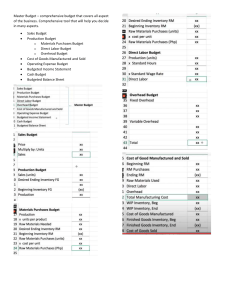
Cost Behavior Variable Costs 1. Total production costs for Jordan, Inc. are budgeted at P2,300,000 for 50,000 units of budgeted output and P2,800,000 for 60,000 units of budgeted output. Because of the need for additional facilities, budgeted fixed costs for 60,000 units are 25 percent more than budgeted fixed costs for 50,000 units. How much is Jordan’s budgeted variable cost per unit of output? A. P 7.50 C. P30.00 B. P16.00 D. P62.50 Y = a +bx a = Y-bx ( 2300000- 50000 x)*1.25 = (2800000-60000x) 2875000-62500x = 2800000-60000x 62500x-60000x =2.875000-2800000 2500x= 75000 X= 30 pesos A= Y-BX A= 2300000- ( 50000 x 30) A= 23000000-1,500000 A= 800,000 A= Y-BX A= 2800000- ( 60000 *30) A= 2800000- 18000000 A= 1000000 15. Total production costs for Carera, Inc. are budgeted at P230,000 for 50,000 units of budgeted output and P280,000 for 60,000 units of budgeted output. Because of the need for additional facilities, budgeted fixed costs for 60,000 units are 25% more than budgeted fixed costs for P50,000 units. How much is Carera’s budgeted variable cost per unit of output? A. P1.60 C. P3.00 B. P1.67 D. P5.00 3. Total production costs for Laguna, Inc. are budgeted at P230,000 for 50,000 units of budgeted output and P280,000 for 60,000 units of budgeted output. Because of the need for additional facilities, budgeted fixed costs for 60,000 units are 25% more than budgeted fixed costs for 50,000 units. How much is Laguna’s total budgeted variable cost at 60,000 units? A. P96,000 C. P180,000 B. P100,200 D. P100,000 16. Mulvey Company derived the following cost relationship from a regression analysis of its monthly manufacturing overhead cost: C = P80,000 + P12M Where C = monthly manufacturing overhead cost M = machine hours The standard error of the estimate of the regression is P6,000. The standard time required to manufacture one six-unit case of Mulvey's angle product is 4 machine hours. Mulvey applies manufacturing overhead to production on the basis of machine hours and its normal annual production is 50,000 cases Mulvey's estimated variable manufacturing overhead cost for a month in which scheduled production is 5,000 cases would be A. P80,000 C. P240,000 B. P320,000 D. P360,000 50000X 4= 20000 200000 x 12 = 240000 1. Which of the following graphs illustrates the behavior of a total variable cost? (E) Graph 1 Graph 2 Total units produced Total units produced Graph 3 Graph 4 Total units produces Total units produced A. Graph 2 B. Graph 3 C. Graph 4 D. Graph 1 Fixed Costs 9. Parts Company wishes to determine the fixed portion of its maintenance expense (a semi-variable expense), as measured against direct labor hours for the first three months of the year. The inspection costs are fixed; the adjustments necessitated by errors found during inspection account for the variable portion of the maintenance costs. Information for the first quarter is as follows: Direct Labor Hours Maintenance Costs January 34,000 P61,000 February 31,000 58,500 March 34,000 61,000 What is the fixed portion of Parts Company’s maintenance expense, rounded to the nearest pesos? A. P28,330 C. P37,200 B. P32,780 D. P40,800 61000-58500/34000-31000 = 2500/3000 = 0.83 A=Y-Bx A= 61000 – ( 34000*.83) A= 61000 – 28220 A = 32780 5. Largo Company wishes to determine the fixed portion of its maintenance expense (a semi-variable expense), as measured against direct labor hours for the first three months of the year. Information for the first quarter is as follows: Direct Labor Hours Maintenance Costs January 25,000 P210,000 February 30,000 240,000 March 27,000 222,000 What is the fixed portion of Largo Company’s maintenance expense? A. P60,000 C. P90,000 B. P30,000 D. P120,000 240000-210000/30000-25000 = 30000/5000 =6 A= Y-BX A= 240000 – (30000* 6) A= 240000-180000 A= 60000 Total Costs 17. Molds Corporation has developed the following flexible budget formula for annual indirect labor costs: Total Cost = P300,000 + P5.00 per machine hour Operating budgets for the current month are based upon 18,000 machine hours of planned machine time. Indirect labor costs included in this planning budget are: A. P300,000 C. P 90,000 B. P390,000 D. P115,000 8. Arens Corporation has developed the following flexible budget formula for annual indirect labor costs: Total Cost = P480,000 + P5.00 per machine hour Operating budgets for the current month are based upon 20,000 machine hours of planned machine time. Indirect labor costs included in this planning budget are: A. P 48,333 C. P100,000 B. P580,000 D. P140,000 Total Cost = (480000/12)+ (5)(20000) TC= 40000 + 100000 TC= 140000 2. Boy & Millie Company uses an annual cost formula for overhead of P72,000 + P1.60 for each direct labor hour worked. For the upcoming month Karla plans to manufacture 96,000 units. Each unit requires five minutes of direct labor. Boy & Millie’s budgeted overhead for the month is A. P12,800 C. P 84,800 B. P18,800 D. P774,000 DLH = 96000*5 DLH= 480000/60 DLH= 8000 TC= (72000/12)+ ( 1.60* 8000) TC= 6000+ 12800 TC= 18800 2. Saldua Company uses a monthly cost formula for overhead of P50,000 + P30.00 for each direct labor hour worked. For the coming year, Saldua plans to manufacture 200,000 units. Each unit requires five minutes of direct labor. Saldua’s total budgeted overhead for the coming year is A. P 550,000 C. P1,200,000 B. P1,100,000 D. P 650,000 DLH = 200000*5 DLH= 1000000/60 DLH= 16666.67 TC= (50000*12)+ (30*16667.67) TC= 600000 + 500000 TC= 1100000 6. The following cost functions were developed for manufacturing overhead costs: Manufacturing Overhead Costs Cost Function Electricity P100 + P20 per direct labor hour Maintenance P200 + P30 per direct labor hour Supervisors’ salaries P10,000 per month Indirect materials P16 per direct labor hour If July production is expected to be 1,000 units requiring 1,500 direct labor hours, estimated manufacturing overhead costs would be A. P109,300 C. P76,300 B. P99,000 D. P10,366 Electricity = 100 + ( 20*1500) = 100+30000 = 30100 Maintenance = 200+ (30 *1500) = 200+45000= 45200 Supervisor salaries= 10000 Indirect materials = 16*1500= 24000 7. El Noche, Inc. has a total of 2,000 rooms in its nationwide chain of hotels. On the average, 70% of the rooms are occupied each day. The company’s operating costs are P21 per occupied room per day at this occupancy level, assuming a 30-day month. This P21 figure contains both variable and fixed cost elements. During October, the occupancy dropped to only 45%. A total of P792,000 in operating cost was incurred during the month. What would be the expected operating costs, assuming that the occupancy rate increases to 60% during November? A. P1,056,000 C. P846,000 B. P756,000 D. P829,500 2000*.70= 1400 * (21*30) = 1400 *630 = 882000 Occupancy 1400 900 882000-792000= 90000 1400-900 = 500 VC per unit = 180 per unit Y= a+bx A= Y-bx A= 792000 – (900*180) A= 792000 – 162000 A= 630000 Cost 882000 792000 Y = a+bx Y= 630000+ (180)(1200) Y= 630000 + 216000 Y = 846000