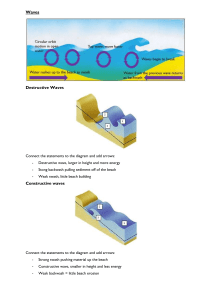
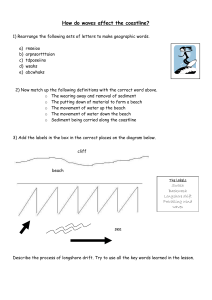
Coastal processes Wave card sort: Constructive wave Steep beach profile More frequent waves Strong backwash carries away lots of sediment Smaller wave height Strong swash moves sediment up the beach Steep angle of wave break scours material away Destructive wave Weak backwash carries away little sediment Larger wave height Waves break less often due to shallow wave angle Gentle beach profile Less frequent waves Weak swash moves little sediment up the beach ---------------------------------- -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Wave card sort: Constructive wave Steep beach profile More frequent waves Strong backwash carries away lots of sediment Smaller wave height Strong swash moves sediment up the beach Steep angle of wave break scours material away Destructive wave Weak backwash carries away little sediment Larger wave height Waves break less often due to shallow wave angle Gentle beach profile Less frequent waves Weak swash moves little sediment up the beach © www.teachitgeography.co.uk 2017 29466 Page 1 of 1 Coastal processes Wave terminology Define these key terms: Fetch: ............................................................................................................. Swash: ............................................................................................................. Backwash: ........................................................................................................ Wave characteristics Using the card sort, complete your table below. Constructive waves Destructive waves Diagram of constructive wave Diagram of destructive wave © www.teachitgeography.co.uk 2017 29466 Page 2 of 2 Coastal processes Look at the diagram below: sea Key B Strong wind Light wind 27 10 A X C 10 How long has it been blowing (hours) land Which wave do you feel would produce the largest wave? Why? ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... Which wind do you feel would produce the smallest wave? Why? ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... Weathering processes: What is weathering? ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... Write a definition of each of the types of weathering. Chemical weathering: .......................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... Biological weathering: ......................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... Mechanical (physical) weathering: .......................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... © www.teachitgeography.co.uk 2017 29466 Page 3 of 3 Coastal processes Mass movement: What is mass movement? ..................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... Write a definition of each of the types of mass movements: Soil creep: ....................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... Slumping: ........................................................................................................ ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... Rock falls:......................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... Coastal erosion: What factors affect the rate of coastal erosion? .......................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... Match up the type of coastal erosion with its definition: Hydraulic power/action Rocks and pebbles are carried by the waves and hit against one another, breaking into smaller and smoother particles. Abrasion Air and water become trapped in the joints and cracks of the cliff. When the wave breaks, the trapped air compresses and weakens the rock causing erosion. Attrition Acids (salts) within the sea water dissolve some types of rock (chalk/limestone) easily eroding them. Solution Bits of rock and sand in the waves and thrown onto the cliffs and beach and act like sandpaper to grind down the cliff surface. © www.teachitgeography.co.uk 2017 29466 Page 4 of 4 Coastal processes Coastal transportation: Sort these statements into the correct order (1 - 6) to explain the process of longshore drift, then annotate the diagram below to explain it in your own words. The sediment is carried up the beach (swash) at the same angle as the waves Longshore drift is a process of transportation The action of the swash and backwash create a zig zag motion along the beach Waves approach the coastline at an angle Slowly the sediment moves along the beach The waves then drag the sediment back down the beach (backwash) at right angles Land Sediment movement Direction of the longshore drift Swash Shoreline Backwash Sea Direction of the prevailing wind © www.teachitgeography.co.uk 2017 29466 Page 5 of 5 Coastal processes Annotate this diagram with the four different types of coastal transportation: Solution Suspension Traction Saltation Sea bed/beach Coastal deposition: What is coastal deposition? ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... When is coastal deposition most likely to occur? ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................... © www.teachitgeography.co.uk 2017 29466 Page 6 of 6