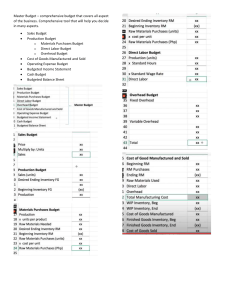
MANAGEMENT ADVISORY SERVICES MANACC – Budgeting • Cash budget c. Capital investment budget Budget It is a financial plan of the resources needed to carry out tasks and meet financial goals. Budgeting Terminologies Master Budget It is a summary of all phases of a company’s plans and goals for the future. It represents a comprehensive expression of management’s plans for the future and how these plans are to be accomplished. Planning It involves the development of objectives and preparation of various budgets to achieve these objectives. Control It involves the steps taken by management to ensure that the objectives set down at the planning stage are attained and to ensure that all parts of the organization function in a manner consistent with organizational policies. Purposes of the Budget a. Defining objectives and goals and formulating strategies to achieve such objectives b. Coordinating the activities of the organization c. Allocating resources d. Communicating management’s approved plans e. Uncovering and preparing for potential bottlenecks in the operations f. Motivating managers g. Setting a standard or benchmark for evaluating actual performance Hierarchy of Budgets a. Operating budget • Budgeted income statement • Sales budget • Production budget • Materials cost budget • Direct labor cost budget • Factory overhead budget • Inventory levels • Cost of Sales budget • Selling and Administrative expenses budget • Financial expense budget b. Financial budget • Budgeted Statement of Financial Position Budgeted Income Statement It refers to projection of revenue, expenses and results of operations for a definite period of time. Cash Budget It is a period-by-period statement of: a. Cash at the start of a budget period; b. Expected cash receipts classified by source; c. Expected cash disbursements, classified by function, responsibility and form; and d. The resulting cash balance at the end of the budget period. Financial Budget It refers to the budget of the financial resources as reflected in the budgeted statement of financial position and cash budget. Static (Fixed) Budget It refers to a projection of cost at a particular or one level of production (usually at normal capacity) for a definite period time period. Flexible (Variable) Budget It refers to a projection of cost at different levels of production for a definite period of time. Participative Budget It refers to a budget prepared using employees at all levels in the organization. Physical Budget It refers to a budget that is expressed in units of materials, number of employees, or number of man-hours or service units rather than in pesos. Planning Budget It is another term for master budget. Production Budget It refers to a production plan of resources needed to meet current sales demand and ensure adequate inventory levels. Page 1 of 2 MANAGEMENT ADVISORY SERVICES MANACC – Budgeting Program Budget It refers to a budget for the major programs or projects that the company plans to undertake. Operating Budget It refers to the plans for the conduct of business for the planning period; it includes the budgeted income statement and all its supporting budgets. Responsibility Budget It refers to a budget for a responsibility center. Rolling / Continuous / Progressive Budget It refers to a budget which is prepared throughout the year, that is, as one month elapses, a budget is prepared for one more month in the future. Sales Budget It refers to a budget that shows the quantity of each product and the revenue expected to be sold. Traditional Budgeting It refers to a system of budgeting which concentrates on the incremental change from the previous year assuming that the previous year’s activities are essential and must be continued. Steps in Developing a Master Budget a. Establish basic goals and long-range plans for the company. b. Prepare a sales forecast for the budget period. c. Estimate the cost of goods sold and operating expenses. d. Determine the effect of budgeted operating results on assets, liabilities and ownership equity accounts. e. Summarize the estimated data in the form of a projected income statement for the budget period and the projected statement of financial position as of the end of the budget period. Steps in Preparing a Flexible Budget a. Determine the relevant range over which activity is expected to fluctuate during the coming period. b. Analyze the costs that will be incurred over the relevant range in order to determine cost behavior patterns (variable, fixed or mixed). c. Separate the costs by behavior and determine the formula for variable and mixed costs. d. Using the formula for the variable portion of the costs, prepare a budget showing what costs will be incurred at various points throughout the relevant range. Zero-Based Budgeting It refers to a system of establishing financial plans beginning with an assumption of no activity and justifying each program or activity level. *** Budget Committee It is a body that oversees the preparation and administration of the budget. It is usually headed by the controller and composed of representation from the different functional areas (marketing, production, finance and administration). Common Budget Periods a. Master budget – quarterly or annual basis b. Capital budget – 5 to 10 years c. Responsibility budget –monthly basis d. Cash budget – day-to-day or monthly basis Page 2 of 2