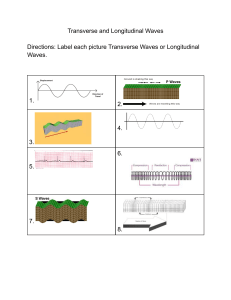
Name:________________Grade & Section:____________Date:___________ ACTIVITY 1: “WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF THE WAVES?” ACTIVITY 2: “WHAT ARE THE PARTS OF THE WAVES?” A wave is a periodic disturbance that moves away from a source and carries energy with it. Transverse, longitudinal, and surface waves are types of mechanical wave. The different types of waves are distinguished according to the direction of vibration of particles with respect to the direction in which the wave travels. Directions: Distinguish the following types of waves as transverse, longitudinal, surface, mechanical, and electromagnetic wave. 1. Waves in a rope are called______________ waves because the individual segments of the rope vibrate perpendicular to the direction in which the waves travel. 2. When each portion of coil spring is alternately compressed and extended, _______________waves are produced. 3. ________________waves are combination of transverse and longitudinal waves. 4. Waves that require a medium for wave propagation are called ________________. 5. __________________waves don’t require a medium for propagation. Directions : Identify the parts of the wave. Choose your answer from the box below. Crest Amplitude A. Wavelength frequency Midpoint rarefaction Trough compression Transverse Wave ________________1. The highest point of the wave ( points A, E, H) ________________2. The lowest point of the wave (points C, J) ________________3. The maximum displacement that the wave moves away from its equilibrium position. (point A to dotted lines) ________________4. The distance between adjacent crests or troughs. (points A to E or E to H) _________________5. The dotted lines in the wave. B. Longitudinal Wave ________________1. The parts where the coils are pressed together. ________________2. The parts where the coils are spread out. Name:________________Grade & Section:____________Date:___________ ACTIVITY 1: “HOW DO YOU DESCRIBE WAVES?” Directions: Compute the frequency and wave speed. Record them in Table 2. Table 2. The speed of a wave. Crest, trough, amplitude, frequency, wavelength, period, wave speed are important terms and quantities used to describe periodic waves. Wavelength (meters) Number of waves (N cycles) Number of Waves (N cycles) Example: 15 cycles Frequency ( N cycles/ 10 seconds) Period of the wave (1/f) (seconds) 15cycles/ 10s=1.5 Hz 1/1.5 Hz=0.67 s 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 48 cycles 20 cycles 30cycles Wave Speed (wavelength x frequency) (m/s) Example: 0.5 m 15 cycles 15 cycles/ 10s=1.5 Hz 0.5m x 1.5 Hz= 0.8 m/s 1.2 m 22 cycles 1. 2. 0.8 m 11 cycles 3. 4. 5.4 m 40 cycles 5. 6. Directions: Compute the frequency and period of a wave. Record them in Table 1. Table 1. Frequency and period of the wave. Frequency (N cycles/10 sec)