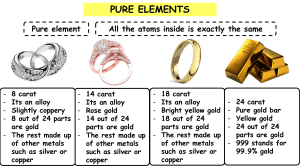
Learners’ Book Answers: Topic 5.3 Metal mixtures Getting started A B C is an element because there is only one type of atom present. is a compound because there are two types of atoms bonded together. is a mixture as there are two types of atom but they are not bonded together? D D is an element as there is only one type of atom present. Think like a scientist: Modelling a metal and an alloy 1 Answers will depend on how successful they are with the practical task. The bubbles should line up in rows, but do not encourage learners to simply give the expected answer at the expense of observations; in other words, learners should be credited for writing what they observed. 2 Other bubbles will move to fill the space. Again, credit what the learners observe. 3 Dependant on what they observe. The expectation is that the rows of bubbles move freely and slide across one another. 4 Dependant on what learners observe. The expectation is that the larger bubble disrupts the rows, so that the bubbles cannot move as freely. Questions 1 An alloy is a mixture of metals. 2 Aluminium is light and easily malleable, which makes it suitable for building planes. 3 An aluminium alloy is used because aluminium is not strong enough to withstand the stresses involved in flight. 4 24 carat gold has 24 parts out of 24 gold; there is no other metal present, so it is pure gold. 5 18 carat gold is an alloy made of 18 parts gold to 6 parts of another metal, such as silver or copper; 24 carat gold is pure gold. 6 Pure silver is not used for coins because it is too expensive and it is not hard enough to stand up to the damage that is caused when coins rub against one another in pockets, purses or vending or counting machines. 7 We don’t use pure copper for our coins because it is too expensive and too soft. Copper also reacts with the air and turns green. 8 Any alloy used inside the body, for example for hip replacements, must be strong and light, and not react with the body tissues. 9 Some glasses frames are made from shape memory alloy metal because they can easily be returned to their original shape by heating, if they get bent. 10 A range of temperatures is given because there is more than one type of bronze. These are made using different proportions of copper and tin, sometimes other metals are added. Each different mixture has a different melting point. 11 Credit any correct shared properties, such as: they are both alloys, have a range of forms and melting points, both contain copper, resistant to corrosion. 12 Credit any correct shared properties, such as: both elements; metals; conduct heat and electricity. 13 Credit any correct different property, such as: copper is reddish in colour whereas tin is white; tin is softer than copper; tin is not as good a conductor as copper; the melting point of copper is much higher (1085 °C) than that of tin (232 °C). Topic 5.5 Acids and alkalis Questions 1 Citrus fruits, tomatoes. Accept drinks such as cola and coffee. 2 They taste sour. 3 Corrosive means that it will dissolve your clothing and skin and cause chemical burns. 4 If you spill acid you should wash the area with lots of water. Topic 7.1 Microorganisms Questions 1 Viruses are not generally considered to be living organisms as they show none of the characteristics of living organisms apart from reproduction, which they can do only when inside a cell. 2 What we see on the surface of the fruit is a very large number of individual cells, i.e. – a colony. Each individual cell is a complete organism. We can only see these cells using a microscope. 3 The cells are arranged end-to-end in long threads. Learners may also mention the circular cells arranged in a sphere. 4 a Look for a drawing of one or two of the bluish-white cells. b Look for a drawing of one of the cells or threads with green colouring. c Labels should show that the plant-like cells have cell walls, and green colouring inside them (which is chlorophyll; the chloroplasts are not visible). Animal cells do not have these features. Think like a scientist: Growing microorganisms from the air 1 Nutrients are materials that organisms need for growth and to provide energy. 2 The purpose of this investigation is to grow microorganisms that have come from the air. You do not want to grow any microorganisms that were there before you took the lid off the dish. 3 Drawings will depend on what has grown on the agar jelly. Topic 7.2 Food chains and webs Getting started 1 Grass deer tiger 2 Leopard Tiger Deer Langur monke y Grass Questions 1 The food chain should show sunlight, then an arrow going to wheat, then an arrow to a chicken and finally an arrow to Arun. 2 This will depend on the learner’s choice of food. 3 Accept any food chain taken from the food web. 4 Acacia tree and grass 5 7 6 3 7 Any two from cheetah, leopard, hyena and aardvark. 8 Any two from: Cheetah (predator) and springbok, zebra or aardvark. Leopard (predator) and hyena, springbok, zebra or aardvark (prey). Aardvark(predator) and termites (prey). Hyena (predator) and springbok (prey). Think like a scientist: Using a food web as a model 1 Learners should recognise that a food web is useful for showing, in a simple and visual way, the feeding relationships between organisms. We can see how energy passes from one organism to another. They should also recognise that the food web is far from a complete representation of what actually occurs. In reality, many more organisms will be part of the web. The model also does not tell us how important each relationship is. For example, do leopards eat mostly hyenas, or are zebras their most important prey? Are sprinbok mostly killed by cheetahs, or are hyenas a more likely predator for them? Workbook Answers: Topic 5.3 Metal mixtures Exercise 5.3 Alloys 1 An alloy is a mixture of metals. 2 Accept any correct answers, such as bronze, nitinol (accept shape memory alloy), duralumin, 18 carat gold, cupronickel. 3 The atoms of iron in a solid piece of iron are lined up in regular rows with the atoms touching each other. The rows of atoms can slide over one another when they are hit. When atoms of another element, such as carbon, are added to the iron, they disrupt the regular pattern of the rows, so they do not slide over one another when they alloy is hit. This makes the alloy much stronger. Answers to this question will depend which alloy is chosen. Credit answers that address the questions in the Workbook and not just a copied list of information from the internet. 3 5.5 Acids and alkalis Exercise 5.5 Acids and alkalis 1 Acid Alkali citric acid, corrosive, nitric acid, sour, lemon juice, cola, vinegar, sharp, harmful sodium hydroxide, washing powder, harmful, corrosive, soap, washing soda Corrosive Safety point Reason wearing safety glasses To protect eyes from sparks and splashes. standing up to work If you spill anything it will not be in your lap. placing bottle stoppers upside down on the bench So that you do not get the chemical on the work surface or dirt into the bottle. 2. 3. Flammable Safety point Reason replacing the bottle stopper as soon as you have finished using the bottle So that you are less likely to have a spill if you knock the bottle over and so that you do not mix up which stopper belongs on which bottle and you do not contaminate the chemicals. working in an orderly way So that you are less likely to have an accident, or mix up what you are doing and use the wrong chemical. Unit 7 Microorganisms in the environment Exercise 7.2B Building up a food web – humans stingrays helmet snails sea urchins queen conch pen shells sea grass phytoplankton 6 Sea grass and phytoplankton 7 Any two of: sea urchins, pen shells, queen conch 8 Any two of: helmet snails, stingrays, humans