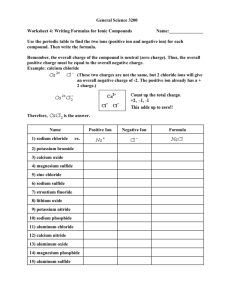
Worksheet ___ - Naming Ionic Compounds Part 1 (Binary compounds with Group 1, 2 or 13 metals) Binary compounds: have only two kinds of elements, if there are three or more it is not a binary compound. Naming 1. Metal goes first and you get the name directly from the periodic table. 2. Non-metal goes second. The ending changes to “ide” Name of element Name at end of compound Name of element Name at end of compound Fluorine Chlorine Bromine Iodine Fluoride Chloride Bromide Iodide Oxygen Sulfur Nitrogen Phosphorus Oxide Sulfide Nitride Phosphide Write the chemical formula for each of the following. 1. lithium chloride 2. beryllium chloride 3. sodium oxide 4. potassium sulfide 5. magnesium phosphide 6. aluminum fluoride 7. calcium nitride 8. magnesium oxide 9. beryllium nitride 10. potassium carbide 11. potassium nitride 12. potassium fluoride 13. aluminum nitride 14. sodium fluoride 15. calcium carbide 16. barium bromide 17. francium phosphide 18. gallium sulfide Write the chemical names of the following compounds. 1. LiF 2. Li2O 3. AlP 4. NaCl 5. K2S 6. Ca3N2 7. MgO 8. BeS 9. Ca2C 10. Li4C 11. AlF3 12. KBr 13. Ga2O3 14. CsI 15. SrAt2 16. Rb3P 17. BaS 18. Al4C3 Worksheet ____ - Naming Ionic Compounds Part 2 (Binary compounds with Group 3 - 12 metals) Naming (STOCK SYSTEM) 1. Metal goes first and you get the name directly from the periodic table. 2. Immediately after the metal in brackets write the charge of the metal ion in roman numerals. 3. Non-metal goes second. The ending changes to “ide” The metals in Groups 3 – 12 can have more then one charge on the ion (polyvalent ions) so when you name them you have to add in the charge of the metal ion by using roman numerals. This method of naming is called the stock system and is used only for the polyvalent ions. There is another method of naming the polyvalent ions, which we will look at in part 3 of naming ionic compounds. Element Antimony Arsenic Cobalt Copper Gold Iron Cations Sb3+ Sb5+ As3+ As5+ Co2+ Co3+ Cu+ Cu2+ Au+ Au3+ Fe2+ Fe3+ Example Name of Cation Antimony (III) Antimony (V) Arsenic (III) Arsenic (V) Cobalt (II) Cobalt (III) Copper (I) Copper (II) Gold (I) Gold (III) Iron (II) Iron (III) Element Lead Manganese Mercury Nickel Tin Titanium Cations Pb2+ Pb4+ Mn2+ Mn4+ Hg+ Hg2+ Ni2+ Ni3+ Sn2+ Sn4+ Ti3+ Ti4+ copper chloride CuCl copper (I) chloride CuCl2 or copper (II) chloride Both are copper chloride Need the charge on copper Write the names of the following compounds. 1. CuO Name of Cation Lead (II) Lead (IV) Manganese (II) Manganese (IV) Mercury (I) Mercury (II) Nickel (II) Nickel (III) Tin (II) Tin (IV) Titanium (III) Titanium (IV) 2. Cu2O 3. Sb2O5 4. Sb2O3 5. PbCl4 6. NiBr2 7. AuP 8. Au3P 9. FeO 10. Sn3P4 11. Fe2C 12. Co4C3 13. Hg3N 14. MnS2 15. AsI5 16. SnO 17. Ti2S3 18. TiF4 Write the chemical formulas of the following 1. manganese (IV) oxide 2. arsenic (V) sulfide 3. cobalt (II) chloride 4. antimony (III) bromide 5. iron (II) carbide 6. gold (I) iodide 7. mercury (II) nitride 8. cobalt (III) phosphide 9. nickel (III) oxide 10. titanium (IV) carbide 11. antimony (V) oxide 12. tin (II) fluoride 13. lead (IV) nitride 14. arsenic (V) bromide 15. gold (II) sulfide 16. antimony (V) phosphide 17. copper (I) oxide 18. gold (I) carbide Worksheet ____- Naming Ionic Compounds Part 3 (Binary compounds with Group 3 - 12 metals) Naming (CLASSICAL SYSTEM) 1. Metal goes first. Some metals use special names. For all of the metals the ending changes to “ous” or “ic” (“ous” is for the lower ion of the metal, while “ic” is for the higher ion of the metal) 2. Non-metal goes second. The ending changes to “ide” Element Antimony Arsenic Cobalt Copper Gold Iron Example Cations Sb3+ Sb5+ As3+ As5+ Co2+ Co3+ Cu+ Cu2+ Au+ Au3+ Fe2+ Fe3+ Name of Cation Antimonous Antimonic Arsenous Arsenic Cobaltous Cobaltic Cuprous Cupric Aurous Auric Ferrous Ferric Element Lead Manganese Mercury Nickel Tin Titanium Cations Pb2+ Pb4+ Mn2+ Mn4+ Hg+ Hg2+ Ni2+ Ni3+ Sn2+ Sn4+ Ti3+ Ti4+ Name of Cation Plumbous Plumbic Manganous Manganic Mercurous Mercuric Nickelous Nickelic Stannous Stannic Titaniumous Titaniumic copper chloride CuCl (Cu+) or cuprous chloride CuCl2 (Cu2+) cupric chloride Both are copper chloride Must indicate the charge with “ous” or “ic” Write the names of the following compounds. 1. CuO 2. Cu2O 3. Sb2O5 4. Sb2O3 5. PbCl4 6. NiBr2 7. AuP 8. Au3P 9. FeO 10. Sn3P4 11. Fe2C 12. Co4C3 13. Hg3N 14. MnS2 15. AsI5 16. SnO 17. Ti2S3 18. TiF4 Write the chemical formulas of the following 1. manganic oxide 2. arsenic sulfide 3. cobaltous chloride 4. antimonous bromide 5. ferrous carbide 6. aurous iodide 7. mercuric nitride 8. cobaltic phosphide 9. nickelic oxide 10. titaniumic carbide 11. antimonic oxide 12. stannous fluoride 13. plumbic nitride 14. arsenic bromide 15. auric sulfide 16. antimonic phosphide 17. cuprous oxide 18. aurous carbide Worksheet ____ - Naming Ionic Compounds Part 4 (For compounds that are not binary) There are groups of non-metals that like to stay together and have a total charge these are called polyatomic ions. Naming 1. Metal goes first and all previous rules for the metals apply. 1a) Group 1, 2, 13 metals name directly from periodic table 1b) Group 3 – 12 metals STOCK SYSTEM name from periodic table plus identify the charge using roman numerals 1c) Group 3 – 12 metals CLASSICAL SYSTEM “ous” identifies lower ion and “ic” identifies higher ion 2. Negative polyatomic ion second and you get the name from the table below. Polyatomic ions Name of polyatomic ion Nitrite Nitrate Sulfite Sulfate Chlorite Chlorate Arsenite Arsenate Ion formula NO2NO3SO32SO42ClO2ClO3AsO33AsO43- Name of polyatomic ion Hydrogen Carbonate (Bicarbonate) Carbonate Phosphate Acetate Cyanide Hydroxide Ammonium Name the following compounds 1. LiNO3 2. Be(HCO3)2 3. AlPO4 4. CaCO3 5. NaNO2 6. Ga(OH)3 7. Cu2SO4 8. Cu(NO3)2 9. Mg3(PO4)2 Ion formula HCO3CO32PO43C2H3O2CNOHNH4+ 10. Sn(OH)4 11. Ba3(AsO4)2 12. (NH4)2CO3 13. Sb(C2H3O2)5 14. KCN 15. Al2(SO3)3 16. FrClO3 17. SrCO3 18. Li3(PO4) Write the chemical formula for the following compounds 1. lithium chlorite 2. beryllium nitrate 3. calcium phosphate 4. aluminum phosphate 5. manganese (IV) hydroxide 6. ammonium sulfate 7. sodium acetate 8. nickel (II) arsenite 9. ferric cyanide 10. cobaltous sulfite 11. auric bicarbonate 12. ammonium phosphate 13. potassium acetate 14. cesium nitrate 15. magnesium arsenite 16. tin (IV) hydroxide 17. antimony (V) arsenate 18. gallium chlorate