result of reduced blood flow through the coronary arteries. This is often the trigger for most heart attacks. An EKG may also diagnose an abnormal heart rhythm, called an arrhythmia. In addition to an EKG, a blood test is also done if a heart attack is suspected. Damaged heart tissue usually releases certain proteins called troponins. Unusually high levels of troponin T and troponin I are often a sign of a heart attack.