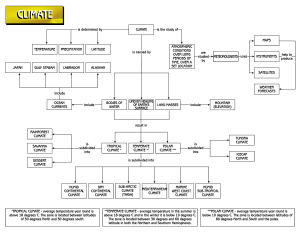
Grade 7 – Asian Studies Topic: Types of Climate Group Members: Angel Octaviano Stephanie Iheruo Meaning of Climate ▫ : a region of the earth having specified climatic conditions ▫ : the average course or condition of the weather at a place usually over a period of years as exhibited by temperature, wind, velocity, and precipitation ▫ : the long-term manifestations of weather and other atmospheric conditions in a given area or country 2 1. Temperate Climate Temperate Climate ▫ Temperate climates are generally defined as environments with moderate rainfall spread across the year or portion of the year with sporadic drought, mild to warm summers and cool to cold waters. ▫ Temperate Asia includes the Japanese islands, the Korean peninsula, Mongolia, most parts of China, and Russian Siberia. 4 The Mongolian-Manchurian grassland, also known as the Mongolian-Manchurian steppe or Gobi-Manchurian steppe, in the temperate grassland biome, is an eco-region in East Asia covering parts of Mongolia, the Chinese Autonomous region of Inner Mongolia, and Northeast China. 2. Maritime Temperate Climate Maritime Temperate Climate ▫ : also known as marine climate ▫ : is the Koppen classification of climate typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring mild summers and cool but not cold winters, with a relatively narrow annual temperature range and few extremes of temperature ▫ : places with maritime temperate climate include Thimphu, Bhutan and the Himalayas. 7 The vast size, huge altitude range, and complex topography of the Himalayas mean they experience a wide range of climates, from humid subtropical in the foothills to cold and dry desert conditions on the Tibetan side of the range. Using the Köppen climate classification, the lower elevations of the Himalayas, reaching in mid-elevations in central Nepal (including the Kathmandu valley), are classified as Cwa, Humid subtropical climate with dry winters. Higher up, most of the Himalayas have a subtropical highland climate (Cwb). 3. Mediterranean Climate Mediterranean Climate ▫ : also known as dry summer climate ▫ : is characterized by dry summers and mild, wet winters ▫ West Asia, Lebanon, Syria, Turkey and Israel experience Mediterranean climate. 10 Temperatures in Israel vary widely, especially during the winter. Coastal areas, such as those of Tel Aviv and Haifa, have a typical Mediterranean climate with cool, rainy winters and long, hot summers. The area of Beersheba and the Northern Negev have a semiarid climate with hot summers, cool winters, and fewer rainy days than the Mediterranean climate. The Southern Negev and the Arava areas have a desert climate with very hot, dry summers, and mild winters with few days of rain. Continental Climate Continental Climate ▫ : exist where cold air masses infiltrate during the winter and warm air masses form in summer under conditions of high sun and long days. ▫ Places with continental climates are as a rule are either far from any moderating effect of oceans or are so situated that prevailing winds tend to head offshore. ▫ Many places in Asia have continental climate including Beijing and Harbin, China, Seoul and Incheon, South Korea, and Sapporo, Japan. 13 Sapporo has a humid continental climate (Köppen), with a wide range of temperature between the summer and winter. Summers are generally warm and humid, but not oppressively hot, and winters are cold and very snowy, with an average snowfall of 4.79 m (15 ft 9 in) per year. Continental Subarctic or Tiaga Climate Continental Subarctic or Taigu Climate ▫ Continental subarctic climate, major climate type of the Köppen classification dominated by the winter season, a long, bitterly cold period with short, clear days, relatively little precipitation (mostly in the form of snow). ▫ Northern Mongolia and Northern China also have a subarctic climate. 16 Mongolia has a high elevation, with a cold and dry climate. It has an extreme continental climate with long, cold winters and short summers, during which most precipitation falls. Winter nights can drop to −40 °C (−40.0 °F) in most years. Thank you for listening to our presentation.