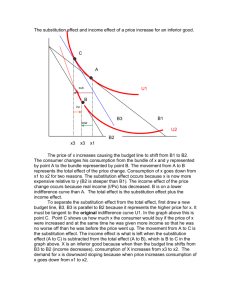
4장 연습문제 1. Suppose the utility function for a firm manager is U = π + bQ, where Q is output, π is profit, and b is a positive constant. How would the firm's output compare with what it would be if the manager's objective was to maximize profit? A. It would be greater than the profit-maximizing output. B. It would be less than the profit-maximizing output. C. It would be the same as the profit-maximizing output. D. None of the preceding statements is correct. 2. Suppose a consumer with an income of $100 is faced with Px = 1 and Py = 1/2. What is the market rate of substitution between good X (horizontal axis) and good Y (vertical axis)? A. 0.50 B. -1.0 C. -2.0 D. -4.0 3. The difference between a price decrease and an increase in income is that A. A price decrease does not affect the consumption of other goods, while an increase in income does. B. An increase in income does not affect the slope of the budget line, while a decrease in price does change the slope. C. A price decrease decreases real income, while an increase in income increases real income. D. A price decrease leaves real income unchanged, while an increase in income increases real income. 4. Joe prefers a three-pack of soda to a six-pack. What properties does this preference violate? A. Completeness B. Transitivity C. More is better D. Diminishing MRS 5. Which of the following is true? A. Indifference curves may intersect. B. At a point of consumer equilibrium, the MRS always equals 1. C. If income increases, a consumer will always consume more of a good. D. None of the preceding statements is correct. 6. If the price of good X is $10 and the price of good Y is $5, how much of good X will the consumer purchase if her income is $15? A. 0 B. 2 C. 3 D. Cannot tell based on the above information. 7. Individuals who purchase services and goods for the purpose of consumption are: A. consumers. B. managers. C. workers. D. agents. 8. What is/are the important things that must be developed when characterizing consumer behavior? A. Individual goals of the firm B. Consumer opportunities C. Individual goals of the firm and consumer opportunities D. Consumer preferences and consumer opportunities 9. The possible goods and services a consumer can afford to consume represents the: A. consumer behavior. B. consumer preferences. C. consumer status. D. consumer opportunities. 10. A situation where a consumer says he does not know his preference ordering for bundles X and Y would violate the property of: A. more is better. B. completeness. C. substitutability. D. complementarity. 11. The affordable bundle that yields the greatest satisfaction to the consumer is: A. the maximum bundle. B. the equilibrium consumption bundle. C. the allowable purchasing bundle. D. the most popular bundle. 12. The absolute value of the slope of the indifference curve is called the: A. marginal revenue. B. average rate of substitution. C. marginal rate of substitution. D. marginal cost. 13. An increase in the price of good X will have what effect on the budget line on a normal XY graph? A. A parallel outward shift of the line B. An increase in the vertical intercept C. A decrease in the horizontal intercept D. A parallel inward shift of the line 14. The property that implies that indifference curves are convex to the origin is:3 A. more is better. B. completeness. C. transitivity. D. diminishing marginal rate of substitution. 15. Which of the following cases violates the property of transitivity? A. A∽B, B∽C, A∽C. B. A≻B, B≻C, A≻C. C. A≻B, B≻C, C≻A. D. None of the statements violates the transitivity property. 16. The property that rules out indifference curves that cross is: A. completeness. B. transitivity. C. diminishing marginal rate of substitution. D. independence. 17. The idea that a consumer is limited to selecting a bundle of goods that is affordable is captured by the: A. budget constraint. B. indifference curve. C. consumer equilibrium. D. price changes. 18. The combinations of goods X and Y that are affordable to the consumer are defined by the: A. consumption set. B. income line. C. budget constraint. D. budget set. 19. What is the maximum amount of good Y that can be purchased if X and Y are the only two goods available for purchase and Px = $5, Py = $10, X = 20, and M = 500? A. 40 B. 25 C. 50 D. 75 20. The upper boundary of the budget set is the: A. indifference curve. B. origin. C. budget line. D. vertical intercept