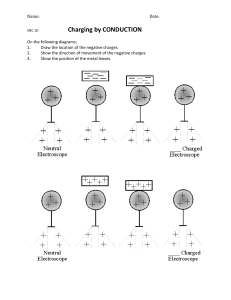
Galileo Galilei pioneered the experimental scientific method and was the first to use a refracting telescope to make important astronomical discoveries. He is often referred to as the “father of modern astronomy” and the “father of modern physics”. Albert Einstein called Galileo the “father of modern science.” ELECTRIC CHARGE General Physics 2 l Quarter 3 l Lecture 1 Lesson 1.1 STATIC ELECTRICITY occurs when an object obtain a net amount of positive and negative electric charges Lightning Strike STATIC ELECTRICITY Electrostatics is the interactions between electric charges that are at rest. CHARGES The two types of electric charge were positive and negative by the American statesman, philosopher, and scientist Benjamin Franklin (1706-1790) Thus, a normal and LAW OF CONSEVATION OF CHARGES Electrons are never created nor destroyed, but are simply transferred from one material to another. Charging by Friction When two different insulating materials are rubbed, electrons get transferred from one body to another. Charging by Contact The process of giving one object a net electric charge by placing it in contact with another object that is already charged. Charging by Polarization Electric polarization refers to the separation of center of positive charge and the center of negative charge in a material. Charging by Induction A charging method that charges an object without actually touching the object to any other charged object. GROUNDING The process of removing the excess charge on an object by means of the transfer of electrons between it and another object of substantial size. When a charged object is grounded, the excess charge is balanced by the transfer of electrons between the charged object and a ground. ELECTRICAL FORCES (Coulomb’s Law) COULOMB’s LAW The magnitude of the electric force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Charles-Augustin de Coulomb NEXT LESSON…