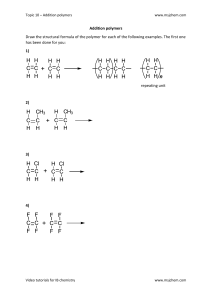
Welcome to World University Of Bangladesh Department of TE, CE and EEE Course title: Chemistry Presented by Dr. Jahida Binte Islam Senior Lecturer in Chemistry Basic Science Division Topics: Polymer Chemistry Definition of Polymer, Mer, Monomer Basic criteria that monomers generally fulfill in products high polymersClassification of Polymer- Addition polymer & Condensation polymer Distinguish between addition and condensation polymerization Application of polymers Polymer chemistry Sub-discipline of chemistry that focuses on the structures of chemicals, chemical synthesis, and chemical and physical properties of polymers and macromolecules. A polymer always consists of thousands of repeating monomers units. However a macromolecule is a giant molecule which may or may not contain monomer units. Polymer Definition: Polymer is a large molecule built up by the repetition of small and simple chemical units and contains high molecular Weight. For example: CH2- CH2- CH2- CH2-Polyethylene Mer: The repeating unit in a polymer chain is known as mer. It is a simple chemical entity and does not exist in normal condition. For example: In polyethylene the repeating unit is -CH2-CH2-, which is not existence in normal condition. Thus, -CH2-CH2- is a mer. Monomer: The simple compounds from which polymers are obtained are called monomers. For Example: n CH2=CH2 → [-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-]n Monomer Polymer Classification of Polymer Classify polymers according to their physical properties--Polymers are classified on the basis of their physical properties or on the action of heat are on three categoriesi. Thermoplastics ii. Elastomers iii. Thermosetting Classify polymers on the basis of structural units--- Polymers are classified on the basis of structural units are two categoriesi. Homo polymers ii. Copolymers Classify polymers on the basis of mode of synthesis--Classify polymers on the basis of mode of synthesis are two categoriesi. Addition polymers ii. Condensation polymers Addition polymer & Condensation polymer Addition polymers: The polymerization process in which the formation of polymers from monomers without the loss of Small molecules, i.e.; in which molecules of monomers are simply added together is called additional polymerization and such polymers are known as addition polymer. For example-- The molecules of ethylene monomer can add on two form polyethylene, in which, the structural identity of ethylene is retained. n CH2=CH2 → [-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-]n Condensation polymers: The polymerization process in which the formation of polymers from the poly functional monomers of organic molecules with the elimination of some small molecules such as, water, HCl, NH3, etc. is called condensation polymerization and the product is called condensation polymer. For Example: n HO-CH2-CH2-OH + n HO-C-CH2-C-OH → HO-(-CH2-CH2-O-C-CH2-C-O)n-H + (n-1)H2O Ethylene glycol Malonic acid Distinguish between addition and condensation polymerization1 Polymers are formed by addition 1 reaction without elimination of any species. Polymers are formed by the indentation of two or more monomers with the elimination of small molecules such as –H2O, NH3, HCL etc. 2 It is a rapid process. It is very slow process. 3 Addition polymerization proceeds by 3 chain mechanism. Condensation polymerization proceed by stepwise inter molecular condensation. 4 Polymers of high molecular weight 4 obtained by additional polymerization. Low molecular weights polymers are obtained by condensation polymerization. 5 Chain length is independent of time. Chain length is dependent on time. 6 The rate of addition polymerization 6 reaction is controlled by the addition of inhibitor or retarder. 2 5 The rate of condensation polymerization reaction is not controlled by such chemicals. Application of polymers: Medicine: Many biomaterials, especially heart valve replacements and blood vessels are made of polymers like Dacron, Teflon and polyurethane. Consumer Science: Plastic containers of all shapes and sizes are light weight and economically expensive than the more traditional containers. Clothing, floor coverings, garbage disposal bags and packaging are other polymer application. Industry: Automobile parts, windshield for fighter planes, pipes, tanks, packing materials, insulation, wood substitutes, adhesive, matrix for composites and elastomers are all polymer application used in the industrial market. Sports: Playground equipment, various balls, golf clubs, swimming pools and protective helmets.
![\t<L Your Name: _[printed]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/013223479_1-5f2dc062f9b1decaffac7397375b3984-300x300.png)