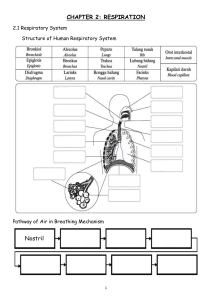
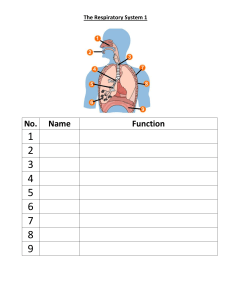
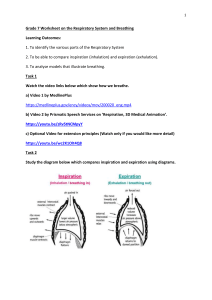
Fundamental Physiology of the Respiratory System Diaphram – Muscular sheath Phrenic Nerve – Important for regulation Alveolar Organistaion Elastic fibre – help expand and contract Alveoli and capillary fused together – reduce distance Macrophage – filter the air Fine membranes are not only at the lungs but also down at respiring tissues Oxygen moves from high concentration to a low concentration Three steps of respiration: 1. Pulmonary ventilation 2. External respiration 3. Internal respiration Divisions of the respiratory tract: Anatomical Upper and lower part Functional Conducting portion Respiratory Portion Damage to pherenic nerve can be very dangerous Three main factors affecting compliance: 1. Levels of surfactant production 2. Connective tissue structure 3. Mobility of thoracic cage The two MODES of quiet breathing: 1. Diaphragmatic (deep) breathing 2. Costal (shallow) breathing Gases are transported in the blood as: Oxyhaemoglobin CO2 dissolved in plasma Carbamonohaemoglobin Bicarbonate ions Major factors regulating O2 – Hb saturation are: Co2 pH Temperature Two main centres that control breathing: 1. Rhythmicity area 2. Pneumotactic area Three important clinical tests: 1. Forced expiratory flow 2. Forced aspiratory flow 3. Peak expiratory flow