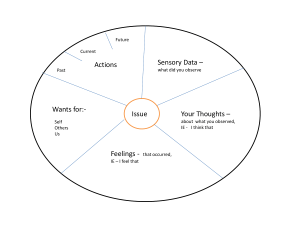
Defense Mechanisms VN 240 Mental Health Defense Mechanisms Use and purpose of Unconscious process to increase one’s security, self-esteem, problem solving Ensure comfort and defend vs. anxiety Defense Mechanisms Types Narcissistic Immature Neurotic Mature Narcissistic Narcissus loved the reflection of his face Birth to 3 years Health adults during periods of severe stress Denial Distortion Delusional projection Narcissistic Denial Distortion Blocking awareness of a painful situation Reshape external reality Delusional projection Form conclusions not based on reality Immature 2 to 4 years Healthy adults with moderate to severe stress and personality disorders Acting out Avoidance Projection Regression Immature Acting out Avoidance Stay away from person, place, situation Projection Expressing unconscious anger overtly Blames thoughts or feelings on another Regression Function at an earlier developmental stage Neurotic Significant level of psychological distress Possible major depression or anxiety Displacement Identification Isolation = rationalization Reaction formation = compensation Repression Neurotic Displacement Isolation Transferring a feeling to a safer object Detaching painful feelings Identification Imitating another Neurotic Reaction formation Substituting an opposite feeling for a real one Repression Unconscious forgetting Mature Middle and later years of childhood Used under minimal stress Altruism Humor Sublimation Suppression Mature Altruism Humor Cannot tolerate a difficult situation Sublimation Transferring one’s dreams to another Diverting unacceptable drives into acceptable activities Suppression Deliberate, conscious forgetting General Adaptation Syndrome Alarm reaction Stage of resistance Body responds to stressor with adrenaline Maintains resistance until stressor disappears Stage of exhaustion Body’s resistance fails Death Maladaptive and Psychotic Behavior Maladaptive Result of ineffective coping and psychosocial maladaptation Psychotic Most severe manifestation of ineffective coping Loss of contact with reality Psychological Responses Anxiety and grief have been described as two major, primary psychological response patterns to stress. A variety of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are associated with each of these response patterns. Adaptation is determined by the extent to which the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors interfere with an individual’s functioning. Psychological Responses Anxiety A diffuse apprehension that is vague in nature and is associated with feelings of uncertainty and helplessness Extremely common in our society Mild anxiety is adaptive and can provide motivation for survival Defenses Mechanism Defined TermsAltruism Sublimation Compensation Suppression Repression Undoing Defenses Mechanism Displacement Fantasy Identification Isolation Rationalization Reaction Formation Acting Out Defenses Mechanism Passive-Aggression Conversion Reaction Projection Regression Denial The Mind is Protecting Itself- (Freud)