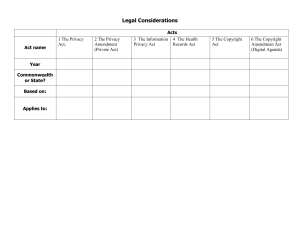
Name: _________________________ ISEC 412-51 Exam #1 Section 1: Multiple Choice (3 Points Each) 1) A(n) ________ investigation is an inquiry held within the confines of organization, that is not meant for public review. A) federal B) judicial C) military D) internal E) none of the above 2) The ________ of an investigation defines precisely what can be searched and what is being looked for. A) scope B) principles C) mediator D) regulator E) none of the above 3) A person cannot self-incriminate themselves in a court of law, because of the: A) First Amendment. B) Fourth Amendment. C) Fifth Amendment. D) Legislated Privacy Act. E) none of the above. 4) The ________, regulates the rights of an individual regarding searches and seizures, as it states that most searches require a warrant. A) First Amendment B) Fourth Amendment C) Fifth Amendment D) Legislated Privacy Act E) none of the above 5) Under the ________, a material witness can only present testimony actually seen or heard first-hand. A) First Amendment B) Fourth Amendment C) Fifth Amendment D) Legislated Privacy Act E) none of the above 1 6) According to the Plain View Doctrine, an officer executing a legally issued arrest or search warrant may seize unrelated evidence if it is: A) deemed fair. B) announced to the suspect. C) located near the scene of the crime. D) found in plain sight. E) none of the above. 7) Which of the following is not one of the ‘particularity requirements’ that are needed when applying for a warrant? A) What is being sought? B) Who is the investigator of the search? C) Where it is expected to be found? D) Who is the target of the search? E) none of the above 8) Which of the following is not one of the four types of privileged information? A) Attorney/Client Privilege B) Teacher/Student Privilege C) Physician/Patient Privilege D) Work-Product Doctrine E) None of the above 9) A ________’s purpose is to suppress evidence based on argument that investigating team corrupted by viewing records it had no right to see. A) civil defender B) legal aid C) judge D) taint team E) none of the above 10) What are the two things that need to be defined in the scope of a warrant? A) Particularity and size B) Size and breadth C) Size and depth D) Particularity and breadth E) None of the above 2 Section 2: Short Answer (5 Points Each) 1) Discuss the differences between the two main types of forensic investigations. 2) List the five types of documentation during an investigation. Give a real-world example of each. 3) How can you tell if a search was ‘unreasonable’? 3 4) Discuss between the two views on passwords during searches. 5) What are the four primary domains of an individual’s right to privacy? 6) Differentiate between ‘warrants’ and ‘subpoenas’. 4 7) What are the four circumstances in which a warrantless search can be undertaken? Give a brief example for each. 8) What are the four types of privacy laws? Give two real-world examples of such legislations. 9) List and describe the Four Keys to Admissibility. 5 10) Name and describe the three approaches to defining ‘plain view’. 6 Section 3: Essay (20 Points) 1) i) Compare and contrast between Kruse and Heiser’s Basic model, and the Casey Model. ii) What steps/tasks are required in each step? 7