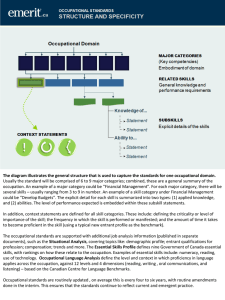
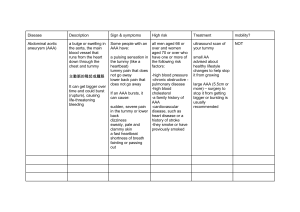
Introduction • The essence of engaging in any work or occupation is to earn a living and enjoy life. Hence, understanding the relation and interaction between work and health is very important in the practice of occupational health and safety • Emphasis here is that work can bring both positive and negative effects to man depending on the health and safety measures put in place. Definition • Occupational health refers to the sum total of activities and program that are engaged upon aiming to attain and maintain the highest level of health and safety for all people who are engaged in any type of work whatever. • ILO expert committee sees it as the promotion and maintenance of the highest degree of physical, mental and social wellbeing of workers in all occupations. Definition Cont’d In summary, it is referred to as all measures adopted or taken to adapt work to man and each man to his job. Reasons for Occupational Health • The rationale for occupational health is to ensure that workers health is safeguarded in their work environment and this can be achieved by providing health care services for the workers at their work place. AIMS AND OBJECTIVES As stated by Joint Committee of World Organization and International Labor Organization: The promotion and maintenance of the highest degree of physical, mental and social well-being of workers in all occupations. The prevention among workers of departure from health caused by their working conditions. Protection The protection of workers in their occupation from risks adverse to health. The planning and maintenance of workers in an occupational environment adopted to his physiological equipment. The adaption of work to man and each man to his job. The point here is that the working environment must be conducive because it often influences the workers state of health. Workers ability to perform their duties satisfactorily depends on the type of environment they are working or accommodated during the working hours.