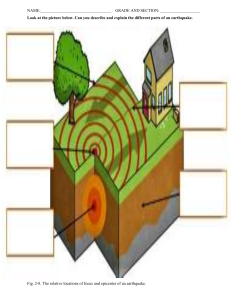
Teacher GENNICA M. TALABOC Grade Level 11 Teaching Date MARCH , 2023 Learning Area Disaster Readiness Risk and Reduction 1 Teaching Time Objectives Content Standards Performance Standards Most Essential Learning Competencies (MELC) Content Learning Resources Teacher’s Guide Pages Learner’s Material Pages Textbook Pages Additional Materials from Learning Resources Procedure TEACHER’S ACTIVITY A. Preparation 1. Prayer 2. Greetings 3. Attendance 4. Review Let’s have first a short recap on our last topic. What was it all about? Quarter At the end of the lesson, students are expected to a. Identify various potential earthquake hazards b. Determine places in their community or at home where they can stay when an earthquake strikes. c. value the importance of knowing the impacts of an earthquake. The learners demonstrate understanding of… Potential earthquake hazards: 1. Ground shaking 2. Ground rupture 3. Liquefaction 4. Earthquake-induced ground subsidence 5. Tsunami 6. Earthquake-induced landslide The learners develop a family emergency preparedness plan to guide them on what to do before, during, and after an earthquake. Identify various potential earthquake hazards (DRR11/12-If-g-17) EARTHQUAKE DEPED Self-Learning Module Earthquake and Its Hazards AVP - YouTube Developmental Method LEARNERS’ ACTIVTY Types of Hazards Very good. What are the types of hazards? Correct! Thank You. 4. Motivation Before we start our new topic this morning, let’s have first this quick “PUNTO-POR-PUNTO” 1.What do you think when you hear earthquake? 2.What is earthquake? 3.What is fault? 4.What is hazard for you? Alright, settle down class. Geologic Hydrologic Atmospheric Biologic Man-made “Student do as told” Are you familiar with the possible hazards of an earthquake? No Ma’am. B. Presentation Be with me this morning as we tackle about more on “Earthquake” Kindly read everyone. “Earthquake” Thank you, class! Pay attention, for at the end of the discussion, all of you are expected to attain these objectives. Everybody please read. a. Identify various potential earthquake hazards b. Determine places in their community or at home where they can stay when an earthquake strikes. c. value the importance of knowing the impacts of an earthquake. Thank you, class! C. Discussion What is an Earthquake? Yes, Jeizel? Thank you! There are two ways of describing the strength of an earthquake. Everybody please read the ways and its definition. A weak to violent shaking of the ground produced by the sudden movement of rock materials below the earth’s surface. 1. Intensity -perceived strength of an earthquake based on relative effect to people and structures; generally higher near the epicenter. 2. Magnitude -based on instrumentally derived information and correlates strength with the amount of total energy released at the earthquake’s point of origin. There are various Potential earthquake hazards. 1. Ground Shaking - If an earthquake generates a large enough shaking intensity, structures like buildings, bridges and dams can be severely damaged, and cliffs and sloping ground destabilised. Perched or stacked objects may fall and injure or bury anyone close by. In the largest earthquakes whole districts can be devastated by the multiple consequences of ground shaking. 2. Ground Displacement along a fault If a structure (a building, road, etc.) is built across a fault, the ground displacement during an earthquake could seriously damage or rip apart that structure. 3. Flooding Flooding can come from many sources such as broken water main pipes, dams that fail due to the earthquake and earthquake-generated tsunamis. When an earthquake breaks a dam or levee along a river, the water from the river or the reservoir floods the area, damaging buildings and maybe sweeping away or drowning people. 4. Fire These fires can be started by broken gas lines and power lines, or tipped over wood or coal stoves. They can be a serious problem, especially if the water lines that feed the fire hydrants are broken, too. 5. Liquefaction Liquefaction occurs when waterlogged sediments are agitated by seismic shaking. This separates the grains from each other, reducing their load bearing capacity. Buildings and other structures can sink down into the ground or tilt over, whilst underground pipes and tanks may rise up to the surface. 6. Landslides and Rockfalls Groundshaking due to earthquakes destabilises cliffs and steep slopes, causing landslides and rockfalls as a significant side-effect. Heavy rain and unconsolidated or fractured rock are exacerbating factors. 7. Tsunami For sure, one of the most dangerous effects of an earthquake is a Tsunami. Tsunamis are giant waves that can cause floods and, in some cases, may reach up to 100 feet in height. These deadly waves strike a great distance from the epicenter. Tsunamis often result from sub-sea faulting of ocean floor sending seismic shocks through the water and creating large waves of low amplitude but of long period, moving at 500-700 mph. Student answer the question. Give natural signs of impending tsunami, class. strong ground shaking from an earthquake: if you are on the coast and there is an earthquake, it may have caused a tsunami, so escape immediately to higher ground or inland, avoiding river valleys; unusual sea-level fluctuations: a noticeable rapid rise or fall in coastal waters is a sign that there may be a tsunami approaching. If you see the water recede quickly and unexpectedly from a beach exposing the ocean floor (the so-called drawback) or a sudden rise of the sea level, escape immediately to higher ground or inland, avoiding river valleys; abnormally huge wave: the first wave in a tsunami wave train is usually not the largest, so if you see an abnormally huge wave, even bigger waves could be coming soon. Run immediately to higher ground or inland, avoiding river valleys; loud ocean roar: if you hear a roaring sound offshore, similar to that of a train or jet aircraft, a tsunami may be approaching, so escape immediately to higher ground or inland, avoiding river valleys. D. Generalization Hazards are events or phenomena that may cause loss of life, injury or other health impacts, property damage, loss of livelihood and services, social and economic disruption or environmental damage. The following are the most common earthquake- related hazards: ground rupture, ground shaking, liquefaction, tsunami, and earthquakeinduced landslides. Earthquake and Its Hazards AVP - YouTube *Values Integration Now class, why is it important to know the impacts of an earthquake? Yes, Christian? With a greater understanding of the causes and effects of earthquakes and how they impact buildings, infrastructure, and society itself, we may be able to reduce damage and loss of life from this destructive phenomenon. Now, let us have another activity. E. Application Group the class into 7 groups Directions: Each group will discussed more about one of the various potential earthquake hazards. IV. Evaluation Ask the learners, based on what they have learned so far, think of their home, what are the possible impacts/ effects of the 5 earthquake hazards to their home/s? V. Assignment Observe potential hazards at home. Student will answer.