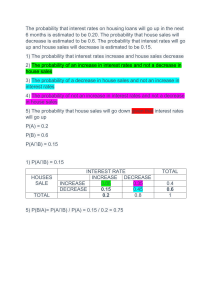
lOMoARcPSD|19240621 Prelim - Credit and Collection Bachelor of Science in Business Management Major in Financial Management (North Eastern Mindanao State University) Studocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university Downloaded by Michelle Jean Flores Albiso (albisomichellejeanf12@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|19240621 THE FUNDAMENTALS OF CREDIT WHAT CREDIT IS? Credit is the privilege of using someone else’s money for a period of time. That privilege is Based on the belief that the person receiving credit will honour a promise to repay the amount Owed at a future date. TYPES OF CREDIT If you borrow money to be used for some special purpose, you are using loan credit. If you Charge a purchase at the time you buy the good or service, you are using sales credit. Trade Credit is used by a business when it receives goods from a wholesaler and pays for them at a Later specified date. USERS OF CREDIT If you as a typical American consumer, you will use credit for many purposes. You may use Credit to buy fairly expensive products that will last for a long time, such as a car, house, or major appliance. Or you may use credit for convenience in making smaller purchases, such as meals and CDs. Paying for medical care, vacations, taxes, and even paying off other debts are other common uses of credit. CREDIT INFORMATION The business that is considering you as a credit risk will generally ask you about your financial Situation and request credit references. THE THREE Cs of CREDIT Character- refers to your honesty and willingness to pay a debt when it is due Capacity- refers to your ability to pay a debt when it is due Capital- is the value of the borrower’s possessions BENEFITS OF CREDIT TO BUSINESSES Businesses benefit in several ways. By being allowed to buy on credit, customers will tend to Purchase more, and the business will increase its profits. If the business buys its merchandise Using trade credit, the merchandise can be paid for after it has been sold to customers. Downloaded by Michelle Jean Flores Albiso (albisomichellejeanf12@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|19240621 BENEFITS OF CREDIT TO CUSTOMERS Ways in which consumers benefit from their use of credit: Convenience- credit can make it convenient for you to buy. There may be times when you do not have enough cash and have a need for something. Immediate possession- credit allows you to have immediate possession of the item that you want. Savings- Credit allows you to buy an item when it goes on sale, possibly at a much lower price. Credit rating- if you buy on credit and pay your bills when they are due, you gain a reputation for being dependable Useful in an emergence- access to credit can help you in an emergence. Having an oil company credit card, for example, can come in handy when you run out of gas and cash at the time. PRECAUTIONS FOR USE OF CREDIT Some problems as a consumer can encounter with unwise use of credit include the following: Overbuying- overbuying is one of the most common hazards of using credit. There are several Ways in which this happens. You may purchase something that is more expensive than you can afford. Or you may be tempted to buy items you don’t really need. Careless buying- careless buying may result if you become lazy in your shopping. Credit can tempt you not to wait for a better price on an item you want. Higher prices- higher prices may be paid. Stores that sell only for cash are able to sell at lower Prices than stores that offer credit. Extending credit is expensive. It requires good account to Keep accurate records of each charge sale and each payment. Downloaded by Michelle Jean Flores Albiso (albisomichellejeanf12@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|19240621 Overuse of credit- overuse of credit can result in too much being owed. Buying now and paying Late may sound like a good idea; but if too many payments are to be made later, the total amount that must be paid can become a problem. Credit- is the privilege of using someone else’s money for a period of time Debtor- anyone who buys on credit or receives a loan Trust- means that the creditor believes that the debtor will honour the promise to pay later Goods and services that have been received and used Loan credit- if you borrow money to be used for some special purpose Sales credit- if you charge a purchase at eh time you buy the good or service Trade credit- is used by a business when it receives goods from a wholesaler and pays for them at a later specified date. Credit references- are businesses or individuals from whom you have received credit in the Past and/or who can help verify your credit record Character- refers to your honesty and willingness to pay a debt when it is due Capacity- refers to your ability to pay a debt when it is due Capital- is the value of the borrower’s possessions Credit rating- if you buy on credit and pay your bills when they are due, you gain a possession For being dependable. In that way, you establish a favorable credit rating. USES OF CREDIT REVOLVING ACCOUNT: Are purchases that can charged at any time but only part of the debt need be paid each month? There is usually a maximum amount which is owed at one particular time. A monthly payment Is required. A finance charge is included to use this type of credit. Downloaded by Michelle Jean Flores Albiso (albisomichellejeanf12@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|19240621 BANK CARDS—these have become quite popular over the past several years the most Common used are VISA and MasterCard. There is usually an annual fee for the privilege of Using these cards. TRAVEL & ENTERTAIMENT—Carte Blance, Diners Club and American Express are the most Widely used entertainment credit cards. A yearly membership fee is charged for use of these Credit cards and it is higher than the annual fee charge by bank cards. These are used for Motels, hotels, restaurants etc. OIL COMPANY CARDS—such as Texaco, Chevron, Shell and Stinker Stations issue their Own unique credit cards. Many oil companies that it costs them way too much to offer credit. So they have left that to credit card companies which is their specialties. RETAIL STORE CARDS—many retail stores are now carrying their own cards. They carry the Name of the department or retail store involved. These are usually very high interest and are Referred to as the “single-purpose” credit cards. USES OF CREDIT CONSUMER LOANS INSTALLMENT LOANS—is one in which you agree to make a certain amount of monthly Payment. SINGLE PAYMENT LOANS—you don’t pay anything until the end of the loan period. PROMISSORY NOTE—is a written promise to pay based on the “debtor’s” excellent credit Rating. COLLATERAL—is a security deposit. Something of value is put against the loan so in the Event it isn’t repaid the company can acquire the property. SECURED LOAN—is simply some type of property that is put up against the loan. COSIGNER—is someone who signs on additionally to a loan and promises to pay if the person Who is first on the loan does not. TOPIC 2 CREDIT HISTORY OVERVIEW, DEFINITION, AND BRIEF HISTORY Downloaded by Michelle Jean Flores Albiso (albisomichellejeanf12@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|19240621 Credit history (also called credit report) is a very important aspect of life. Some people do not Understand the importance of credit history until they are denied credit. Situations like this do Not happen when consumers have a full understanding of their credit and credit history. Every Aspect of credit plays an important role in whether or not creditors lend credit to customers. Credit History Definition & Overview Consumers’ credit history is kept in a document known as the credit report. Credit history is An in depth account of how well lenders manage their credit. When creditors extend credit to Their consumers, they keep a record of the payment history and report is to one of the 3 credit Agencies. Late payments and missed payments are reported to the credit agencies who in Turn record the information on the credit report. The report of customers’ credit history is Available to them to see as well as potential lenders who may be considering lending credit to Customers. Credit history makes up the largest percentage of a credit scores. Consumers Should know that credit history accounts for 35% of a credit score. Consumers should know that their credit history consists of past and present accounts. Do not Think for one second that paying off bills automatically increases the credit score. Credit history Consists of open and closed accounts on mortgages, credit cards, and loans. Credit history Can remain on the credit report for many years after the late or missed payments. Bankruptcies And defaulted loans also play a part in credit history. Something else can lead to lower credit scores that can affect credit history: high credit Balances. Just because payments are always on time does not mean that credit history Remains intact. When cardholders have less than 50% of available credit on their credit cards, Their credit score lowers. For example, a credit card with a $1,000 credit limit with only $300 Of available credit can hurt credit history. The History of Credit Reports/Credit The practice of offering consumer credit began during the 18th century. Western Union started The first official credit system of the modern age in 1914. Many other large companies followed In Western Union’s path. World War II created the need for an established credit system. Businesses began to grown after World War II so there was a great need for more credit in the economy. The establishment of the credit system began to strengthen. Consumer credit use created the need for a universal system that allowed lenders to share Credit information about their customers in order to make good credit decisions. The first credit Agencies consisted of non-profit groups Downloaded by Michelle Jean Flores Albiso (albisomichellejeanf12@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|19240621 owned by participating merchants. By the 1970s, there Were over 2,000 credit reporting agencies around the country. During that same time, large Companies that offered credit created their own systems to maintain credit records, which Limited credit decision agencies around the country. The record keeping became very time Consuming so these large companies moved to consolidating these agencies on a national And regional basis. By 1998, there were more than 500 credit bureaus in the United States. The three main credit scores that emerged were Trans Union, Equifax, and Experian. Why Credit History Matters Credit history determines whether lenders extend credit. It is important that consumers Understand that credit history accounts for the largest portion of a credit score. The first thing That potential lenders look at is the payment history on the credit report. Late payments, Defaults, and bankruptcy send up red flags for potential lenders. Credit history may affect interest rates. Lenders offer their best interest rates on mortgages, Car loans, and credit cards to those with the best credit ratings. Those with credit histories that Reflect high credit limits and late payments may still qualify for credit, but they may receive the Highest interest rates on the market. Good credit history is necessary for customers who want to purchase homes. Many people Dream of owning their own home. That dream may never come for those with a poor credit History. High interest rates can make a significant difference on large investments such as Homes. Good credit history can save consumers thousands of dollars in interest along with The monthly payments. Credit history is important to consumers who want to receive credit. Mistakes on credit reports That can affect credit history are very common. It is very important that consumers receive a Credit report from each of the three credit agencies each year to assure that their credit history Is correct. Once consumers ruin their credit history, it is extremely hard to get back on track. Always use credit wisely. TOPIC 3 Credit Banking: Meaning, Functions and Purpose of Credit Banking Credit: Meaning and Functions: With the introduction and use of money credit also came into existence. Credit is created when One party (a person, a firm or an Downloaded by Michelle Jean Flores Albiso (albisomichellejeanf12@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|19240621 institution) lends money to another party, the borrower. Thus, Credit is generally understood to mean the finance provided to others at a certain rate of Interest. The act of lending and borrowing creates both credit and debit. Whereas debt means the Obligation to pay the finance borrowed, the credit means the claim to receive these money Payments from the other party. Every credit involves debt, that is, obligation to pay money and Therefore creates claim. The act of borrowing and lending and thereby the creation of credit is a special type of Exchange transaction which involves future payment of the principal sum borrowed as well as The rate of interest on it. The lending and borrowing of money and the institution of money Lending came into vogue ever since money was invented by man. In the modern times there Are a variety of institutions which specialise in borrowing and lending of money. The bank credit is only one form of credit. Money lenders, indigenous bankers, credit Cooperative societies, commercial and cooperative banks, industrial financial institutions, L.I.C. export finance houses etc. are all credit institutions and do the business of borrowing And lending money. Different credit institutions lend money for different purposes and are Collectively called the financial system. Thus commercial banks are only one segment, though An important one, of the financial or credit system of an economy. Credit institutions can be differentiated according to the type and purpose of credit they offer. There are credit institutions which lend money only for agriculture. There are others which Provide credit only to industries and still others to finance exports only. Credit institutions also differ in respect of the duration of period for which they lend money to Their clients. Some provide short-term credit, some mediumterm credit and others only long-term credit. We shall study only one type of creditinstitution, namely, the commercial banks. Functions of Credit: The main function of credit is to relieve the constraint imposed by balanced budgets on Economic agents, that is, to meet the financial requirements of investors who have to spend More on trade and investment than their own savings. Accordingly, it is through the means of credit that the surplus funds with some individuals and Institutions are made available to the deficit spenders, that is, those who are required to spend More than their resources, for instance, traders, companies, Downloaded by Michelle Jean Flores Albiso (albisomichellejeanf12@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|19240621 investors. It is the performance of this function, that is, the transferring surplus funds of some to meet The spending by the businessmen and investors, that the banking and other segments of the Financial system are able to promote savings and investment, to ensure better allocation of Financial resources and thereby to encourage economic growth in the economy. But, for the Credit system to perform these functions, it needs to be efficiently managed and controlled. If credit is not efficiently managed, it can cause inflation or deflation, recession and Unemployment in the economy. Besides, the mismanagement of credit can lead to Misallocation of investible resources and thereby hinder economic growth. It can also cause Concen-tration of economic power in a few hands and exploitation of weaker sections and thus Work against the achievement of social justice. Purpose or End-Uses of Credit: Credit is required for different purposes and by all sectors of the economy. Therefore, there is Need for the proper allocation of credit between different uses and sectors if the society is to Achieve its objectives. When credit is demanded and used for productive purposes, it may be Used to finance the needs of working capital or for fixed investment (i.e. capital equipment, Machinery etc.). The broad categories of economic activity for which credit for productive pur-poses is Demanded are: (a) Agriculture,. (b) Industry, (c).Construction, and (d) Trade, both domestic and foreign Further, in each of these categories, the allocation of credit between different users is of crucial Importance from the viewpoint of economic growth and social justice. Thus, in agriculture Allocation of credit between large landowners and small farmers has been a matter of serious Debate. Likewise, the allocation of credit between the large-scale industries and small- scale Industries has been a major concern in India’s credit policy. Credit policy in India in recent years has emphasised certain priority sectors such as Agriculture, small Downloaded by Michelle Jean Flores Albiso (albisomichellejeanf12@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|19240621 scale industries, export and weaker sections of society such as small and Marginal farmers, young entrepreneurs for whom greater amount of credit is to be made available. TOPIC 4 CLASSIFICATION OF CREDIT The major sources of credit can be classified into institutional or formal and noninstitutional Sources. Non-Institutional The non-institutional or informal sources are those which do not have any uniformity in their Lending procedure, their interest rate or their collateral requirement. Loan from such sources Are usually made directly to the borrower by the lender and are prevalent in areas where Individuals are quite familiar with and share confidence in one another. In other words, the Lender knows the borrower and reasonably vouch-safe for his (borrower’s) integrity. The Relative ease of obtaining the loans devoid of administrative delays, non-insistence by the Lender on security or collateral from the borrower and flexibility built into repayment Programmes has made the non-institutional sources very popular among the peasant farmers. Non-institutional sources however have such limitations as smallness of loan, high interest Rates etc. Notable examples under this source include -Merry go rounds These are funds to which a group of individuals sharing common characteristic make a Contribution of a fixed amount of money, handed to one person. Each member is able to make Use of the money in turn, making allowance for a member in dire need of a loan or advance. These are granted without interest payment. Downloaded by Michelle Jean Flores Albiso (albisomichellejeanf12@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|19240621 -Money Lenders These people usually make their money outside the rural community but later settle down in Villages giving loans to farmers at exorbitant interest rates. Some farmers who pledge their Lands, crops and buildings have lost them due to their inability to pay the high interest rates Charged on the principal when due. -Friends and Relatives This is part of cultural heritage whereby the prosperous help their less fortunate relatives and Friends with loans. In some cases, the loan is not collected back. Institutional Sources The institutional sources are those recognized institutions which follow standardized Procedures of lending. They lend at regulated interest but normally require some collateral. The loans from this source are always large compared with those obtained from non institutional sources. Under this sources include -Cooperatives Formal cooperatives can be regarded as a transition or an interphase between formal and Informal credit sources. Cooperatives especially savings and credit cooperatives (SACCOS) Also play an important role in saving. -Commercial Banks These are institutions set up by the government or group of private individuals with the aim of Accepting savings and deposit from members of the public as well as granting them credit Whenever they are in need. Those farmers who keep their money in such banks may be able To get loan from the bank. But due to the inability of most farmers to offer suitable collateral Security coupled with the risky and uncertainty nature of agricultural business, commercial Banks often prefer to lend to borrowers engaged in non – agricultural ventures which are less Prone to risk and uncertainty. -Specialise Banks Downloaded by Michelle Jean Flores Albiso (albisomichellejeanf12@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|19240621 These are institutions specially set up to meet the need of a particular sector of the economy. For instance, the Agricultural Finance Corporation (AFC) was specifically established to cater .For the agricultural sector of the economy 1. Short-term Loans. The short- term loans purchases like are generally advanced to meeting annual recurring Seeds, feeds, fertilizers, hired labour, expenses on herbicides, pesticides and machinery Service charges. It is therefore termed “seasonal loans or production loans or crop loans” and It is usually expected that the loans (principal) and the interest would be repaid through the Income received through the enterprise in which it is invested. Time limit to repay such a loan Is usually one year or at most 18 months. 2. Medium-term Loans Are advanced for comparatively longer span assets like machines, wells, threshers, sheds for Livestock, shelter, farm structures, irrigation structures etc. The returns accrued from the use Of such assets are usually spread over more than one production season. Repayment period Spans between 15 months and 5 years. 3. Long-term Loans These are related to long life assets like land, farm buildings construction of permanent Drainages or irrigation system etc. which require large sum of money as initial investment. Benefits generated through such assets are spread over the entire life span of the asset. Repayment period ranges from 5 years to 20 years. Classification according to Purpose of the Loan Credit could be classified based on the purpose of the loan such as crop loan, Poultry/dairy/piggery loan, machinery and equipment loan, forestry loan, fishery loans etc. This Type of loan signifies relationship between time of usage and the rate of returns (profitability).Sometimes loans could be classified as “production loan” or “consumption loan. Downloaded by Michelle Jean Flores Albiso (albisomichellejeanf12@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|19240621 Classification according to Security offered Loans can be classified as secured and unsecured loans. Securities are usually advanced Against tangible assets like land, livestock or any capital asset, as either medium or long term Loans. Note that credit worthiness may sometimes count much more than the security offered, Which if doubtful, may result in wilful default. Secured loans can be further classified on the Basis of the type of security offered as: Mortgage loans: Where legal mortgage of tangible and intangible properties like land, land Improvement and other infrastructures are offered. (ii) Hypothecated loans: Where legal ownership of assets e.g. machinery and equipment, Financed remains with the lender though physically possessed by the borrowers. Promissory Note A promissory note is the primary legal document in most loan contract. It is the written promise Of the borrower to repay the loan. When advancing loan funds, the lender receives in exchange A note signed by the borrower promising to pay the lender a certain stated principal with Interest on a certain date as specified in the note. Mortgages This is ranked second to the promissory note. It is not only an additional note but a Complement. A mortgage is a list of certain property set aside to guarantee the payment of a Loan which is set in a promissory note. Mortgages are identical to promissory note in their chief Provisions. They are also sometime called indentures. The mortgage in addition to identifying The property to back up the promissory note contains provisions which establish a priority of Claims among lenders according to the filling or according the mortgage in a court of law. Sometimes a Downloaded by Michelle Jean Flores Albiso (albisomichellejeanf12@gmail.com) lOMoARcPSD|19240621 bond and not a promissory note accompanies the mortgage but the general Effect is the same. There are several types of mortgages 1. Real Estate Mortgage: Real estate in law is land and laded property. The important Feature of real-estate mortgage is the unchanging character of the security. 2. Chattel Mortgage: These are mortgage on movable property such as animals. Purchase on Contract This is sometime simply referred to as hire purchase contract. This involves the transfer Contract Property to the buyer or the purchaser while with the title of the property remains with the seller Until the last instalment is paid. Hence purchase on contract is sometimes referred to as Conditional sales contract. Downloaded by Michelle Jean Flores Albiso (albisomichellejeanf12@gmail.com)