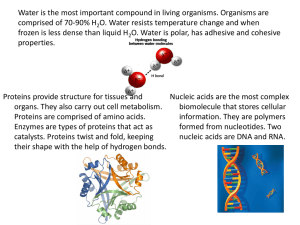
What is your favorite food? Introduction to Biomolecules What is Biomolecules? • Bio-means “life” • Molecules-means ‘two or more atoms” What is Biomolecules? • Any molecules that are produced by a living organisms, including large macromolecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. Four major categories of Biomolecules: • Carbohydrates • LIpids • Proteins • Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates • Most common biomolecule • Primary energy source of our body • Building block/momomer:monosaccharides • Elements: C-H-O Carbohydrates • Classifications: 1.Monosaccharides 2.Disaccharides 3.Polysaccharides Monosaccharides • Simple sugars (C6H12O6) Glocuse (blood sugar) Fructose (fruit sugar) Galactose (found in milk with glucose) Disaccharides • Double sugars (C12H22O11) Maltose (malt sugar) Lactose (milk sugar) Sucrose (table sugar) Starch • Used for energy storgae in plants • They provide a quick form of energy for the body Glycogen • Used for energy storage in animals • When the body doesn’t need glucose for energy, it stores in te liver and muscles in the form of glycogen Cellulose • Found in plants, in cell walls and bark of tress • Gives us fiber Chitin • Forms the exoskeleton of certain insects and crustaceans Proteins • Body-building molecules which help us grow • Transport molecules in and out of the cell • Control the speed of chemical reactions Proteins • Used for growth and repair • Buiding blocks: amino acids Proteins • General formula: RCH(NH2)COOH. R is a side chain, usually an amino acid • Elements: C-H-O-N Proteins • Enzymes Nucleic Acids • These biomolecules are not necessarily from food • Biomolecular components of hereditary materials and are present in DNA Nucleic Acids • Building blocks: nucleotides • Elements: C-H-O-N-P Lipids • Store more energy than carbohydrates and proteins • Building block: fatty acids • General formula: CH3(CH2)nCOOH • Elements:C-H-O Lipids • Examples: Steroids, cholesterol, fats, oils, nuts, waxes • They are hydrophobic Unsaturated Saturated Lipids What is biomolecules? What are the major functions of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acid? State the function of biological molecules in organisms. How will you justify carbohydrates as the most important biomolecules? or what do you think for you is considered as the most important biomolecules in our body?explain why. Activity Make a cartoon, or comic that tells a: a scary story a funny story an adventure story Objectives 1. Describe the function and structures of lipids, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and proteins. 2. Show the relationship between lipids, nucleic acids, proteins and carbohydrates including the elements that make up the molecules.