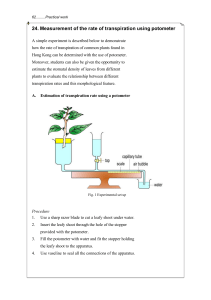
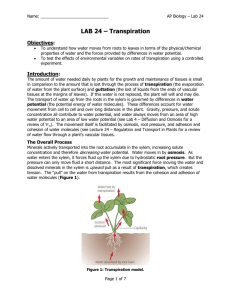
A potometer, also known as a transpirometer, is a device used to measure the rate of transpiration, or the rate of water loss from a plant's leaves. Potometer readings are typically affected by environmental factors such as temperature, light, humidity, breeziness, and the plant's available water supply. Inserting a leaf-bearing plant stem snugly into a piece of plastic tubing and connecting the tubing to a pipette, or graduated length of glass tubing, full of water, yields a very simple potometer. Potometers are frequently assembled underwater, with everything submerged except the leaves, to prevent any air from entering the apparatus. The level of water in the pipette changes over time.