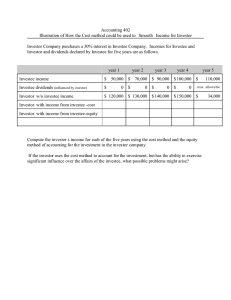
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING THEORY & PRACTICE INVESTMENT IN EQUITY SECURITIES QUIZZER Investment in Equity Securities INVESTMENT IN EQUITY SECURITIES Essay Questions Dividends and splits 1. When are dividends considered earned? In this connection, three dates are important in accounting for dividends, namely: 1. Date of declaration is the date on which the payment of dividends is approved by the board of directors. 2. Date of record is the date on which the stock and transfer book is closed for registration. Only those shareholders registered as of this date are entitled to receive dividends. 3. Date of payment is the date on which the dividends declared shall be paid. PAS 18, paragraph 29, provides that "dividends shall be recognized as revenue when the shareholder's right to receive payment is established". Accordingly, the dividends shall be recognized as revenue on the date of declaration. 2. Describe and discuss the accounting treatment of the following: 1. 2. 3. 4. Cash dividends Property dividends Liquidating dividends Stock dividends 1. Cash dividends, as the title suggests, are in the form of cash. As a rule, such dividends are treated as income but if the equity method is used, the same should be credited to the investment account. 2. Property dividends or dividends in. kind are dividends in the form of property or assets other than cash. The property may be in the form of another entity's share, inventory, equipment and other noncash asset. Property dividends are normally treated as income at the fair value of the property received. 3. Liquidating dividends represent return of investment and therefore are not income. 4. Stock dividends are in the form of the issuing entity's own shares. The IAS term for Essay Questions Page 1 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING stock dividend is "bonus issue". Stock dividends may be the same as those held or different from those held. Stock dividends are not income. Stock dividends of the same kind are recorded only by means of a memorandum entry on the part of the investor. Such stock dividends do not affect the total cost of the investment but reduce the cost of the investment per share. 3. Discuss the accounting treatment of stock dividends which are different from those held. As stated earlier, stock dividends are not income whether they are the same or different kind. When the stock dividends are of different kind, the procedure is to allocate the cost of the original investment between the original shares and the "different" stock dividends on the basis of fair value. For example, if the original investment is ordinary share and the investor receives preference share as stock dividend, the stock dividend is recorded by debiting investment in preference share and crediting investment in ordinary share for the amount allocated to the stock dividend. Accordingly, the stock dividends of different kind reduce the total cost of the original investment because a new investment account is set up for the stock dividends received. 4. Discuss the accounting treatment for shares received, in lieu of cash dividends. When cash dividends are declared and received, it is without doubt that they are income. A problem will arise when shares are received in lieu of cash dividends declared. It is generally accepted that shares received in lieu of cash dividends are income at the fair value of the shares received. In the absence of the fair value of the shares received, the income is equal to the cash dividends that would have been received. Shares received in lieu of cash dividends are recorded by debiting investment in shares and crediting dividend income. 5. Discuss the accounting treatment for cash received in lieu of stock dividends. When stock dividends are declared and received, unquestionably they are not income. A problem will arise when cash is received in lieu of stock dividends. In this case, the "as if approach is followed. This means that the stock dividends are assumed to be received and subsequently sold at the cash received. Therefore, gain or loss may be recognized. Essay Questions Page 2 Investment in Equity Securities 6. Discuss share split. Share split may be split up or split down. A share split up is a transaction whereby the outstanding shares are called in and replaced by a larger number, accompanied by a reduction in the par or stated value of each share. A share split down is a transaction whereby the outstanding shares are called in and replaced by a smaller number, accompanied by an increase in the par or stated value. Share split does not affect the total cost of investment. But there is a decrease or an increase in the cost per share because the total cost now will apply to a larger or smaller number of shares. Only a memorandum entry is made to record the receipt of new shares by virtue of share split. Stock rights 7. What is a stock right? A stock right or preemptive right is a legal right granted to shareholders to subscribe for new shares issued by a corporation at a specified price during a definite period. The IAS term for stock right is "right issue". A stock right is inherent in every share. A shareholder receives one right for one share owned. A stock right is valuable to an investor because the price at which the new shares are sold is generally below the prevailing market price. The purpose of the stock right is to enable the shareholders to preserve their equity or proportionate interest in the corporation. The ownership of stock right is evidenced by an instrument or a certificate known as share warrant. 8. Explain the procedure when stock rights are accounted for separately? PAS 39 and PFRS 9 do not address this accounting issue categorically. But unquestionably, a stock right is a form of a financial asset. In this regard, there is a divergence of opinion among academicians and theoreticians. There are two schools of thought on the matter, namely: Essay Questions Page 3 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING 1. Stock rights are accounted for separately. 2. Stock rights are not accounted for separately. 9. Explain the measurement of stock rights. Under Application Guidance B5.4.14 of PFRS 9, all investments in equity instruments and contracts on those instruments must be measured at fair value. Stock rights as a form of equity financial instrument are measured initially at fair value. In other words, a portion of the carrying amount of the original investment in equity securities is allocated to the stock rights at an amount equal to the fair value of the stock rights. The reason for such an allocation is that stock rights are independent of the original shares from which they are derived. When stock rights are issued, the investor is now the owner of two financial assets, namely the original shares and the related stock rights. Stock rights are normally classified as current assets if the rights are accounted for separately. 10. Explain why stock rights are not accounted for separately. Stock rights may be recognized as embedded derivative but not a "stand-alone" derivative. An embedded derivative is a "component of a hybrid or combined contract (host contract) . with the effect that some of the cash flows of the combined contract vary in a way similar to a stand-alone instrument". PFRS 9, paragraph 4.3.3, provides that an embedded derivative shall be separated from the host contract and accounted for separately under certain conditions. However, PFRS 9, paragraph 4.3.3, further provides that if the host contract is within the scope of PFRS 9, the classification requirements of PFRS 9 are applied to. the combined host contract in its entirety. This simply means that if the host contract is a financial asset, the embedded derivative is not separated. Moreover, under PFRS 9, paragraph 4.3.3, if the host contract is measured at fair value through profit or loss, the embedded derivative is not separated. Accordingly, the stock right as an embedded derivative is not accounted for separately because the host contract "investment in equity instrument" is a financial asset measured at fair value through profit or loss. 11. Which approach is followed in accounting for stock rights? Admittedly, this subject matter is not a well-settled issue. In fact, PFRS 9, paragraph 4.3.4, states that "this standard does not address whether an embedded derivative shall be Essay Questions Page 4 Investment in Equity Securities presented separately in the statement of financial position". The authors strongly believe that the approach "not accounted for separately" stands on solid and authoritative ground. However, stay tuned and let us wait and see what the Financial Reporting Standards Council will say on this accounting issue. 12. What is the meaning of "theoretical" or "parity" value of stock right? The theoretical or parity value is the assumed fair value of the stock right that is derived from the market value of the share. 13. What are the formulas for the computation of the theoretical or parity value of stock right? The formulas for the computation of the theoretical or parity value of the stock right are: 1. When the share is selling right-on: Market value of share right-on minus subscription price = Value of one right Number of rights to purchase one share plus 1 2. When share is selling ex-right: Market value of share ex-right minus subscription price Number of rights to purchase one share = Value of one right Investment in associates 14. Define significant influence, control, associate and subsidiary. Significance influence is the power to participate in the financial and operating policy decisions of the investee but not control or joint control over those policies. Control is the power to govern the financial and operating policies of an entity so as* to obtain benefits from its activities. Under PFRS 10, an investor controls an investee when the investor is exposed or has rights to variable returns from the involvement with the investee and has the ability to affect those returns through the power over the investee. PAS 28, paragraph 3, simply defines an associate as "an investor has significant influence". entity over which the Appendix A of PFRS 10 on consolidated financial statements simply defines a subsidiary as "an entity that is controlled by another entity". Essay Questions Page 5 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING In other words, the party controlling another entity is known as the parent and the party controlled is known as the subsidiary. Technically, the parent and the subsidiary are known as affiliates. 15. When does an investor have significant influence? The assessment of significant influence is a matter of judgment. However, PAS 28, paragraph 5, provides a practical guidance to assist management in making such assessment If the investor holds, directly or indirectly through subsidiaries, 20% or more of the voting power of the investee, it is presumed that the investor has significant influence, unless it can be clearly demonstrated that this is not the case. Conversely, if the investor holds, directly or indirectly through subsidiaries, less than 20% of the voting power of the investee, it is presumed that the investor does not have significant influence, unless such influence can be clearly demonstrated. A substantial or majority ownership by another investor does not necessarily preclude an investor from having significant influence. PAS 28, paragraph 6, provides that the existence of significant influence by an investor is usually evidenced in one or more of the following ways: a. Representation in the board of directors b. Participation in policy making process c. Material transactions between the investor and the investee d. Interchange of managerial personnel e. Provision of essential technical information 16. Explain the treatment of potential voting rights in relation to having significant influence. An entity may own share warrants, debt or equity instruments that are convertible into common shares that have the potential, if exercised or converted, to give the entity additional voting power. PAS 28, paragraph 7, provides that the existence of such potential voting rights is considered in assessing whether an entity has significant influence. However, when potential voting rights exist, the investor's share of profit or loss of the investee and of changes in the investee's equity is determined on the basis of "present ownership interest" and does not reflect the possible exercise or conversion of potential voting rights. Essay Questions Page 6 Investment in Equity Securities 17. When does an investor lose significant influence? An entity loses significant influence over an investee when it loses the power to participate in the financial and operating policy decisions of the investee. The loss of significant influence can occur with or without change in the absolute or relative ownership interest. For example, the loss of significant influence could occur when an associate becomes subject to control of a government, court, administrator or regulator. The loss of significant influence could also occur as a result of a contractual agreement. 18. Explain the equity method of accounting. The equity method is based on the economic relationship between the investor and the investee. The investor and the investee are viewed as a single economic unit. The equity method is applicable when the investor has a significance influence over the investee. Under the equity method, the investment is initially recorded at cost but it is subsequently increased by the net income of the investee and decreased by the net loss and dividend payments of the investee. Note that the investment must be in ordinary shares. If the investment is in preferrence shares, the equity method is not appropriate regardless of the percentage because the preference share is a nonvoting equity. The investment in preference shares may be accounted for as at fair value through profit or loss or at fair value through other comprehensive income or nonmarketable investment. Technically, if the investor has significant influence but not control over the investee, the investee is said to be an associate or associated company. The investment in associate accounted for using the equity method shall be classified as noncurrent asset. Accordingly, under the equity method, the investment in ordinary shares shall be appropriately described as investment in associate. If the investor has control over the investee, the investor is known as the parent and the investee is known as the subsidiary. In this case, the investment in ordinary shares is described as investment in subsidiary. 19. What do you understand by the "excess of cost over carrying amount" of interest acquired? If the cost of an investment exceeds the carrying amount of the underlying net assets acquired, the difference is termed as "excess of cost over carrying amount". The excess of cost over carrying amount may be due to the following: a. Undervaluation of the investee's depreciable assets b. Goodwill Essay Questions Page 7 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING In practice, it is often difficult to determine which specific identifiable assets are undervalued. If the assets of the investee- are fairly valued, accountants frequently attribute the excess of cost over carrying amount of the underlying net assets to goodwill. If the excess is attributable to undervaluation of depreciable assets, it is amortized over the remaining life of the depreciable assets. The amortization of the excess of cost over carrying amount is recorded by debiting investment income and crediting the investment account. If the excess is attributable to goodwill, it is not amortized but the entire investment in associate is tested for impairment at each reporting date. 20. What is the treatment of "excess of net fair value over cost"? PAS 28, paragraph 32, provides that the excess of the investor's share of the net fair value of the associate's identifiable assets and liabilities over the cost of the investment is included as income in the determination of the investor's share of the associate's profit or loss in the period in which the investment is acquired. 21. Discuss the accounting procedure where the associate is with "heavy losses". PAS 28, paragraph 38, provides that if an investor's share of losses of an associate equals or exceeds the carrying amount of an investment, the investor discontinues recognizing its share of further losses. The investment is reported at nil or zero value. The carrying amount of the investment in associate is not just the balance of the account "investment in associate" The carrying amount of the investment in associate also includes other long-term interests in an associate, such as long-term receivables, loans and advances. However, trade receivables and any long-term receivables for which adequate collateral exists, such as secured loans, are excluded from the carrying amount of an investment in associate. Additional losses are provided for or a liability is recognized to the extent that the investor has incurred legal or constructive obligations or made payments on behalf of the associate. If the associate subsequently reports income, the investor resumes including its share of such income after its share of the income equals the share of losses not recognized. 22. Explain the impairment of an investment in associate. If there is an indication that an investment in associate may be impaired, PAS 28, paragraph 40 in conjunction with PAS 36 on "impairment of assets" requires that an impairment loss shall be recognized "whenever the carrying amount of the investment in associate exceeds its recoverable amount". The recoverable amount is measured as the higher between fair value less cost of disposal and value in use. Essay Questions Page 8 Investment in Equity Securities Fair value is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. Value in use is the present value of the estimated future cash flows expected to arise from the continuing use of an asset and from the ultimate disposal. The value in use of an investment in associate is the investor's share in either of the following: a. Present value of estimated future cash flows expected to be generated by the investee, including cash flows from operations of the investee and the proceeds from the ultimate disposal of the investment. b. Present value of the estimated future cash flows expected to arise from dividends to be received from the investment and from the ultimate disposal. Under appropriate assumptions, both methods give the same result. Any resulting impairment loss for the investment is allocated first to any remaining goodwill. 23 Explain the treatment when the investee has an outstanding preference shares. a. When an associate has outstanding cumulative preference shares, the investor shall compute its share of earnings or losses after deducting the preference dividends, whether or not such dividends are declared. b. When an associate has outstanding noncumulative preference shares, the investor shall compute its share of earnings after deducting the preference dividends only when declared. 24. Explain the treatment of "other changes in the equity of the investee" that have not been recognized in profit or loss. Adjustments to the carrying amount of the investment in associate may be necessary for changes in the investor's proportionate interest in the investee arising from changes in the investee's equity that have not been recognized in the investee's profit or loss. Such changes include those arising from revaluation of property, plant and equipment and from foreign exchange translation differences. The investor's share of those- changes is recognized directly in equity of the investor. 25. What are some adjustments in the investee's operations before an investor computes its share in the investee's profits or losses? 1. The most recent available financial statements of the associate are used by the investor in applying the equity method. Essay Questions Page 9 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING When the reporting dates of the investor and the investee are different, the associate shall prepare for the use of the investor financial statements as of the same date as the financial statements of the investor unless it is impracticable to do so. In any case, the difference between the reporting date of the associate and that of the investor shall be no more than three months. 2. If an associate uses accounting policies other than those of the investor, adjustments shall be made to conform the associate's accounting policies to those of the investor. 3. Profits and losses resulting from upstream and downstream transactions between an investor and an associate are recognized in the investor's financial statements only to the extent of the unrelated investors' interest in the associate. In other words, the unrealized profit and loss from upstream and downstream transactions must be eliminated in determining the investor's share in the profit or loss of the associate. "Upstream" transactions are sales of assets from an associate to the investor. "Downstream" transactions are sales from the investor to the associate. The investor's share in the associate's profits and losses resulting from these transactions is eliminated. 26. When shall an investor discontinue the equity method? PAS 28, paragraph 22, provides that an investor shall discontinue the use of the equity method from the date that it ceases to have significant influence over an associate. Consequently, the investor shall account for the investment as financial asset at fair through profit or loss, or financial asset at fair value through other comprehensive income or nonmarketable investment. However, PAS 28, Basis for Conclusion 18, does not permit an investor that continues to have significant influence over an associate not to apply the equity method even if the associate is operating under severe long-term restrictions that significantly impair its ability to transfer funds to the investor. Significant influence must be lost before the equity method ceases to be applicable. Essay Questions Page 10 Investment in Equity Securities 27. What is the measurement of the investment in associate on the date significant influence is lost? PAS 28, paragraph 22, provides that on the date the significant influence is lost, the investor shall measure any retained investment in associate at fair value. The difference between the carrying amount of the investment at the date the significant influence is lost, and the fair value of the retained investment plus any proceeds received from disposal of any part interest in the associate, shall be included in profit or loss. Paragraph 22 further provides that the fair value of the investment at the date it ceases to be an associate shall be regarded as fair value on initial recognition as a financial asset. 28. What are the specific circumstances when an investment in associate shall not be accounted for using the equity method? PAS 28, paragraph 17, provides that an investment in associate shall not be accounted for using the equity method if the investor is a parent that is exempt from preparing consolidated financial statements or if all of the following apply: a. The investor is a wholly-owned subsidiary, or a partially-owned subsidiary of another entity and the other owners do not object to the investor not applying the equity method. b. The investor's debt and equity instruments are not traded in a public market, meaning domestic or foreign stock exchange or "over the counter" market. c. The investor did not file or it is not in the process of fifing its financial statements with the SEC for the purpose of issuing any class of instruments in a public market. d. The ultimate or any intermediate parent of the investor produces consolidated financial statements available for public use that comply with Philippine Financial Reporting Standards. In these circumstances, the investment is accounted for as at fair value through profit or loss, or at fair value through other comprehensive income or nonmarketable investment. 29. Explain the treatment of an investment in associate that is "classified as held for sale". PAS 28, paragraph 20, provides that if the investment in associate is classified as held for sale, it is accounted for in accordance with PFRS 5 which specifically mandates that any noncurrent asset classified as "held for sale" shall be measured at the lower of carrying amount and fair value less cost of disposal. Essay Questions Page 11 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING 30. What is the method of accounting for an investment of less than 20%? If the investor holds, directly or indirectly, through subsidiaries less than 20% of the voting power of the investee, it is presumed that the investor does not have significant influence, unless such influence can be clearly demonstrated. In this case, the investment is accounted for either at fair value or at cost. The fair value method is applicable to financial asset at fair value through profit or loss or financial asset at fair value through other comprehensive income. The cost method is usually applied with respect to investment in unquoted equity instrument or nonmarketable equity investment. Under the fair value and cost method, the investor does not share in the profit or loss of the investee because this method is based on the legal relationship between the investor and the investee. The investor and the investee are independent of the other. In applying the fair value and cost method, dividends received from an associate are recognized as dividend income, regardless of whether the dividends originated from preacquisition retained earnings or postacquisition retained earnings. There is no longer a distinction between preacquisition dividends and postacquisition dividends. 31. Explain investment in associate achieved in stages. An investor may acquire an ownership interest in an investee on a certain date but the investee may not be classified as an associate until a later date. For example, an investor holds a 10% interest in an investee on January 1, 2013. The investor acquires additional 10% interest in the same investee on January 1, 2014 enabling the investor to exercise significant influence over the investee. In 2013, the investment is accounted for under the cost or fair value method. However, in 2014, the investment is accounted for under the equity method because the investee is now an associate. Essay Questions Page 12 Investment in Equity Securities This scenario or phenomenon is known as "investment in associate achieved in stages." 32. Explain the accounting for investment in associate achieved in stages. The investment in associate achieved in stages is not covered by PAS 28. This investment in associate is parallel to business combination achieved in stages. PFRS 3, paragraph 42, provides that in a business combination achieved in stages, the acquirer shall remeasure the previously held equity interest at fair value and recognize the resulting gain or loss in profit or loss. By inference, this "fair value approach" should be followed when an associate is acquired in stages. 33. Explain the "fair value approach" in accounting for investment in associate achieved in stages. The following accounting procedures should be followed for investment in associate achieved in stages: a. The existing interest in the associate is remeasured at fair value with any change in fair value included in profit or loss. b. If the existing interest is accounted for at fair value through other comprehensive income, any previous unrealized gain or loss is reclassified to profit or loss. c. The fair value of the existing interest plus the cost of the additional interest acquired constitutes the total cost of the investment for the initial application of the equity method. d. The total cost of the investment for the initial application of the equity method minus the carrying amount of the net assets acquired at the date significant influence is obtained equals excess of cost over carrying amount or excess net fair value. Essay Questions Page 13 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING Multiple Choice - Theory Dividends & splits 1. It is the date on which the stock and transfer book of the entity is closed for registration. Only those shareholders registered as of this date are entitled to receive dividends. A. Date of declaration C. Date of payment B. Date of mailing the dividend check D. Date of record FA © 2014 2. Dividends are recognized on the A. Date of declaration B. Date of issuing statements C. Date of record FA © 2014 D. Date of statement of financial position 3. At which of the following dates has the shareholder theoretically realized income from dividend? A. The date of record B. The date the dividend is declared C. The date the dividend check is mailed by the entity D. The date the dividend check is received by the shareholder. TOA © 2013 4. An investor owns 10% of the ordinary shares of an investee throughout the year. The investee has no preference shares outstanding. The investor's interest gives the right to A. Be paid 10% of the investee's profits in cash each year. B. Receive dividend equal to 10% of the par value each year. C. Receive dividends equal to 10% of the total dividend paid by the investee for the year to shareholders. D. Keep investee from issuing any additional shares unless the investor is willing to buy 10% of the newly issued shares. FA © 2014 5. Shares received in lieu of cash dividend are recorded as A. Stock dividends B. Income at fair value of the shares received C. Income at par value of the shares received D. Income at the cash dividend that would have been received 6. FA © 2014 Cash received in lieu of stock dividends is accounted for as A. Dividend income B. Return of investment C. Partly dividend income and partly return of investment FA © 2014 D. If the stock dividends are received and subsequently sold and gain or loss is recognized MCQ - Theory Page 14 Investment in Equity Securities 7. 8. 9. Property dividends are recorded A. By means of memorandum only B. As dividend income at fair value of the property C. As dividend income at carrying amount of the property D. As return of investment and therefore credited to investment account FA © 2014 Liquidating dividends are credited to A. Income B. Investment account C. Retained earnings D. Share capital FA © 2014 What is the effect of stock dividend of the same class? A. Increase in investment account and increase in cost per share B. No effect on investment account but increase in cost per share C. No effect on investment account but decrease in cost per share D. Decrease in investment account and decrease in cost per share FA © 2014 10. When stock dividends of different class are received A. Cash is debited and dividend income is credited B. No formal entry is made but only a memorandum C. A new investment account is debited and dividend income is credited FA © 2014 D. A new investment account is debited and the original investment account is credited 11. Cash received in lieu of stock dividends is accounted for as A. Dividend income B. Return of investment C. Partly dividend income and partly return of investment D. If the stock dividends are received and subsequently sold at the cash received and gain or loss is recognized TOA © 2013 12. What is the effect of share split up? A. Increase in number of shares and increase in cost per share B. Increase in number of shares and decrease in cost per share C. Decrease in number of shares and increase in cost per share D. Decrease in number of shares and decrease in cost per share MCQ - Theory FA © 2014 Page 15 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING Cost method 13. When an investor uses the cost method to account for investment in ordinary shares, cash dividends received by the investor from the investee should be recorded as A. Dividend income B. A deduction from the investment account C. An addition to the investor's share of the investee's profit D. A deduction from the investor's share of the investee's profit FA © 2014 14. An investor uses the cost method to account for an investment in ordinary shares. A portion of the dividends received this year were in excess of the investor's share of investee's earnings subsequent to the date of investment. The amount of dividend revenue that should be reported in the investor's income statement for this year would be A. Zero B. The total amount of dividends received this year C. The portion of the dividends received this year that were in excess of the investor's share of investee's earnings subsequent to the date of investment D. The portion of the dividends received this year that were not in excess of the investor's share of investee's earnings subsequent to the date of investment. FA © 2014 15. An investor uses the cost method to account for investment in ordinary shares. Dividends received in excess of the investor's share of investee's earnings subsequent to the date of investment FA © 2014 A. Decrease the investment account C. Increase the dividend revenue account B. Do not affect the investment account D. Increase the investment account 16. An investor uses the cost method of accounting for its 15% ownership in an investee. At yearend, the investor has a receivable from the investee. How should the receivable be reported? A. The total receivable should be reported separately. B. The total receivable should be offset against the investee's payable to the investor. C. The total receivable should be included as part of the investment, without separate disclosure. D. Eighty-five percent of the receivable should be reported separately, with the balance offset against the investee's payable to the investor. TOA © 2013 Investment in associates 17. It is an entity over which the investor has significant influence. A. Associate C. Mutual fund B. Investee D. Venture capital organization FA © 2014 MCQ - Theory Page 16 Investment in Equity Securities 18. Which of the following statements best describes the term "significant influence"? A. The mutual sharing in the risks and benefits of a combined entity B. The contractually agreed sharing of control over an economic entity C. The holding of a significant proportion of the share capital in another entity FA © 2014 D. The power to participate in the financial and operating policy decisions of an entity 19. Which of the following statements is true concerning significant influence? I. If an investor holds, directly or indirectly, less than 20% of the voting power of the investee, it is presumed that the investor does not have significant influence, unless such influence can be clearly demonstrated. II. If an investor holds, directly or indirectly, 20% or more of the voting power of the investee, it is presumed that the investor does have significant influence, unless it can be clearly demonstrated that this is not the case. III. A substantial or majority ownership by another investor does not necessarily preclude an investor from having significant influence. A. II only C. I and II only B. Ill only D. I, II and III FA © 2014 20. When an entity holds between 20% and 50% of the voting power of an investee, which of the following statements is true? A. The investor must use the equity method. B. The investor must use the fair value method. C. The investor must use the fair value method unless it can be clearly demonstrated that the investor has significant influence over the investee. D. The investor should use the equity method unless circumstances indicate that it is unable to exercise significant influence over the investee. FA © 2014 21. The equity method is not required to be applied when the associate has been acquired and held with a view to its disposal within a certain time period. What is the period within which the associate must be disposed of? A. In the near future B. Six months from the end of reporting period C. Twelve months from the end of reporting period D. Twelve months from date of classification as held for sale FA © 2014 22. The equity method is not applicable under all of the following circumstances, except A. The investor is a wholly-owned subsidiary. B. The investor's debt and equity instruments are not traded. C. The ultimate parent of the investor produces consolidated financial statements. D. The investor is in the process of filing financial statements with SEC for the purpose of issuing debt and equity instruments in a public market. FA © 2014 MCQ - Theory Page 17 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING 23. What should happen when the financial statements of an associate are not prepared as of the same date as the financial statements of the investor? A. As long as the gap is not greater than three months, there is no problem. B. The financial statements of the associate prepared up to a different date shall be used as normal. C. The associate shall prepare financial statements for the use of the investor at the same date as that of the investor. D. Any major transactions between the date of the financial statements of the investor and that of the associate shall be accounted for. FA © 2014 24. The excess of the investor's share of the net fair value of the associate's net assets over the cost of the investment is A. A deferred gain. B. Credited to retained earnings directly C. Included in other comprehensive income. D. Included in the determination of the investor's share of the associate's profit or loss in the period in which the investment is acquired. FA © 2014 25. When an investor purchases sufficient ordinary shares to gain significant influence over the investee, what is the proper accounting treatment of any excess of cost over carrying amount of net assets acquired? A. The excess remains in the investment account until it is sold. B. The excess is immediately expensed in the period in which the investment is made. C. The excess is charged to retained earnings at the time the investor resells the investment. D. The excess is amortized over the time period that is reasonable in the light of the underlying cause of the excess. FA © 2014 26. An investor uses the equity method to account for 30% investment. Amortization of the investor's share of the excess of fair value over carrying amount of depreciable assets at the date of the purchase shall be reported in the investor's income statement as part of A. Amortization of goodwill C. Equity in earnings of investee B. Depreciation expense D. Other expense FA © 2014 27. An investor uses the equity method to account for investment in ordinary shares. The purchase price implies a fair value of the investee's depreciable assets in excess of the investee's net asset carrying values. The investor's amortization of the excess A. Decreases the goodwill account B. Decreases the investment account C. Does not affect the investment account D. Increases the investment revenue account FA © 2014 MCQ - Theory Page 18 Investment in Equity Securities 28. An investor uses the equity method to account for purchase of another entity's ordinary shares at the beginning of the current year. On the date of acquisition, the fair value of the investee's inventory and land exceeded their carrying amount. How would the inventory excess and land excess affect respectively the investor's reported equity in earnings of the investee for the current year? A. Decrease and Decrease C. Increase and No effect B. Decrease and No effect D. Increase and Increase FA © 2014 29. Goodwill arising from an investment in associate is A. Included in the carrying amount of the investment and not amortized. FA © 2014 B. Excluded from carrying amount of the investment but charged to retained earnings. C. Included in the carrying amount of the investment and amortized over the useful life. D. Excluded from carrying amount of the investment but charged to expense immediately. 30. How is goodwill arising on the acquisition of an associate dealt with in the financial statements? A. It is amortized. B. It is impairment tested individually. C. It is written off against profit or loss. FA © 2014 D. Goodwill is not recognized separately within the carrying amount of the investment. 31. If there is any excess of the investor's share of the net fair value of the associate's identifiable assets and liabilities over the cost of the investment, that is, "bargain purchase", how should that excess be treated? A. It should be included in retained earnings. B. It should be included in other comprehensive income. C. It should be disclosed separately as part of the investor's equity. D. It should be included as income in the determination of the investor's share of the associate's profit or loss for the period. TOA © 2013 32. Under the equity method of accounting for investments, an investor recognizes its share of the earnings in the period in which the A. Investee pays dividend B. Investor sells the investment C. Investee declares a dividend D. Earnings are reported by the investee in its financial statements FA © 2014 MCQ - Theory Page 19 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING 33. When an investor uses the equity method to account for investment in ordinary shares, the investment account will be increased when the investor recognizes A. A cash dividend received from the investee. B. A proportionate interest in the net income of the investee. C. Periodic amortization of the goodwill related to the purchase. D. Depreciation related to the excess of market value over carrying amount of the investee's depreciable assets at the date of purchase by the investor. FA © 2014 34. If an associate has outstanding cumulative preference shares, held by outside interests, the investor computes its share of profit or loss A. Without regard for preference dividends. B. After adjusting for the preference dividends only when declared, FA © 2014 C. After adjusting for preference dividends which were actually paid during the year. D. After adjusting for the preference dividends, whether or not the dividends have been declared. 35. An investor uses the equity method to account for its 30% investment in ordinary shares of an investee. Amortization of the investor's share of the excess of fair value over carrying amount of depreciable assets at the date of the purchase should be reported in the investor's income statement as part of A. Amortization of goodwill C. Equity in earnings of investee B. Depreciation expense D. Other expense TOA © 2013 36. An investor uses the equity method to account for its purchase of another entity's ordinary shares. On the date of acquisition, the fair value of the investee's inventory and land exceeded their carrying amount. How do these excesses of fair value over carrying amount affect the investor's reported equity in earnings of the investee for the current year? TOA © 2013 A. B. C. D. Inventory excess Decrease Decrease Increase Increase Land excess Decrease No effect Increase No effect 37. An investor uses the equity method to account for an investment in ordinary shares. After the date of acquisition, the investment account of the investor would A. Not be affected by its share of the earnings or losses of the investee B. Be increased by its share of the earnings of the investee, and decreased by its share of the losses of the investee C. Be increased by its share of the earnings of the investee, but not be affected by its share of the losses of the investee D. Not be affected by its share of the earnings of the investee, but be decreased by its share of the losses of the investee FA © 2014 MCQ - Theory Page 20 Investment in Equity Securities 38. 39. When an investor uses the equity method to account for investment in ordinary shares, the investment account will be increased when the investor recognizes A. A cash dividend received from the investee B. A proportionate interest in the net income of the investee C. Periodic amortization of the goodwill related to the purchase D. Depreciation related to the excess of market value over carrying amount of the investee's depreciable assets at the date of purchase by the investor. TOA © 2013 When an investor uses the equity method to account for investment in ordinary shares, cash dividends received by the investor from the investee shall be recorded as A. Dividend income B. A deduction from the investment account C. A deduction from the investor's share of the investee's profits FA © 2014 D. A deduction from the shareholders' equity account, dividends to shareholder. 40. When an investor purchases sufficient ordinary shares to gain significant influence over the investee, what is the proper accounting treatment of any excess of cost over the carrying amount of the net assets acquired? A. The excess remains in the investment account until it is sold. B. The excess is immediately expensed in the period in which the investment is made. C. The excess is charged to retained earnings at the time the investor resells the investment. D. The excess is amortized over the time period that is reasonable in the light of the underlying cause of the excess. TOA © 2013 41. An investor uses the equity method to account for investment in ordinary shares. The purchase price implies a fair value of the investee's depreciable assets in excess of the investee's net asset carrying amount. The investor's amortization of the excess TOA © 2013 A. Decreases the goodwill account C. Does not affect the investment account B. Decreases the investment account D. Increases the investment revenue account 42. On January 1 of the current year, an entity purchased 10% of another entity's ordinary shares. The entity purchased additional shares bringing the ownership up to 40% of the investee's ordinary shares outstanding on August 1 of the current year. During October of the current year, the investee declared and paid a cash dividend on all of the outstanding ordinary shares. How much income from the investment should be reported for the year? A. 40% of investee's income for the current year B. Amount equal to dividends received from the investee C. 40% of investee's income from August 1 to December 31 only D. 10% of investee's income from January 1 to July 31, plus 40% of investee's income from August 1 to December 31 TOA © 2013 MCQ - Theory Page 21 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING 43. An investor shall discontinue the use of the equity method when A. The associate operates under severe long-term restrictions. B. The investor ceases to have control over the associate. C. The business activities of the investor and associate are dissimilar. D. The investor ceases to have significant influence over the associate. FA © 2014 44. An investor shall discontinue the use of the equity method from the date I. The investor ceases to have significant influence over an associate. II. The associate operates under severe long-term restrictions that significantly impair the ability to transfer funds to the investor. A. I only C. Both I and II B. II only D. Neither I nor II TOA © 2013 45. When the investor discontinues the use of the equity method because significant influence is lost, the investment in associate retained by the investor shall be measured at A. Amortized cost C. Fair value B. Carrying amount D. Original cost FA © 2014 46. If under the equity method, an investor's share of losses of an associate equals or exceeds the carrying amount of an investment, which of the following statements is incorrect? A. The investment is reported at NIL value. B. The investor ordinarily discontinues its share of further losses. C. If the associate subsequently reports profit, the investor resumes its share of the profit without regard to the share of net loss not previously recognized. TOA © 2013 D. Additional losses are provided or a liability is recognized to the extent that the investor has incurred legal or constructive obligations or made payments on behalf of the associate. 47. How is the impairment test carried out for an investment in associate? A. The carrying amount of the investment shall be compared with the market value. B. The goodwill is separated from the rest of the investment and is impairment tested individually. C. The entire carrying amount of the investment is tested for impairment by comparing the recoverable amount with carrying amount. D. The recoverable amounts of all investments in associates shall be assessed together to determine whether there has been an impairment on all investments. TOA © 2013 MCQ - Theory Page 22 Investment in Equity Securities 48. How is the impairment test carried out for an associate? A. The goodwill is impairment tested individually. B. The carrying amount of the investment shall be compared with the market value. C. The recoverable amounts of all investments in associates shall be assessed together. D. The entire carrying amount of the investment is tested for impairment by comparing the recoverable amount with the carrying amount. FA © 2014 49. In its financial statements, an investor uses the equity method of accounting for its 30% ownership in an investee. At year-end, the investor has a receivable from the investee. How should the receivable be reported in the investor's financial statements for the current year? A. The total receivable should be disclosed separately. B. The total receivable should be included as part of the investment in associate, without separate disclosure. C. None of the receivable should be reported, but the entire receivable should be offset against investee's payable to the investor. D. Seventy percent of the receivable should be separately reported, with the balance offset against 30% of investee's payable to the investor. TOA © 2013 50. Which of the following statements is incorrect concerning the equity method? A. The investment in associate is initially recorded at cost. B. Distributions received from the investee reduce the carrying amount of the investment. C. The investor's share of the profit or loss of the investee is not recognized in the investor's profit or loss. D. The investment in associate is increased or decreased by the investor's share of the profit or loss of the investee after the date of acquisition. TOA © 2013 51. Which of the following statements is incorrect concerning the equity method? A. The investment in associate is initially recorded at cost. B. Dividends received from the associate are accounted for as income.. C. The investor's share of the profit or loss of the investee is recognized in the investor's profit or loss. D. The investment in associate is increased or decreased by the investor's share of the profit or loss of the investee after the date of acquisition. FA © 2014 52. At the beginning of the current year, an investor acquired 30% of the ordinary shares of another entity. In the current year, the investee has net earnings which exceeded dividends paid. The investor mistakenly recorded these transactions using the cost method instead of the equity method of accounting. What effect would this have on investment account, net earnings and retained earnings, respectively? FA © 2014 MCQ - Theory Page 23 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING A. Overstate, overstate, overstate B. Overstate, understate, understate C. Understate, overstate, understate D. Understate, understate, understate Cost method to equity method 53. On January 1 of the current year, an entity purchased 10% of another entity's ordinary shares. The entity purchased additional shares bringing the ownership up to 40% on August 1 of the current year. During October of the current year,' the investee declared and paid a cash dividend on all of the outstanding ordinary shares. How much income from the investment should the entity report for the current year? A. 40% of investee's income for the current year B. Amount equal to dividends received from the investee C. 40% of investee's income from August 1 to December 31 only D. 10% of investee's income from January 1 to July 31, plus 40% of investee's income from August 1 to December 31 FA © 2014 Presentation & disclosure 54. An investor uses the equity method for 30% interest. At year-end, the investor has a receivable from the investee. How should the receivable be reported in investor's financial statements for the current year? A. The total receivable should be disclosed separately. B. The total receivable should be included as part of the investment in associate, without separate disclosure. C. None of the receivable should be reported, but the entire receivable should be offset against the investee's payable to the investor. D. Seventy percent of the receivable should be separately reported, with the balance offset against 30% of the investee's payable to the investor. FA © 2014 55. An investor uses the cost method for its 15% ownership in an investee. At year-end, the investor has a receivable from the investee. How should the receivable be reported in the investor's year-end financial statements? A. The total receivable should be reported separately. B. The total receivable should be included as part of the investment, without separate disclosure. C. The total receivable should be offset against the investee's payable to the investor, without separate disclosure. D. Eighty-five percent of the receivable should be reported separately, with the balance offset against the investee's payable to the investor. FA © 2014 MCQ - Theory Page 24 Investment in Equity Securities Multiple Choice – Problems: Cost Method Nonmonetary exchange 1. On July 1, 2014, Impervious Company exchanged a land for 25,000 ordinary shares of Ace Company. On this date, the carrying amount of the land was P2,500,000 and the fair value was P3,000,000. On July 1, 2014, the carrying amount of Ace Company's share was P60 and the market value was P150. On December 31, 2014, Ace Company had 250,000 ordinary shares and the carrying amount per share was P80. What amount should be reported on December 31, 2014 as investment in Ace Company? A. 1,500,000 C. 3,000,000 B. 2,500,000 D. 3,750,000 FA © 2014 Dividend income Cost method 2. On January 1, 2014, Happy Company purchased 10% of Rose Company's ordinary share capital for P6,000,000. Rose Company reported net income of P500,000 for 2014 and P2,000,000 for 2015, and paid dividend of P3,000,000 on December 31, 2015. What amount should be reported as dividend income for 2015? A. 200,000 C. 300,000 B. 250,000 D. 500,000 FA © 2014 3. Cobb Company purchased 10,000 shares representing 2% ownership of Roe Company on February 15,2014. Cobb Company received a stock dividend of 2,000 snares on March 31, 2014, when the carrying amount per share was P350 and the market value per share was P400. Roe Company paid a cash dividend of PI 5 per share on September 15, 2014. In the income statement for the year ended October 31, 2014, what amount should be reported as dividend income? A. 150,000 C. 880,000 B. 180,000 D. 980,000 P1 © 2014 4. Wood Company owns 20,000 shares of Arlo Company's 200,000 shares of P100 par, 6% cumulative, nonparticipating preference share capital and 10,000 shares representing 2% ownership of Arlo's ordinary share capital. During 2014, Arlo declared and paid preference dividends of P2,400,000. No dividends had been declared or paid during 2013. In addition, Wood received a 5% stock dividend on ordinary share from Arlo when the quoted market price of Arlo's ordinary share was P10. What amount should be reported as dividend income in the 2014 income statement? A. 120,000 C. 240,000 B. 125,000 D. 245,000 P1 © 2014 MCQ – Problems: Cost Method Page 25 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING 5. On January 1, 2014, Wynn Company bought 15% of Parr Company's ordinary shares outstanding for P6,000,000. Wynn appropriately accounted for this investment by the cost method. The investee reported net income of P3,000,000 for 2014 and P9,000,000 for 2015. No dividend was paid in 2014 but the investee paid dividend of P15,000,000 in 2015. What amount of dividend income should be reported in 2015? A. 450,000 C. 1,800,000 B. 1,350,000 D. 2,250,000 P1 © 2014 Gain (loss) on disposal 6. On January 1, 2014, Adam Company purchased as a long-term investment 100,000 ordinary shares of Mill Company for P40 a share. On December 31, 2014, the market price of Mill's share was P35, reflecting a temporary decline in market price. On December 28, 2015, Adam Company sold 80,000 shares of Mill Company for P30 a share. For the year ended December 31, 2015, what amount should be reported as loss on disposal of long-term investment? A. 400,000 C. 900,000 B. 800,000 D. 1,000,000 P1 © 2014 7. During 2014„ Reminiscent Company bought shares of another entity to be held for trading. June 1 20,000 shares @P100 2,000,000 December 1 30,000 shares @P120 3,600,000 5,600,000 The transactions for 2015 are as follows: January 10 Received cash dividend at P10 per share. January 20 Received 20% stock dividend. December 10 Sold 30,000 shares at P125 per share. What is the gain on sale of investment using the FIFO approach? A. 150,000 C. 950,000 B. 550,000 D. 1,150,000 FA © 2014 Stock rights 8. Valedictory Company issued rights to subscribe to its stock, the ownership of 4 shares entitling the shareholders to subscribe for 1 share at P100. Vast Company owned 50,000 shares of Valedictory Company with total cost of P5,000,000. The share is quoted right-on at 125. The stock rights are accounted for separately. What is the cost of the new investment if all of the stock rights are exercised by Vast Company? A. 1,250,000 C. 1,500,000 B. 1,450,000 D. 1,562,500 FA © 2014 MCQ – Problems: Cost Method Page 26 Investment in Equity Securities 9. Haste Company invested in shares of another entity. Number of shares Cost 2012 20,000 2,000,000 2013 40,000 3,500,000 In 2014, the entity received 60,000 rights to purchase one share at P80. Five rights are required to purchase the share. At issue date, rights had a market value of P5 each. The entity used rights to purchase 10,000 additional shares of the investee and allowed the rights not exercised to lapse. What amount was debited to investment account for the purchase of the additional new shares? A. 800,000 C. 1,050,000 B. 900,000 D. 1,100,000 FA © 2014 10. On January 1, 2014, Animosity Company purchased 50,000 shares of another entity for P3,800,000. On October 1, 2014, the entity received 50,000 stock rights from the investee. Each right entitled the shareholder to acquire one share for P80. The market price of the investee's share was P100 immediately before the rights were issued and P90 immediately after the rights were issued. On December 1, 2014, the entity exercised all stock rights. On December 31, 2014, the entity sold 25,000 shares at P90 per share. The stock rights are not accounted for separately. If the FIFO approach is used, what is the gain on sale of investment that should be recognized in the current year? A. 250,000 C. 350,000 B. 300,000 D. 600,000 FA © 2014 11. On March 1, 2014, Evan Company purchased 10,000 ordinary shares of LVC at P80 per share. On September 30, 2014, Evan received 10,000 stock rights to purchase an additional 10,000 shares at P90 per share. The stock rights had an expiration date on February 1, 2015. On September 30, 2014, LVC's share had a market value P95 and the stock right had a market value of P5. What amount should be reported on September 30, 2014 for investment in stock rights? A. 50,000 C. 100,000 B. 60,000 D. 150,000 P1 © 2014 12. Rice Company owned 30,000 ordinary shares of Wood Company acquired on July 31, 2014, at a total cost of PI, 100,000. On December 1,2014, Rice received 30,000 stock rights from Wood. Each right entitles the holder to acquire one share at P45. The market price of Wood's share on this date was P50 and the market price of each right was P10. Rice sold its rights on December 31, 2014 for P450,000 less a P10,000 commission. What amount should be reported as gain from the sale of the rights? A. 140,000 C. 240,000 B. 150,000 D. 250,000 P1 © 2014 MCQ – Problems: Cost Method Page 27 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING 13. Adam Company owned 50,000 ordinary shares of Bland Company. These 50,000 shares were purchased by Adam in 2012 for P120 per share. On August 30,2014, Bland distributed 50,000 stock rights to Adam. Adam was entitled to buy one new share of Bland Company for P90 cash and two of these rights. On August 30,2014, each share had a market value of P130 and each right had a market value of P20. What total cost should be recorded for the new shares that are acquired by exercising the rights? A. 2,250,000 C. 3,250,000 B. 3,050,000 D. 5,500,000 P1 © 2014 14. Excelsia Company issued rights to subscribe to its stock, the ownership of 4 shares entitling the shareholders to subscribe for 1 share at P100. Jealina Company owns 50,000 shares of Excelsia Company with total cost of P5,000,000. The share is quoted right-on at 125. The stock rights are accounted for separately. What is the cost of the new investment if all of the stock rights are exercised by Jealina Company? A. 1,250,000 C. 1,500,000 B. 1,450,000 D. 1,562,500 P1 © 2014 15. On January 1, 2014, Mylene Company purchased 50,000 shares of another entity for P3,600,000. On October 1,2014, the entity received 50,000 stock rights from the investee. Each right entitled the shareholder to acquire one share for P85. The market price of the investee's share was P100 immediately before the rights were issued and P90 immediately after the rights were issued. On December 1, 2014, the entity exercised all stock rights. On December 31, 2014, the entity sold 25,000 shares at P90 per share. The stock rights are not accounted for separately. The FIFO approach is used. What is the gain on sale of investment that should be recognized in 2014? A. 125,000 C. 450,000 B. 287,500 D. 700,000 P1 © 2014 Comprehensive Questions 16 & 17 are based on the following information. P1 © 2014 On January 1,2012, Christopher Company purchased 20,000 shares of Bay Company, P100 par, at P110 per share. On March 1, 2012, Bay Company issued rights to Christopher Company, each permitting the purchase of 1/4 share at par. No entry was made. The bid price of the share was 140 and there was no quoted price for the rights. On April 1,2012, Christopher Company paid for the new shares charging the payment to the investment account. Since Christopher Company felt that it had been assessed by Bay Company, the dividends received from Bay Company in 2012 and 2013 (10% on December 31 of each year) are credited to the investment account until the debit was fully offset. Bay Company declared annual dividend MCQ – Problems: Cost Method Page 28 Investment in Equity Securities of P2,500,000 for the year ended December 31,2012 and 2013. On January 1, 2014, Christopher Company received 50% stock dividend from Bay Company. On same date, the shares received as stock dividend were sold at P160 per share and the proceeds were credited to income. On December 31,2014, the shares of Bay Company were split 2 for 1. Christopher Company found that each new share was worth P5 more than the P110 paid for the original shares. Accordingly, Christopher Company debited the investment account with the additional shares received at P110 per share and credited income. On June 30,2015. Christopher Company sold one-half of the investment at P92 per share and credited the proceeds to the investment account. 16. What is the balance of the investment on December 31, 2015 as it was kept by Christopher Company? A. 2,200,000 C. 3,150,000 B. 2,650,000 D. 4,950,000 17. Using the average method, what is the correct balance of the investment on December 31, 2015? A. 0 C. 1,800,000 B. 900,000 D. 2,200.000 Multiple Choice – Problems: Equity Method Purchase price 18. On January 1, 2014, Power Company purchased 25% of the outstanding ordinary shares of an investee. During the current year, the investee reported net income of P4,200,000 and distributed dividends of PI,800,000. The carrying amount of the investment on December 31, 2014 was P3,200,000 after applying the equity method. What was the purchase price paid for the investment? A. 1,700,000 C. 3,800,000 B. 2,600,000 D. 4,700,000 FA © 2014 19. On January 1, 2014, Small Company purchased 25% of Big Company. No "excess" resulted from the purchase. Small Company appropriately carried this investment at equity and the carrying amount of the investment was PI,900,000 on December 31, 2014. Big Company reported net income of Pi,200,000 for the current year and paid cash dividend of P480,000 on December 31, 2014. What amount did Small Company pay for the 25% interest in Big Company? A. 1,720,000 C. 2,080,000 B. 2,020,000 D. 2,320,000 FA © 2014 MCQ – Problems: Equity Method Page 29 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING 20. On July 1, 2014, Miller Company purchased 25% of Wall Company's outstanding ordinary shares and no goodwill resulted from, the purchase. Miller appropriately carried this investment at equity and the balance in Miller's investment account was P1,900,000 at December 31, 2014. Wall Company reported net income of PI,200,000 for the year ended December 31, 2014, and paid dividend totaling P480,000 on December 31,2014. How much did Miller pay for the 25% interest in Wall? A. 1,720,000 C. 2,020,000 B. 1,870,000 D. 2,170,000 P1 © 2014 Dividend revenue 21. Green Company owned 30% of the outstanding ordinary shares and 100% of the outstanding noncumulative nonvoting preference shares of Gold Company. In the current year, Gold Company declared dividend of P1,000,000 on ordinary share capital and P600,000 on preference share capital. What amount of dividend revenue should be reported for the current year? A. 0 C. 600,000 B. 300,000 D. 900,000 FA © 2014 Loss from investment 22. On January 1, 2011, Bart Company acquired as a long term investment for P7,000,000, a 40% interest in Hall Company when the fair value of Hall's net assets was PI 7,500,000. Hall Company reported the following net losses: 2011 5,000,000 2012 7,000,000 2013 8,000,000 2014 4,000,000 On January 1, 2013, Bart Company made cash advances of P2,000,000 to Hall Company. On December 31, 2014, it is not expected that Bart Company will provide further financial support for Hall Company. What amount should be reported in 2014 as loss from investment? A. 600,000 C. 1,600,000 B. 1,000,000 D. 4,000,000 P1 © 2014 Investment income Net income 23. On July 1, 2014, Focus Company purchased 30,000 shares of Eagle Company's 100,000 outstanding ordinary shares for P200 per share. On December 15, 2014, Eagle Company paid P1,000,000 in dividends. Eagle Company's net income for 2014 was P5,000,000 earned evenly throughout the year. What amount of income from the investment should be reported for 2014? MCQ – Problems: Equity Method Page 30 Investment in Equity Securities A. 150,000 B. 300,000 C. 750,000 D. 1,500,000 FA © 2014 24. On July 1, 2014, Denver Company purchased 30,000 shares of Eagle Company's 100,000 outstanding ordinary shares for P200 per share. On December 15, 2014, the investee paid P400,000 in dividends to the ordinary shareholders. The investee's net income for the year ended December 31, 2014 was P1,200,000, earned evenly throughout the year. What amount of income from the investment should be reported in 2014? A. 60,000 C. 180,000 B. 120,000 D. 360,000 P1 © 2014 25. On January 1, 2014, Peer Company acquired as a long-term investment a 20% interest in another entity. Peer Company paid P7,000,000 for this investment when the fair value of the net assets was P35,000,000. The investor can exercise significant influence over the investee's operating and financial policies. For the year ended December 31, 2014, the investee reported net income of P6,000,000 and paid cash dividend of P4,000,000. What amount of revenue from the investment should be reported for 2014? A. 400,000 C. 800,000 B. 600,000 D. 1,200,000 FA © 2014 26. On January 1, 2014, Dyer Company acquired as a long-term investment a 20% ordinary share interest in Eason Company. Dyer paid P7,000,000 for this investment when the fair value of Eason's net assets was P35,000,000. Dyer can exercise significant influence over Eason's operating and financial policies. For the year ended December 31,2014, the investee reported net income of P4,000,000 and declared and paid cash dividends of P1,600,000. What amount of revenue from the investment should be reported for 2014? A. 320,000 C. 800,000 B. 480,000 D. 1,120,000 P1 © 2014 27. On July 1, 2014 Blush Company purchased 20% of the outstanding ordinary shares of an investee for P4,000,000 when the fair value of net assets was P20,000,000. Blush Company has the ability to exercise significant influence over the operating and financial policies of the investee. The following data concerning the investee are available: Net income Dividend declared and paid MCQ – Problems: Equity Method 12 months ended December 31,2014 3,000,000 1,900,000 6 months ended December 31,2014 1,600,000 1,000,000 Page 31 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING In the income statement for the year ended December 31, 2014, what amount of income should be reported from the investment? A. 200,000 C. 380,000 B. 320,000 D. 600,000 FA © 2014 28. On January 1, 2014, Mega Company acquired 10% of the outstanding voting shares of Sony Company. On January 1, 2015, Mega Company gained the ability to exercise significant influence over financial and operating policies of Sony Company by acquiring 20% of Sony Company's outstanding ordinary shares. The two purchases were made at prices proportionate to the value assigned to Sony Company's net assets which equaled their carrying amounts. Sony Company reported the following: 2014 2015 Dividends paid 2,000,000 3,000,000 Net income 6,000,000 6,500,000 What amount should be reported as investment income for 2015? A. 650,000 C. 1,300,000 B. 900,000 D. 1,950,000 FA © 2014 Net income less preferred dividend 29. Norm Company owned 20% of Love Company's preference share capital and 50% of the ordinary share capital. Love Company's share capital outstanding on December 31, 2014 is as follows: 10% cumulative preference share capital 2,000,000 Ordinary share capital 7,000,000 Love Company reported net income of P5,000,000 for the year ended December 31, 2014. What amount should be recorded as investment income for the year ended December 31, 2014? A. 2,400,000 C. 2,600,000 B. 2,500,000 D. 2,700,000 FA © 2014 30. Moss Company owned 20% of Dubro Company's preference share capital and 80% of the ordinary share capital on December 31, 2014. 10% cumulative preference share capital 5,000,000 Ordinary share capital 7,000,000 The investee reported net income P3,000,000 for the year ended December 31, 2014. What is the equity in earnings of the investee for 2014? MCQ – Problems: Equity Method Page 32 Investment in Equity Securities A. 2,100,000 B. 2,300,000 C. 2,000,000 D. 2,400,000 P1 © 2014 Net income, amortization of excess cost 31. Breezy Company purchased 35% of an associate on January 1, 2014 for PI 1,200,000 when the carrying amount of net assets was P32,400,000. On that day, the market value of the net assets equaled their carrying amount with the following exceptions: Carrying amount Market Equipment 7,000,000 5,600,000 Building 1,600,000 2,600,000 The equipment has a remaining useful life of 5 years, and the building has a remaining useful life of 10 years. The associate reported net income of P3,200,000 and cash dividends of P1,000,000 for the current year. What is the investment income for the current year? A. 987,000 C. 1,183,000 B. 1,120,000 D. 1,260,000 FA © 2014 32. On January 1, 2014, Ronald Company purchased 40%) of the outstanding ordinary shares of New Company, paying P6,400,000 when the carrying amount of the net assets of New Company equaled PI2,500,000. The difference was attributed to equipment which had a carrying amount of P3,000,000 and a fair market value of P5,000,000 and to building which had a carrying amount of P2,500,000 and a fair value of P4,000,000. The remaining useful life of the equipment and building was 4 years and 12 years, respectively. During 2014, New Company reported net income of P5,000,000 and paid dividends of P2,500,000. What amount should be reported as investment income for 2014? A. 1,000,000 C. 1,800,000 B. 1,750,000 D. 2,000,000 P1 © 2014 33. Sage Company bought 40% of Eve Company's outstanding ordinary shares on January 1, 2014, for P4,000,000. The carrying amount of Eve's net assets at the purchase date totaled P9,000,000. Fair values and carrying amounts were the same for all items except for plant and inventory, for which fair values exceeded their carrying amounts by P900,000 and P100,000, respectively. The plant has an 18-year life. All inventory was sold during 2014. During 2014, the investee reported net income of P1,200,000 and paid a P200,000 cash dividend. What amount should be reported as investment income in the income statement for the year ended December 31, 2014? A. 320,000 C. 420,000 B. 360,000 D. 480,000 P1 © 2014 MCQ – Problems: Equity Method Page 33 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING 34. On January 1, 2014, Anne Company purchased 20% of the outstanding ordinary shares of Dune Company for P4,000,000, of which PI,000,000 was paid in cash and P3,000,000 is payable with 12% annual interest on December 31,2014. Anne also paid P500,000 to a business broker who helped find a suitable business and negotiated the purchase. At the time of acquisition, the fair values of Dune's identifiable assets and liabilities were equal to their carrying amounts except for an office building which had a fair value in excess of carrying amount of P2,000,000 and an estimated life of 10 years. Dune's shareholders' equity on January 1,2014 was PI3,000,000. During 2014T Dune Company reported net income of P5,000,000 and paid dividend of P2,000,000. What amount of income should be reported for 2014 as a result of the investment? A. 620,000 C. 885,000 B. 810,000 D. 960,000 P1 © 2014 35. On January 1,2014, Occidental Company purchased 40% of the outstanding ordinary shares of Manapla Company for P3,500,000 when the net assets of Manapla amounted to P7,000,000. At acquisition date, the carrying amounts of the identifiable assets and liabilities of Manapla were equal to their fair value, except for equipment for which the fair value was P1,500,000 greater than its carrying amount and inventory whose fair value was P500,000 greater than its cost. The equipment has a remaining life of 4 years and the inventory was all sold during 2014. Manapla Company reported net income of P4,000,000 for 2014 and paid no dividends during 2014. What is the maximum amount of the "equity in earnings of the investee"? A. 1,250,000 C. 1,600,000 B. 1,350,000 D. 1,700,000 P1 © 2014 Maximum amount 36. On April 1, 2014, August Company purchased 40% of the outstanding ordinary shares of an associate for P4,000,000. On this date, the investee's net assets totaled P8,000,000 and August Company cannot attribute the excess of cost of the investment over the equity in the investee's net assets to any particular factor. The investee reported net income of PI,000,000 for the current year. What is the maximum amount which could be included in August Company's income before tax to reflect its "equity in earnings of the investee" for the current year? A. 270,000 C. 360,000 B. 300,000 D. 400,000 FA © 2014 MCQ – Problems: Equity Method Page 34 Investment in Equity Securities 37. On April 1, 2014, Ben Company purchased 40% of the outstanding ordinary snares of Clarke Company for P10,000,000. On that date, Clarke's net assets were P20,000,000 and Ben cannot attribute the excess of the cost of its investment in Clarke over its equity in Clarke's net assets to any particular factor. The investee's net income for 2014 is P5,000,000. What is the maximum amount which could be included in 2014 income before tax to reflect the "equity in net income of investee"? A. 1,400,000 C. 1,850,000 B. 1,500,000 D. 2,000,000 P1 © 2014 Carrying amount Cost method 38. On January 1, 2014, Subtle Company purchased 20% of Lax Company for P3,000,000. This investment did not give Subtle Company the ability to exercise significant influence over Lax Company. During the current year, Lax Company reported net income of P3,500,000 and paid cash dividends of P4,000,000. What is the carrying amount of the investment in Lax Company on December 31, 2014? A. 2,200,000 C. 3,000,000 B. 2,900,000 D. 3,700,000 FA © 2014 Step acquisition 39. Pare Company purchased 10% of Tot Company's 100,000 outstanding ordinary shares on January 1, 2014 for P500,000. On December 31,2014, Pare purchased an additional 20,000 shares of Tot for P1,500,000. Tot had not issued any additional shares during 2014. The investee reported earnings of P3,000,000 for 2014. The fair value of the 10% interest is P900,000 on December 31, 2014. What is the carrying amount of the investment in associate on December 31, 2014? A. 2,000,000 C. 2,400,000 B. 2,300,000 D. 2,900,000 P1 © 2014 40. Flame Company purchased 10% of an investee's 100,000 outstanding ordinary shares on January 1, 2014 for P1,000,000. On December 31, 2014, Flame Company purchased additional 20,000 shares of the investee for P3,000,000. On same date, the fair value of the 10% interest was Pi,400,000. The investee had not issued any additional shares during 2014. The investee reported net income of P8,000,000 for the current year but paid no dividends. What amount should be reported on December 31, 2014 as investment in associate? A. 4,000,000 C. 4,800,000 B. 4,400,000 D. 5,200,000 FA © 2014 MCQ – Problems: Equity Method Page 35 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING 41. On January 1, 2014, Mega Company acquired 10% of the outstanding ordinary shares of Penny Company for P4,000,000. On January 1,2015, Mega gained the ability to exercise significant influence over financial and operating control of Penny by acquiring an additional 20% of Penny's outstanding ordinary shares for P 10,000,000. The fair value Penny's net assets equaled carrying amount. The fair value of the 10% interest on January 1,2015 was P6,000,000. For the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2015, the investee reported the following: 2014 2015 Dividend paid 2,000,000 3,000,000 Net income 6,000,000 6,500,000 What is the carrying amount of the investment in associate on December 31, 2015? A. 15,050,000 C. 16,700,000 B. 16,000,000 D. 17,050,000 P1 © 2014 Percent of net assets 42. Accurate Company acquired 30% of the issued share capital of an investee for Pi,000,000 on January 1, 2013. The accumulated profits of the investee on this date totaled P2,000,000. The abbreviated statement of financial position of the investee on December 31, 2014 is as follows: Sundry net assets 6,000,000 Share capital, P10 par 1,000,000 Share premium 2,000,000 Retained earnings 3,000,000 The fair value of the net assets of the investee at the date of acquisition was P5,000,000. The recoverable amount of the net assets of the investee is deemed to be P7,000,000 on December 31, 2014. What amount should be reported on December 31, 2014 as investment in associate? A. 1,000,000 C. 1,800,000 B. 1,500,000 D. 2,100,000 FA © 2014 Net income, dividend 43. On January 1, 2014, Bliss Company purchased 10% of Red Company's outstanding ordinary shares for P4,000,000. Bliss Company is the largest single shareholder in Red Company and Bliss Company's officers are a majority on Red Company's board of directors. Red Company reported net income of P5,000,000 for the current year and paid dividends of P1,500,000. On December 31, 2014, what amount should be reported as investment in associate? A. 3,850,000 C. 4,350,000 B. 4,000,000 D. 4,500,000 FA © 2014 MCQ – Problems: Equity Method Page 36 Investment in Equity Securities 44. On January 1, 2014, Kean Company purchased 30% interest in Pod Company for P2,500,000. On this date Pod's shareholders' equity was P5,000,000. The carrying amounts of Pod's identifiable net assets approximated their fair values, except for land whose fair value exceeded its carrying amount by P2,000,000. The investee reported net income of P1,000,000 for 2014 and paid no dividends. On December 31, 2014, what amount should be reported as investment in associate? A. 2,100,000 C. 2,760,000 B. 2,200,000 D. 2,800,000 P1 © 2014 45. On January 1, 2014, Saxe Company purchased 20% of Lex Company's ordinary shares outstanding for P6,000,000. The "acquisition cost is equal to the carrying amount of the net assets acquired. During 2014, the investee reported net income of P7,000,000 and paid cash dividend of P4,000,000. What is the balance in the investment in associate on December 31, 2014? A. 5,200,000 C. 6,600,000 B. 6,000,000 D. 7,400,000 P1 © 2014 46. On January 1, 2014, Dell Company paid PI8,000,000 for 50,000 ordinary shares of Case Company which represent a 25% interest in the net assets of Case. The acquisition cost is equal to the carrying amount of the net assets acquired. Dell has the ability to exercise significant influence over Case. Dell received a dividend of P35 per share from Case in 2014. The investee reported net income of P9,600,000 for the year ended December 31, 2014. On December 31, 2014, what amount should be reported as investment in associate? A. 18,000,000 C. 20,400,000 B. 18,650,000 D. 22,150,000 P1 © 2014 Net income, dividend, amortization of excess cost 47. On January 1, 2014, Flair Company purchased 30% interest in an investee for P2,500,000. On this date, the investee's shareholders' equity was P5,000,000. The carrying amounts of the investee's identifiable net assets approximated their fair values, except for land whose fair value exceeded its carrying amount by P2,000,000. The investee reported net income of P1,000,000 for the current year and paid no dividend. On December 31, 2014, what amount should be reported as investment in associate? A. 2,200,000 C. 2,760,000 B. 2,700,000 D. 2,800,000 FA © 2014 48. On January 1, 2014, Courteous Company purchased 30% of the outstanding ordinary shares of an investee for P5,160,000. At the date of acquisition, the investee's net assets had a carrying amount of P11,800,000. Depreciable assets with an average remaining life of 4 MCQ – Problems: Equity Method Page 37 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING years have a current fair value that is P2,600,000 in excess of carrying amount. The remaining difference cannot be attributed to any identifiable tangible or intangible asset. At the end of 2014, the investee reported net income of P3,600,000 and paid cash dividends of P400,000. What amount should be reported as investment in associate on December 31, 2014? A. 4,715,000 C. 5,925,000 B. 5,883,000 D. 6,120,000 FA © 2014 49. On January 1, 2014, Magic Company purchased 40% of the outstanding ordinary shares of an investee paying P2,560,000 when the carrying amount of the net assets of the investee equaled P5,000,000. The difference was attributed to equipment which had a carrying amount of P1,200,000 and a fair market value of P2,000,000, and to building with a carrying amount of P1,000,000 and a fair market value of Pi,600,000. The remaining useful life of the equipment and building was 4 years and 12 years, respectively. During the current year, the investee reported net income of P1,600,000 and paid dividends of PI,000,000. What is the carrying amount of the investment in associate on December 31, 2014? A. 2,550,000 C. 2,800,000 B. 2,700,000 D. 3,050,000 FA © 2014 50. Alpha Company acquired 20,000 shares of Beta Company on January 1, 2014 at PI20 per share. Beta Company had 80,000 shares outstanding with a carrying amount of P8,000,000. The difference between the carrying amount and fair value of Beta Company on January 1,2014 is attributable to a broadcast license which is an intangible asset. Beta Company recorded earnings of P3,600,000 and P3,900,000 for 2014 and 2015, respectively, and paid per-share dividend of P16 in 2014 and P20 in 2015. Alpha Company has a 20-year straightline amortization policy for the broadcast license. What is the carrying amount of the investment in associate on December 31, 2015? A. 2,400,000 C. 3,555,000 B. 3,515,000 D. 4,275,000 P1 © 2014 51. On January 1, 2014, Mighty Company acquired 20% of the outstanding ordinary shares of an investee for P7,000,000. This investment gave Mighty Company the ability to exercise significant influence over the investee. The carrying amount of the acquired net assets was P6,000,000. The excess of cost over carrying amount was attributed to an identifiable intangible asset which was undervalued on investee's statement of financial position and which had a remaining useful life of ten years. For the year ended December 31, 2014, the investee reported net income of PI,800,000 and paid cash dividend of P600,000 on its ordinary shares. On December 31, 2014, what is the carrying amount of the investment in associate? MCQ – Problems: Equity Method Page 38 Investment in Equity Securities A. 6,780,000 B. 6,900,000 C. 7,000,000 D. 7,140,000 FA © 2014 52. In January 2014, Farley Company acquired 20% of the outstanding ordinary shares of Davis Company for P8,000,000. This investment gave Farley the ability to exercise significant influence over Davis. The carrying amount of the acquired shares was P6,000,000. The excess of cost over carrying amount was attributed to a depreciable asset which was undervalued on Davis' statement of financial position and which had a remaining useful life often years. For the year ended December 31, 2014, the investee reported net income of P1,800,000 and paid cash dividends of P400,000 and thereafter issued 5% stock dividend. What is the carrying amount of the investment in associate on December 31, 2014? A. 7,720,000 C. 8,000,000 B. 7,800,000 D. 8,080,000 P1 © 2014 53. On January 1, 2014, Bing Company purchased 30,000 shares of Latt Company's 200,000 outstanding ordinary shares for P6,000,000. On that date, the carrying amount of the acquired shares on Latt's books was P4,000,000. Bing attributed the excess of cost over carrying amount to patent. The patent has a remaining useful life of 10 years. During 2014, Bing's officers gained a majority on Latt's board of directors. Latt Company reported earnings of P5,000,000 for the year ended December 31,2014, and declared and paid dividend of P3,000,000 during 2014. On December 31, 2014, the investee's ordinary share was trading over-the-counter at P15. What is the carrying amount of the investment in associate on December 31, 2014?. A. 6,000,000 C. 6,300,000 B. 6,100,000 D. 6,750,000 P1 © 2014 54. On January 1,2014, Cyber Company bought 30% of the outstanding ordinary shares of Free Company for P5,000,000 cash. Cyber Company accounts for this investment by the equity method. At the date of acquisition, Free Company's net assets had a carrying amount of P12,000,000. Depreciable assets with an average remaining life of five years have a current market value that is P2,500,000 in excess of their carrying amount. The remaining difference between the purchase price and the carrying amount of the underlying equity cannot be attributed to any identifiable tangible or intangible asset. Accordingly, the remaining difference is allocated to goodwill. At the end of 2014, Free Company reported net income of P4,000,000. During 2014, Free Company declared and paid cash dividends of P1,000,000. What is the carrying amount of the investment in associate on December 31, 2014? A. 5,000,000 C. 5,750,000 B. 5,400,000 D. 5,900,000 P1 © 2014 MCQ – Problems: Equity Method Page 39 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING 55. On January 1, 2014, Marie Company purchased 40% of the outstanding ordinary shares of Lester Company paying P2,560,000 when the carrying amount of the net assets of Lester equaled P5,000,000. The difference was attributed to equipment which had a carrying amount of P1,200,000 and a fair value of P2,000,000, and to building with a carrying amount of P1,000,000 and a fair value of P1,600,000. The remaining useful life of the equipment and building was 4 years and 12 years, respectively. During 2014, Lester Company reported net income of P1,600,000 and paid dividends of P1,000,000. What is the carrying amount of the investment in associate on December 31,2014? A. 2,550,000 C. 2,800,000 B. 2,700,000 D. 3,050,000 P1 © 2014 56. On January 1, 2014, Bridge Company purchased 25,000 shares of the 100,000 outstanding shares of River Company for a total of P1,000,000. At the time of the purchase, the carrying amount of River Company's equity was P3,000,000. River Company assets having a market value greater than carrying amount at the time of the acquisition were as follows: Carrying amount Market value Remaining life Inventory 400,000 500,000 Less than 1 year Equipment 2,000,000 2,500,000 5 years Goodwill 0 400,000 Indefinite River Company's net income in 2014 was P700,000. Dividends per share paid by River Company amounted to P3 in 2014. What is the carrying amount of the investment in associate on December 31,2014? A. 1,000,000 C. 1,075,000 B. 1,050,000 D. 1,100,000 P1 © 2014 Net loss, dividend 57. On January 1,2014, Alpha Company acquired 40% of the outstanding ordinary shares of an investee for P6,500,000. The carrying amount of the net assets of the investee equaled P12,500,000. Any excess of cost over carrying amount is attributable to goodwill. During the year, the investee reported net loss of P4,000,000 and paid dividends of P2,500,000. What is the carrying amount of the investment on December 31,2014? A. 3,900,000 C. 5,500,000 B. 4,900,000 D. 6,500,000 P1 © 2014 Deficit, net income, dividends 58. Smart Company had 100,000 ordinary shares outstanding. Globe Company acquired 30,000 shares of Smart Company for P120 per share in 2012. The securities are being held as longterm investment. Changes in retained earnings for Smart Company are as follows: MCQ – Problems: Equity Method Page 40 Investment in Equity Securities Retained earnings (deficit), January 1, 2014 (500,000) Net income for 2014 700,000 Retained earnings, December 31,2014 200,000 Net income for 2015" 800,000 Cash dividend paid on December 31, 2015 (400,000) Retained earnings, December 31,2015 600,000 What is the carrying amount of the investment in associate on December 31, 2015? A. 3,600,000 C. 3,930,000 B. 3,780,000 D. 4,080,000 FA © 2014 59. Pillar Company acquired a 30% equity interest in an investee for P400,000 on January 1, 2014. For the year ended December 31, 2014, the investee earned profit of P80,000 and paid no dividend. For the year ended December 31, 2015, the investee incurred loss of P32,000 and paid a dividend of P10,000. In the statement of financial position on December 31, 2015, what is the carrying amount of the investment in associate? A. 400,000 C. 414,400 B. 411,400 D. 438,000 FA © 2014 Net income, cash dividend, revaluation surplus 60. Chur Company acquired a 40% interest in Flim Company for PI,700,000 on January 1, 2014. The shareholders' equity of Flim Company on January 1 and December 31,2014 is presented below. January 1 December 31 Share capital 3,000,000 3,000,000 Revaluation surplus 1,300,000 Retained earnings 1,000,000 1,500,000 On January 1,2014, all the identifiable assets and liabilities of Flim Company were recorded at fair value. Flim Company reported profit of P700,000, after income tax expense of P300,000 and paid dividend of P200,000 to shareholders during the current year. The revaluation surplus is the result of the revaluation of land recognized by Flim Company on December 31,2014. Additionally, depreciation is provided by Flim Company on the diminishing balance method whereas Chur Company used the straight line. Had Flim Company used the straight line, the accumulated depreciation would be increased by P200,000. What is the carrying amount of the investment in associate on December 31,2014? A. 1,700,000 C. 2,320,000 B. 1,900,000 D. 2,420,000 P1 © 2014 MCQ – Problems: Equity Method Page 41 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING Comprehensive Questions 61 thru 63 are based on the following information. P1 © 2014 On January 1,2014, Haven Company acquired 20% of the ordinary shares of an associate for P6,000,000. On this date, all the identifiable assets and liabilities of the associate were recorded at fair value. An analysis of the acquisition showed that goodwill of P300,000 was acquired. The net income and dividend of the associate for 2014 and 2015 were as follows: 2014 2015 Net income 3,000,000 4,000,000 Dividend paid 1,000,000 1,500,000 In December 2014, the associate sold inventory to Haven Company for P900,000. The cost of the inventory was P600,000. This inventory remained unsold by Haven Company on December 31, 2014. However, it was sold by Haven Company in 2015. In December 2015, the associate sold inventory to Haven Company for P750,000. The cost of the inventory was P500,000. This inventory remained unsold by Haven Company on December 31,2015. 61. What is the investor's share in the profit of the associate for 2014? A. 540,000 C. 648,000 B. 600,000 D. 660,000 62. What is the investor's share in the profit of the associate for 2015? A. 750,000 C. 810,000 B. 800,000 D. 860,000 63. What is the carrying amount of the investment in associate on December 31,2015? A. 6,000,000 C. 6,850,000 B. 6,790,000 D. 6,900,000 Questions 64 thru 66 are based on the following information. P1 © 2014 On January 1,2014, Marissa Company acquired 25% of the outstanding shares of an investee at a total cost of P7,000,000. At the time, the carrying amount of net assets of the investee totaled P24,000,000. The investee owned equipment with 5-year remaining life and with a fair value of P2,000,000 more than carrying amount. The investee owned land with a fair value of P1,000,000 more than carrying amount. The investee earned net income of P5,000,000 evenly during the current year. The investee declared and paid a cash dividend of P3,000,000 to shareholders at year-end. The fair value of the investment at year-end isP7,500,000. MCQ – Problems: Equity Method Page 42 Investment in Equity Securities 64. What is the goodwill arising from the investment in associate? A. 0 C. 500,000 B. 250,000 D. 750,000 65. What is the investment income for 2014? A. 650,000 B. 900,000 C. 1,150,000 D. 1,250,000 66. What is the carrying amount of the investment in associate on December 31,2014? A. 7,000,000 C. 7,500,000 B. 7,400,000 D. 8,150,000 Questions 67 thru 69 are based on the following information. P1 © 2014 On January 1,2014, Interlude Company acquired a 30% interest in an investee at a cost of P3,200,000. The equity of the investee on the date of acquisition was P6,000,000, consisting of P4,000,000 share capital and P2,000,000 retained earnings. All the identifiable assets and 1 liabilities of the investee were recorded at fair value except for an equipment with a fair value of P3,000,000 greater than carrying amount. The remaining useful life of the equipment is 5 years. On December 31, 2014, Interlude Company had inventory costing P2,000,000 on hand which had been purchased from the investee. A profit of P600,000 had been made on the sale. During the current year, the investee reported net income of P4,000,000 and paid dividend of PI ,500,000. The equity of the investee on December 31,2014 showed the following: Share capital 4,000,000 Retained earnings 3,500,000 Retained earnings appropriated 1,000,000 Revaluation surplus 2,000,000 The revaluation surplus arose from a revaluation of land made on December 31,2014. The retained earnings appropriated arose from a transfer of unappropriated retained earnings to retained earnings appropriated for contingencies. 67. What is the goodwill from the acquisition of the investment? A. 0 C. 700,000 B. 500,000 D. 1,400,000 68. What is the investment income for 2014? A. 750,000 C. 1,020,000 B. 840,000 D. 1,200,000 69. What is the carrying amount of the investment in associate on December 31,2014? A. 3,200,000 C. 3,690,000 B. 3,590,000 D. 4,190,000 MCQ – Problems: Equity Method Page 43 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING Questions 70 thru 72 are based on the following information. P1 © 2014 On January 1, 2014, Forensic Company acquired a 10% interest in an investee for P3,000,000. The investment was accounted for using the cost method. On January 1, 2015, the entity acquired a further 15% interest in the investee for P6,750,000. On such date, the carrying amount of the net assets of the investee was P36,000,000 and the fair value of the 10% interest was P4,500,000. The fair value of the net assets of the investee is equal to carrying amount except for an equipment whose fair value exceeds carrying amount by P4,000,000. The equipment has a remaining life of 5 years. The investee reported net income of P8,000,000 for 2015 and paid dividend of P5,000,000 on December 31,2015. 70. What is the gain on remeasurement to equity to be recognized for 2015? A. 0 C. 2,250,000 B. 1,500,000 D. 4,500,000 71. What is the goodwill arising from the acquisition on January 1,2015? A. 350,000 C. 1,350,000 B. 1,250,000 D. 2,250,000 72. What is the carrying amount of the investment in associate on December 31,2015? A. 11,250,000 C. 12,000,000 B. 11,800,000 D. 14,300,000 Questions 73 thru 75 are based on the following information. FA © 2014 Grant Company acquired 30% of South Company's voting share capital for P2,000,000 on January 1, 2014. Grant's 30% interest in South gave Grant the ability to exercise significant influence over South's operating and financial policies. During 2014, South earned P800,000 and paid dividends of P500,000. South reported earnings of P1,000,000 for the six months ended June 30, 2015, and P2,000,000 for the year ended December 31, 2015. On July 1, 2015, Grant sold half of the investment in South for P1,500,000 cash. On such date, the investment is measured at fair value through other comprehensive income. South paid dividends of P600,000 on October 1, 2015. The fair value of the retained investment is Pl.600,000 on July 1, 2015 and Pl,800,000 on December 31, 2015. 73. What amount should be recognized as investment income for 2014 as a result of the investment? A. 150,000 C. 500,000 B. 240,000 D. 800,000 MCQ – Problems: Equity Method Page 44 Investment in Equity Securities 74. In the December 31, 2014 statement of financial position, what is the carrying amount of the investment? A. 2,000,000 C. 2,240,000 B. 2,090,000 D. 2,300,000 75. What total amount should be included in profit or loss for 2015 from the investment? A. 305,000 C. 710,000 B. 350,000 D. 910,000 Questions 76 thru 79 are based on the following information. FA © 2014 On January 1, 2014, Mountaineer Company acquired a 30% interest in an associate for P5,000,000. The equity of the associate at the date of acquisition consisted of share capital of P16,000,000 and retained earnings of P5,000,000. All the identifiable assets and liabilities of the associate were recorded at fair value. The associate reported the following: 2014 2015 Profit before tax 3,000,000 4,000,000 Income tax expense 900,000 1,200,000 Dividend paid 2,500,000 . 2,000,000 76. What is the goodwill arising from the acquisition? A. 0 C. 1,000,000 B. 500,000 D. 2,000,000 77. What is the investment income for 2014? A. 0 B. 630,000 C. 750,000 D. 900,000 78. What is the investment income for 2015? A. 0 B. 600,000 C. 840,000 D. 1,200,000 79. What is the carrying amount of the investment in associate on December 31, 2015? A. 4,620,000 C. 5,120,000 B. 5,000,000 D. 6,470,000 Questions 80 thru 83 are based on the following information. P1 © 2014 Grant Company acquired 30% of South Company's voting share capital for P2,000,000 on January 1, 2014. Grant's 30% interest in South gave Grant the ability to exercise significant influence over South's operating and financial policies. During 2014, South earned P800,000 and paid dividend MCQ – Problems: Equity Method Page 45 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING of P500,000. South reported earnings of P1,000,000 for the 6 months ended June 30,2015, and P2,000,000 for the year ended December 31,2015.OnJulyl,2015, Grant sold half of the investment in South for PI,500,000 cash. South paid dividend of P600,000 on October 1,2015. The fair value of the retained investment is P1,600,000 on July 1, 2015 and PI,800,000 on December 31, 2015. The retained investment is to be held as financial asset at fair value through other comprehensive income. 80. Before income tax, what amount should be included in the 2014 income statement as a result of the investment? A. 150,000 C. 500,000 B. 240,000 D. 800,000 81. In the December 31,2014 statement of financial position, what is the carrying amount ofthe investment in associate? A. 2,000,000 C. 2,240,000 B. 2,090,000 D. 2,300,000 82. In the 2015 income statement, what amount should be reported as gain from the sale of investment? A. 245,000 C. 350,000 B. 305,000 D. 455,000 83. In the 2015 income statement, what amount should be reported as gain from remeasurement ofthe retained investment? A. 405,000 C. 710,000 B. 605,000 D. 910,000 Questions 84 thru 87 are based on the following information. P1 © 2014 Glorious Company acquired 40% interest in an associate, Alta Company, for P5,000,000 on January 1,2014. At the acquisition date, there were no differences between fair value and carrying amount of identifiable assets and liabilities. Alta Company reported the following net income and dividend for 2014 and 2015: 2014 2015 Net income 2,000,000 3,000,000 Dividend paid 800,000 1,000,000 The following transactions occurred between Glorious Company and Alta Company: * On January 1,2014, Alta Company sold an equipment costing P500,000 to Glorious Company for P800,000. Glorious Company applied a 10% straight line depreciation. MCQ – Problems: Equity Method Page 46 Investment in Equity Securities * On July 1,2015, Alta Company sold an equipment for P900,000 to Glorious Company. The carrying amount of the equipment is P500,000 at the time of sale. The remaining life of the equipment is 5 years and Glorious Company used the straight line depreciation. * On December 1,2015, Alta Company sold an inventory to Glorious Company for P2,800,000. The inventory had a cost of P2,000,000 and was still on hand on December 31,2015. 84. What is the investor's share in the profit of the associate for 2014? A. 680,000 C. 800,000 B. 692,000 D. 920,000 85. What is the investor's share in the profit of the associate for 2015? A. 720,000 C. 748,000 B. 732,000 D. 880,000 86. What is the carrying amount of the investment in associate on December 31,2014? A. 5,000,000 C. 5,372,000 B. 5,360,000 D. 5,692,000 87. What is the carrying amount of the investment in associate on December 31, 2015? A. 5,692,000 C. 5,720,000 B. 5,704,000 D. 6,120,000 Multiple Choice Problems: Cost Method & Equity Method Dividend income Cost & equity method 88. Day Company received dividends from share investments during the year ended December 31, 2014 as follows: * A stock dividend of 4,000 shares from Parr Company on July 31, 2014 when the market price of Parr's share was P20. Day owns less than 1% of Parr's share capital. * A cash dividend of P150,000 from Lark Company in which Day owns a 25% interest. A majority of Lark's directors are also directors of Day. What amount of dividend revenue should be reported in 2014? A. 0 C. 150,000 B. 80,000 D. 230,000 P1 © 2014 89. During the current year, Veto Company held 30,000 shares of Rock Company's 100,000 outstanding shares and 6,000 shares of Sand Company's 300,000 outstanding shares. During the current year, Veto received P300,000 cash dividend from Rock, P15,000 cash MCQ – Problems: Cost Method & Equity Method Page 47 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING dividend and 3% stock dividend from Sand. The closing price of Sand share is P150. What amount should be reported as dividend revenue for the current year? A. 15,000 C. 342,000 B. 315,000 D. 442,000 FA © 2014 90. Wray Company provided the following data for 2014: • On September 1, Wray received a P500,000 cash dividend from Seco Company in which Wray owns a 30% interest. • On October 1, Wray received a P60,000 liquidating dividend from King Company. Wray owns a 5% interest in King. • Wray owns a 2% interest in Bow Company, which declared a P2,000,000 cash dividend on November 15,2014 payable on January 15,2015. What amount should be reported as dividend income for 2014? A. 40,000 C. 560,000 B. 100,000 D. 600,000 P1 © 2014 91. Salvo Company received the following dividends from share investments during the current year: • A cash dividend of P80,000 from Rain Company in which Salvo Company owns a 2% interest. • A cash dividend of P450,000 from Water Company in which Salvo Company owns a 30% interest. • A stock dividend of 5,000 shares from Soil Company was received at year-end when the market value was P10 per share. What amount of dividend revenue should be reported for the current year? A. 80,000 C. 530,000 B. 130,000 D. 580,000 FA © 2014 92. Wry Company provided the following information pertaining to dividends from investments for the current year: • On September 1, Wry Company received a P500,000 cash dividend from Seco Company in which Wry Company owns a 30% interest. • On October 15, Wry Company received a P60,000 liquidating dividend from King Company. Wry Company owns a 5% interest in King Company. • Wry Company owns a 2% interest in Bow Company which declared a P2,000,000 cash dividend on November 15 to shareholders of record on December 31 payable on January 31 of next year. What amount should be reported as dividend income for the current year? A. 40,000 C. 560,000 B. 100,000 D. 600,000 FA © 2014 MCQ – Problems: Cost Method & Equity Method Page 48 Investment in Equity Securities Income from Investments 93. Solaire Company acquired 100,000 ordinary shares of Sun Company and 300,000 ordinary shares of Star Company. Both Sun Company and Star Company had 1,000,000 ordinary shares outstanding. Sun Company reported net income of P3,000,000 and paid dividends of P2,000,000 during the current year. Star Company reported net income of P4,000,000 and paid dividends of P1,000,000 during the current year. What total amount of income from the investments should be reported for the current year? A. 500,000 C. 1,400,000 B. 1,200,000 D. 1,500,000 FA © 2014 MCQ – Problems: Cost Method & Equity Method Page 49 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING ANSWER KEY THEORY 1.D 2.A 3.B 4.C 5.B 6.D 7.B 8.B 9.C 10.D 11.D 12.B 13.A 14.B 15.C 16.A 17.A 18.D 19.D 20.D 21.D 22.D 23.C 24.D 25.D Answer Key 26.C 27.B 28.B 29.A 30.D 31.D 32.D 33.B 34.D 35.C 36.B 37.B 38.B 39.B 40.D 41.B 42.C 43.D 44.A 45.C 46.C 47.C 48.D 49.A 50.C 51.B 52.D 53.C 54.A 55.A Page 50 Investment in Equity Securities ANSWER KEY PROBLEMS 1.C 26.C 2.C 27.B 3.B 28.D 4.C 29.A 5.D 30.C 6.B 31.C 7.D 32.B 8.C 33.C 9.C 34.D 10.C 35.B 11.A 36.B 12.A 37.B 13.C 38.C 14.C 39.C 15.C 40.B 16.B 41.D 17.B 42.C 18.B 43.C 19.A 44.D 20.B 45.C 21.C 46.B 22.B 47.D 23.C 48.C 24.C 49.B 25.D 50.B Answer Key 51.D 52.D 53.B 54.C 55.B 56.B 57.A 58.B 59.B 60.D 61.A 62.C 63.C 64.B 65.C 66.B 67.B 68.B 69.D 70.B 71.B 72.B 73.B 74.B 75.C 76.B 77.B 78.C 79.C 80.B 81.B 82.B 83.A 84.B 85.C 86.C 87.C 88.A 89.A 90.A 91.A 92.A 93.C Page 51 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING ANSWER EXPLANATION 1. Answer is (C). Fair value of asset given (land) 2. Answer is (C). Cash (10% x 3,000,000) Dividend income Answer is (B). Original shares Stock dividend Total shares Dividend income (12,000 x P15) 3. 3,000,000 300,000 300,000 10,000 2,000 12,000 180,000 4. Answer is (C). Dividend income on preference share 5. Answer is (D). Dividend income (15% x 15,000,000) 2,250,000 Under the cost and fair value method, dividends received are now totally recognized as income. There is no longer a distinction between preacquisition and postacquisition retained earnings. 6. Answer is (B). Sale price Cost of investment sold Loss on disposal of investment 7. (20,000/200,000 = 10% x 2,400,000) Answer is (D). FIFO approach Original shares Stock dividend - 20% Total shares Sale price (30,000x125) Cost of shares sold: From June 1 (24,000 shares) From December 1 ( 6,000 shares) (6,000/36,000 x 3,600,000) Gain on sale Answer Explanation & Solutions (80,000 x 30) (80,000 x 40) June 1 20,000 4,000 24,000 240,000 2,400,000 (3,200,000) ( 800,000) December 1 30,000 6,000 36,000 3,750,000 2,000,000 600,000 2,600,000 1,150,000 Page 52 Investment in Equity Securities Average approach Sale price Cost of shares sold (30,000 / 60,000 x 5,600,000) Gain on sale 8. Answer is (C). Theoretical value of right Initial cost of rights Cash paid for new shares Cost of new investment 9. Answer is (C). Total cost of rights 10,000 shares x 5 rights Cash paid Cost of rights exercises Total cost of 900 shares 3,750,000 2,800,000 950,000 (125 - 100 / 4 + 1) (50,000 x 5) (50,000 / 4 = 12,500 x 100) 5.00 250,000 1,250,000 1,500,000 (60,000 x 5) 300,000 50,000 rights 800,000 250,000 1,050,000 (10,000 x 80 (50,000 x 5) 10. Answer is (C). Original investment New investment acquired thru stock rights (50,000 x 80) Total Shares 50,000 50,000 100,000 Cost 3,800,000 4,000,000 7,800,00 FIFO Approach Sale price Cost of shares sold Gain on sale (25,000 x 90) (25,000/50,000 x 3,800,000) 2,250,000 1,900,000 350,000 Average Approach Sales price Cost of shares sold Gain on sale 2,250,000 (25,000/100,000 x 7,800,000) 2,250,000 1,950,000 300,000 11. Answer is (A). Initial measurement of stock rights (10,000 rights x 5) Under PFRS 9, stock rights are initially measured at fair value. Answer Explanation & Solutions 50,000 Page 53 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING 12. Answer is (A). Net sale price Initial cost of rights sold Gain on sale of rights (450,000 - 10,000) (30,000 x 10) 440,000 (300,000) 140,000 13. Answer is (C). Initial cost of rights Cash paid for new shares Total cost of new shares (50,000x20) (25,000 x 90) 1,000,000 2,250.000 3,250,000 14. Answer is (C). Theoretical value of right Initial cost of rights Cash paid for new shares Cost of new investment (125 - 100 / 4 + 1) (50,000 x 5) (50,000 / 4 = 12,500 x 100) 5.00 250,000 1,250,000 1,500,000 15. Answer is (C). Original investment New investment acquired through stock rights (50,000 x 85) Total FIFO approach Sale price Cost of shares sold Gain on sale Average approach Sale price Cost of shares sold Gain on sale (25,000x90) (25,000 / 50,000 x 3,600,000) (25,000 /100,000 x 7,850,000) 16. Answer is (B). 1/1/2012 4/1/2012 12/31/2012 12/31/2013 12/31/2014 Answer Explanation & Solutions (20,000x110) (5,000 x 100) (10% x 2,500,000) (10% x 2,500,000) (25,000x110) Shares 20,000 5,000 --25,000 Shares 50,000 50,000 100,000 Cost 3,600,000 4,250,000 7,850,000 2,250,000 1,800,000 450,000 2,250,000 1,962,500 287,500 Cost 2,200,000 500,000 (250,000) ( 250,000) 2,750,000 Page 54 Investment in Equity Securities 6/30/2015 (25,000x92) Investment account per book (25,000) 25,000 (2,300,000) 2,650,000 Shares 20,000 5,000 12,500 37,500 (12,500) 25,000 25,000 50,000 (25,000) 25,000 Cost 2,200,000 500,000 . 2,700,000 (900,000) 1,800,000 . 1,800,000 (900,000) 900,000 (25% x 4,200,000) (25% x 1,800,000) 2,600,000 1,050,000 (450,000) 3,200,000 (25% x 1,200,000) (25% x 480,000) 1,720,000 300,000 (120,000) 1,900,000 17. Answer is (B). 1/1/2012 (20,000x110) 4/1/2012 (5,000x100) 1/1/2014 (50% x 25,000) Balance 1/1/2014 (12,500/37,500 x 2,700,000) Balance 1231/2014 (2 for split) Balance 4/30/2015 (1/2x1,800,000) Balance, December 31, 2015 18. Answer is (B). Purchase price (squeeze) Net income Cash dividend Carrying amount, 12/31 19. Answer is (A). Acquisition cost (squeeze) Share in net income Share in cash dividend Carrying amount – 12/31 20. Answer is (B). Acquisition cost, July 1 (SQUEEZE) 1,870,000 Add: Share in net income from July 1 to December 31 (1,200,000 x 6/12 x 25%) 150,000 Total 2,020,000 Less: Share in cash dividend (25% x 480,000) 120,000 Investment balance, December 31 1,900,000 The acquisition cost is "squeezed" by working back from the investment balance on December 31,2014. Moreover, the investor shares only in the net income of the investee from the date of acquisition, July 1,2014 to December 31, 2014. In the absence of any statement to the Answer Explanation & Solutions Page 55 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING contrary, the net income is earned evenly during the year. However, the investor shares in full in the dividends paid on December 31, 2014. 21. Answer is (C). (100% x 600,000) 600,000 Only the dividend on preference share capital is recognized as dividend revenue. The equity method is not applicable to investment in preference shares regardless of the interest. 22. Answer is (B). Original cost 7,000,000 Cash advances 2,000,000 Total 9,000,000 Net loss from 2011 to 2013 (40% x 20,000,000) (8,000,000) Carrying amount of investment -12/31/2013 1,000,000 Share in net loss of 2014 (40% x 4,000,000) 1,600,000 Loss to be reported in 2014 should be equal to the investment balance only 1,000,000 PAS 28, paragraph 38, provides that if under equity method an investor's share of losses of an associate equals or exceeds the carrying amount of an investment, the investor discontinues recognizing its share of further losses. The investment is reported at NIL or zero value. 23. Answer is (C). Interest Investment income (30,000/ 100,000) (5,000,000 x 6/12 x 30%) 24. Answer is (C). Interest acquired (30,000/100,000) Share in net income from July 1 to December 31, 2014 (1,200,000 x 6 / 12 x 30%) 25. Answer is (D). Investment income 20% x 6,000,000 30% 750,000 30% 180,000 1,200,000 26. Answer is (C). Share in net income (20% x 4,000,000) 800,000 Under the equity method, the investor recognizes as income its share of the investee's earnings. Cash dividends are not recorded as income but a reduction of the investment account. 27. Answer is (B). Investment income Answer Explanation & Solutions (20% x 1,600,000) 320,000 Page 56 Investment in Equity Securities 28. Answer is (D). Investment income in 2014 29. Answer is (A). Net income Less: Preference dividend Net income to ordinary shares Investment income (30% x 6,500,000) (10% x 2,000,000) (50% x 4,800,000) 1,950,000 5,000,000 200,000 4,800,000 2,400,000 30. Answer is (C). When an investee has outstanding cumulative preference share capital, an investor should compute its share of earnings after deducting the investee's preference dividends, whether or not such dividends are declared. Net income 3,000,000 Preference dividend (10% x 5,000,000) (500,000) Net income to ordinary shares 2,500,000 Share in net income - ordinary shares (80% x 2,500,000) 2,000,000 31. Answer is (C). Acquisition cost 11,200,000 Net assets acquired (35% x 32,400,000) 11,340,000 Excess of carrying amount over cost (140,000) Equipment - carrying amount higher than market value (1,400,000 x 35%) (490,000) Building - market value higher than carrying amount (1,000,000 x 35%) 350,000 (140,000) Share in net income (35% x 3,200,000) 1,120,000 Amortization of excess: Overdcprcciation of equipment (490,000/5) 98,000 Underdepreciation of building (350,000/10) (35,000) Investment income 1,183,000 The amortization of the equipment is added because the equipment is overvalued. The amortization of the building is deducted because the building is undervalued. 32. Answer is (B). Acquisition cost Net assets acquired Excess of cost Excess attributable to equipment Excess attributable to building Answer Explanation & Solutions (40% x 12,500,000) (40% x 2,000,000) (40% x 1,500,000) 6,400,000 5,000,000 1,400,000 800,000 600,000 1,400,000 Page 57 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING Share in net income Amortization of excess: Equipment Building Investment income (40% x 5,000,000) 2,000,000 (800,000/4) (600,000/12) ( 200,000) (50,000) 1,750,000 33. Answer is (C). Acquisition cost Net assets acquired (40% x 9,000,000) Excess of cost over carrying amount 4,000,000 (3,600,000) 400,000 The excess of cost is identified as follows: Understatement of plant (40% x 900,000) Understatement of inventory (40% x 100,000) Total excess of cost 360,000 40,000 400,000 Share in net-income (40% x 1,200,000) Less: Amortization of excess of cost: Depreciation of plant (360,000/18) Inventory (totally sold) Investment income 480,000 20,000 40,000 60,000 420,000 34. Answer is (D). Acquisition cost (4,000,000 + 500,000) 4,500,000 Carrying amount of net assets acquired (20% x 13,000,000) 2,600,000 Excess of cost 1,900,000 Excess attributable to building (20% x 2,000,000) 400,000 Excess attributable to goodwill - not amortized 1,500,000 Note that the broker fee or transaction cost of P500,000 is capitalized as cost of the investment in associate. Share in net income (20% x 5,000,000) 1,000,000 Amortization of excess of cost: Attributable to building (400,000 /10) ( 40,000) Investment income 960,000 35. Answer is (B). Cost Carrying amount of interest acquired Excess of cost over carrying amount Excess applicable to equipment Answer Explanation & Solutions (40% x 7,000,000) (40% x 1,500,000) 3,500,000 2,800,000 700,000 (600,000) Page 58 Investment in Equity Securities Excess applicable to inventory (40% x 500,000) Excess of fair value over cost PAS 28, paragraph 32, provides that any excess of the net fair value of identifiable net assets is included in investment income. Share in net income (40% x 4,000,000) Excess of fair value over cost Excess of cost over carrying amount: Equipment (600,000/4) Inventory - all sold Investment income ( 200,000) ( 100,000) the associate's 1,600,000 100,000 (150,000) ( 200,000) 1,350,000 36. Answer is (B). Cost Less: Net assets acquired (40% x 8,000,000) Excess of cost or goodwill Share in net income from April 1 to Dec. 31 (1,000,000 x 9/12 x 40%) 4,000,000 3,200,000 800,000 300,000 37. Answer is (B). Share in net income from April 1 to Dec. 31, 2014 (5,000,000 x 9 / 12 x 40%) 1,500,000 Acquisition cost Less: Carrying amount of net assets acquired Goodwill - not amortized (40% x 20,000,000) 10,000,000 8,000,000 2,000,000 38. Answer is (B). Investment in Lax Company = 3,000,000 39. Answer is (C). Fair value of 10% interest 900,000 Cost on December 31 (20,000/100,000 shares = 20%) 1,500,000 Carrying amount - December 31, 2014 2,400,000 If the investment in associate is achieved in stages, the existing interest is remeasured at fair value with any change in fair value included in profit or loss. The fair value of the existing interest plus the cost of the new interest equals the total cost of investment on the initial application of the equity method starting 2015. Answer Explanation & Solutions Page 59 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING 40. Answer is (B). Fair value of 10% interest Acquisition cost – 12/31 Total cost 1,400,000 3,000,000 4,400,000 41. Answer is (D). Fair value of 10% interest 6,000,000 Cost of 20% new interest 10,000,000 Total cost of investment - January 1, 2015 16,000,000 Share in net income for 2015 (30% x 6,500,000) 1,950,000 Share in cash dividend for 2015 (30% x 3,000,000) ( 900,000) Carrying amount - December 31, 2015 17,050,000 Note that there is no excess of cost over carrying amount because the fair value of the net assets of the investee equaled carrying amount. 42. Answer is (A). Investment in associate (30% x 6,000,000) 1,800,000 Another approach Acquisition cost 1,000,000 Postacquisition profits (3,000,000-2,000,000) x 30% 300,000 Excess net fair value 500,000 Investment in associate 1,800,000 Acquisition cost 1,000,000 Net assets acquired (30% x 5,000,000) 1,500,000 Excess net fair value - included in investment income 500,000 The investment in associate is not impaired because the carrying amount of P1,800,000 is lower than the recoverable amount of P2,100,000 (30% x 7,000,000). 43. Answer is (C). PAS 28, paragraph 5, provides that if the investor holds, directly or indirectly through subsidiaries, less than 20% of the voting power of the investee, it is presumed that the investor does not have significant influence, unless such influence can be clearly demonstrated. Well's position as Rea's largest single shareholder and the presence of Well's officers as a majority of Rea's board of directors demonstrate that Well does have significant influence despite the 10% ownership. Accordingly, the equity method is used. Acquisition, January 1 4,000,000 Add: Share in net income (10% x 5,000,000) 500,000 Total 4,500,000 Answer Explanation & Solutions Page 60 Investment in Equity Securities Less: Share in cash dividends (10% x 1,500,000) Carrying amount of investment, December 31 150,000 4,350,000 44. Answer is (D). Acquisition cost Less: Carrying amount of net assets acquired (30% x 5,000,000) Excess of cost over carrying amount Less: Amount attributable to undervaluation of land (30% x 2,000,000) Goodwill - not amortized 2,500,000 1,500,000 1,000,000 600,000 400,000 Acquisition cost, January 1 2,500,000 Add: Share in net income (30% x 1,000,000) 300,000 Carrying amount of investment 2,800,000 The excess of cost attributable to the land is not amortized because the land is nondepreciable. 45. Answer is (C). Acquisition cost 6,000,000 Add: Share in net income (20% x 7,000,000) 1,400,000 Total 7,400,000 Less: Share in cash dividend (20% x 4,000,000) 800,000 Carrying amount 6,600,000 PAS 28, paragraph 5, provides that if an investor holds, directly or indirectly through subsidiaries, 20% or more of the voting power of the investee, it is presumed that the investor does have significant influence, unless it can be clearly demonstrated that this is not the case. The equity method of accounting is used if the investment is 20% or more of the voting power of the investee. Under the equity method, the investment account is increased by the investor's share of the investee's earnings and decreased by the investor's share ofthe investee's losses. Dividend received from the investee reduces the carrying amount ofthe investment 46. Answer is (B). Acquisition cost - January 1 Add: Share in net income (25% x 9,600,000) Total Less: Cash dividend received (50,000 x P35) Carrying amount of investment - December 31 Answer Explanation & Solutions 18,000,000 2,400,000 20,400,000 1,750.000 18,650.000 Page 61 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING 47. Answer is (D). Acquisition cost Less: Carrying amount of net assets acquired (30% x 5,000,000) Excess of cost over carrying amount Less: Amount attributable to undervaluation of land (30% x 2,000,000) Goodwill - not amortized 2,500,000 1,500,000 1,000,000 600,000 400,000 Acquisition cost, January 1 2,500,000 Add: Share in net income (30% x 1,000,000) 300,000 Carrying amount of investment 2,800,000 The excess of cost attributable to the land is not amortized because the land is nondepreciable. 48. Answer is (C). Acquisition cost Net assets acquired Excess of cost Attributable to depreciable assets Attributable to goodwill Acquisition cost Share in net income Share in dividends Amortization Investment balance – 12/31 49. Answer is (B). Acquisition cost Net assets acquired Excess of cost Attributable to equipment Attributable to building Acquisition cost Net income Cash dividend Amortization of excess: Answer Explanation & Solutions (30% x 11,800,000) (30% x 2,600,000) 5,160,000 3,540,000 1,620,000 780,000 840,000 (30% x 3,600,000) (30% x 400,000) (780,000/4) 5,160,000 1,080,000 (120,000) (195,000) 5,925,000 (40% x 5,000,000) 2,560,000 2,000,000 560,000 (40% x 800,000) (40% x 600,000) (40% x 1,600,000) (40% x 1,000,000) 320,000 240,000 560,000 2,560,000 640,000 (400,000) Page 62 Investment in Equity Securities Equipment (320,000 / 4) Building (240,000 /12) Carrying amount of investment – 12/31/2014 (80,000) (20,000 2,700,000 50. Answer is (B). Acquisition cost (20,000 x 120) Net assets acquired (25% x 8,000,000) Excess of cost over carrying amount 2,400,000 2,000,000 400,000 Acquisition cost Share in net income: 2014 (25% x 3,600,000) 2015 (25% x 3,900,000) Share in cash dividend: 2014 (20,000 x 16) 2015 (20,000 x 20) Amortization of excess: 2014 (400,000/20) 2015 Carrying amount of investment - December 31, 2015 51. Answer is (D). Acquisition cost Share in net income Share in cash dividend Amortization of excess Carrying amount (20% x 1,800,000) (20% x 600,000) (1,000,000/10) 52. Answer is (D). Original cost Share in net income (20% x 1,800,000) Share in cash dividends (20% x 400,000) Amortization of excess of cost (2,000,000 / 10) Carrying amount of investment - December 31,2014 Acquisition cost Less: Carrying amount of interest acquired Excess of cost over carrying amount The excess of cost over the carrying amount of the underlying equity Answer Explanation & Solutions 2,400,000 900,000 975,000 (320,000) (400,000) (20,000) (20,000) 3,515,000 7,000,000 360,000 (120,000) (100,000) 7,140,000 8,000,000 360,000 (80,000) (200,000) 8,080,000 8,000,000 6,000,000 2,000,000 acquired which is Page 63 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING attributable to undervaluation of a depreciable asset should be amortized over the remaining useful life of the depreciable asset. Such amortization is recorded by debiting investment income and crediting investment in associate. 53. Answer is (B). Acquisition cost Carrying amount of net assets acquired Excess of cost applicable to patent 6,000,000 4,000,000 2,000,000 Acquisition cost 6,000,000 Share in net income (5,000,000 x 15%) 750,000 Share in cash dividend (3,000,000 x 15%) (450,000) Amortization of patent (2,000,000 / 10) (200,000) Carrying amount of investment 6,100,000 Interest acquired (30,000 / 200,000) 15% The equity method is used even if the investment is less than 20% because the officers of the investor entity are a majority of the board of the investee entity indicating significant influence. 54. Answer is (C). Acquisition cost Net assets acquired (30% x 12,000,000) Excess of cost over carrying amount Excess attributable to depreciable assets (30% x 2,500,000) Excess attributable to goodwill Acquisition cost Share in net income Share in cash dividend Amortization of depreciable assets Carrying amount of investment 55. Answer is (B). Acquisition cost Net assets acquired Excess of cost over carrying amount Attributable to equipment Attributable to building Answer Explanation & Solutions (30% x 4,000,000) (30% x 1,000,000) (750,000 / 5) (40% x 5,000,000) (40% x 800,000) (40% x 600,000) 5,000,000 3,600,000 1,400,000 750,000 650,000 5,000,000 1,200,000 (300,000) (150,000) 5,750,000 2,560,000 2,000,000 560,000 320,000 240,000 560,000 Page 64 Investment in Equity Securities Acquisition cost 2,560,000 Net income (40% x 1,600,000) 640,000 Cash dividend (40% x 1,000,000) ( 400,000) Amortization of excess: Equipment (320,000/4 ) (80,000) Building (240,000/12) ( 20,000) Carrying amount of investment - December 31, 2014 2,700,000 56. Answer is (B). Acquisition cost Net assets acquired (25% x 3,000,000) Excess of cost over carrying amount Excess attributable to inventory Excess attributable to equipment Excess attributable to goodwill Acquisition cost Share in net income Amortization of excess: Inventory Equipment Cash dividend Carrying amount of investment (25% x 100,000) (25% x 500,000) (25% x 400,000) 25,000 125,000 100,000 250,000 1,000,000 175,000 (25% x 700,000) (25,000) (25,000) ( 75,000) 1,050,000 (125,000/5) (25,000x3) 57. Answer is (A). Acquisition cost Share in net loss (40% x 4,000,000) Share in cash dividend (40% x 2,500,000) Carrying amount - December 31, 2014 58. Answer is (B). Acquisition cost Deficit on January 1, 2014 Carrying amount of investment - January 1, 2014 Net income for 2014 Net income for 2015 Cash dividend on 12/31/2015 Carrying amount of investment - December 31, 2015 Answer Explanation & Solutions 1,000,000 750,000 250,000 6,500,000 (1,600,000) (1,000,000) 3,900,000 (30,000 x 120) (30% x 500,000) 3,600,000 (150,000) 3,450,000 (30% x 700,000) 210,000 (30% x 800,000) 240,000 (30% x 400,000) ( 120,000) 3,780,000 Page 65 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING Another approach Acquisition cost Share in retained earnings - December 31, 2015 (30% x 600,000) Carrying amount of investment - December 31, 2015 59. Answer is (B). Acquisition cost Share in profit – 2014 Share in loss – 2015 Share in dividend – 2015 Carrying amount – 12/31/2015 (30% x 80,000) (30% x 32,000) (30% x 10,000) 3,600,000 180,000 3,780,000 400,000 24,000 (9,600) (3,000) 411,400 60. Answer is (D). Acquisition cost 1,700,000 Net assets acquired (40% x 4,000,000) 1,600,000 Goodwill - not amortized 100,000 Acquisition cost 1,700,000 Net income (40% x 700,000) 280,000 Cash dividend (40% x 200,000) (80,000) Revaluation surplus (40% x 1,300,000) 520,000 Carrying amount of investment - December 31,2014 2,420,000 There is no need to adjust for the difference in depreciation method. If both entities have chosen a method that best reflects the flow of benefits as the assets are consumed, then there is no policy difference. 61. Answer is (A). Net income for 2014 3,000,000 Unrealized profit on 12/31/2014 inventory of Haven (900,000-600,000) ( 300,000) Adjusted net income 2,700,000 Investor's share (20% x 2,700,000) 540,000 Another approach Share in net income Share in unrealized profit Investor's share (20% x 3,000,000) 600,000 (20% x 300,000) ( 60,000) 540,000 62. Answer is (C). Net income for 2015 Realized profit on 12/31/2014 inventory of Haven Company Answer Explanation & Solutions 4,000,000 300,000 Page 66 Investment in Equity Securities Unrealized profit on 12/31/2015 inventory of Haven Company (750,000 - 500,000) ( 250,000) Adjusted net income 4,050,000 Investor's share (20% x 4,050,000) 810,000 63. Answer is (C). Acquisition cost Share in profit of associate - 2014 Share in cash dividend - 2014 (20% x 1,000,000) Share in profit of associate - 2015 Share in cash dividend - 2015 (20% x 1,500,000) Carrying amount - December 31, 2015 6,000,000 540,000 ( 200,000) 810,000 (300,000) 6,850,000 64. Answer is (B). Acquisition cost Carrying amount of net assets acquired Excess of cost Attributable to equipment Attributable to land Goodwill 7,000,000 6,000,000 1,000,000 ( 500,000) ( 250,000) 250,000 (25% x 24,000,000) (25% x 2,000,000) (25% x 1,000,000) 65. Answer is (C). Share in net income (25% x 5,000,000) 1,250,000 Amortization of excess attributable to equipment (500,000/5) ( 100,000) Investment income 1,150,000 The excess attributable to land and the excess attributable to goodwill are not amortized. 66. Answer is (B). Acquisition cost 7,000,000 Share in net income 1,250,000 Share in cash dividend ( 750,000) Amortization of excess attributable to equipment (500,000/5) (100,000) Carrying amount - December 31, 2014 7,400,000 There is no impairment loss on the investment in associate because the carrying amount of P7,400,000 is lower than the fair value of P7,500,000 at year-end. 67. Answer is (B). Acquisition cost Net assets acquired (30% x 6,000,000) Answer Explanation & Solutions 3,200,000 (1,800,000) Page 67 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING Excess of cost Excess attributable to equipment (30% x 3,000,000) Goodwill 68. Answer is (B). Net income for 2014 Unrealized profit on 12/31/2014 inventory Adjusted net income Investor's share (30% x 3,400,000) Depreciation of equipment (900,000 / 5) Investment income 69. Answer is (D). Acquisition cost Investment income Cash dividend (30% x 1,500,000) Revaluation surplus (30% x 2,000,000) Carrying amount - December 31, 2014 1,400,000 ( 900,000) 500,000 4,000,000 ( 600,000) 3,400,000 1,020,000 ( 180,000) 840,000 3,200,000 840,000 (450,000) 600,000 4,190,000 70. Answer is (B). Fair value of 10% interest 4,500,000 Carrying amount of 10% interest 3,000,000 Gain on remeasurement to equity 1,500,000 If the investment is achieved in stages, the existing interest is remeasured at fair value with any change in fair value included in profit or loss. 71. Answer is (B). Fair value of 10% interest 4,500,000 Cost of additional 15% interest 6,750,000 Total cost of investment 11,250,000 Fair value of net assets acquired (25% x 36,000,000) 9,000,000 Excess of cost 2,250,000 Excess attributable to equipment (25% x 4,000,000) 1,000,000 Goodwill 1,250,000 The fair value of the existing interest plus the cost of the new interest equals the total cost of the investment on the initial application of the equity method on January 1,2015. 72. Answer is (B). Answer Explanation & Solutions Page 68 Investment in Equity Securities Total cost - January 1, 2015 11,250,000 Share in net income (25% x 8,000,000) 2,000,000 Share in cash dividend (25% x 5,000,000) ( 1,250,000 Amortization of excess ( 1,000,000 / 5) ( 200,000) Carrying amount - December 31, 2015 11,800,000 The excess of cost over carrying amount attributable to goodwill is not amortized. 73. Answer is (B). Share in 2014 net income (30% x 800,000) 240,000 74. Answer is (B). Acquisition cost, January 1,2014 Add: Share in 2014 net income Total Less: Share in 2014 dividend (30% x 500,000) Carrying amount of investment, December 31,2014 2,000,000 240,000 2,240,000 150,000 2,090,000 75. Answer is (C). Carrying amount – 12/31/2014 Share in net income up to 6/30/2015 (30% x 1,000,000) Carrying amount – 6/30/2015 2,090,000 300,000 2,390,000 Sales price Carrying amount sold Gain on sale (2,390,000 x ½) Fair value of retained investment Carrying amount of retained investment Gain from remeasurement to fair value Total profit and loss (305,000 + 405,000) 1,500,000 1,195,000 305,000 1,600,000 1,195,000 405,000 710,000 76. Answer is (B). (5,000,000 – 4,500,000) = 500,000 77. Answer is (B). Investment income (3,000,000 – 900,000) x 30% 630,000 78. Answer is (C). Investment income (4,000,000 – 1,200,000) x 30% 840,000 Answer Explanation & Solutions Page 69 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING 79. Answer is (C). Acquisition cost Investment income for 2014 Cash dividend for 2015 Investment income for 2015 Cash dividend for 2015 Carrying amount – 12/31/2015 (30% x 2,500,000) (30% x 2,800,000) (30% x 2,800,000) (30% x 2,000,000) 5,000,000 630,000 (750,000) 840,000 (600,000) 5,120,000 (30% x 800,000) 240,000 81. Answer is (B). Acquisition cost, January 1,2014 Add: Share in 2014 net income Total Less: Share in 2014 dividend (30% x 500,000) Carrying amount of investment, December 31,2014 2,000,000 240,000 2,240,000 150,000 2,090,000 80. Answer is (B). Share in 2014 net income 82. Answer is (B). Carrying amount of investment, December 31, 2014 Add: Share in net income from January 1 to June 30, 2015 (30% x 1,000,000) Carrying amount of investment, June 30,2015 Sale price Cost of investment sold (2,390,000/2) Gain from sale of investment 83. Answer is (A). Fair value - July 1, 2015 Carrying amount of retained investment Gain from remeasurement 2,090,000 300,000 2,390,000 1,500,000 (1,195,000) 305,000 1,600,000 1,195,000 405,000 Fair value - December 31,2015 1,800,000 Fair value-July 1,2015 1,600,000 Unrealized gain on financial asset 200,000 The unrealized gain of P200,000 is reported as other comprehensive income in the 2014 statement of comprehensive income because the retained investment is accounted for as financial asset at fair value through other comprehensive income. Answer Explanation & Solutions Page 70 Investment in Equity Securities 84. Answer is (B). Net income for 2014 Unrealized profit on sale of equipment sold on 1/1/2014 Realized profit on equipment sold on 1/1/2014 Adjusted net income Investor's share (40% x 1,730,000) 2,000,000 (800,000-500,000) ( 300,000) (10% x 300,000) 30,000 1,730,000 692,000 85. Answer is (C). Net income for 2015 3,000,000 Realized profit on equipment sold on 1/1/2014 (10% x 300,000) 30,000 Unrealized profit on sale of equipment on 7/1/2015 (900,000-500,000) ( 400,000) Realized profit on equipment sold on 7/1/2015 (400,000/5x1/2) 40,000 Unrealized profit on ending inventory on 12/31/2015 (2,800,000-2,000,000) (800,000) Adjusted net income 1,870,000 Investor's share (40% x 1,870,000) 748,000 86. Answer is (C). Acquisition cost Share in profit of associate - 2014 Cash dividend-2014 (40% x 800,000) Carrying amount - December 31, 2014 87. Answer is (C). Carrying amount - January 1,2015 Share in profit of associate - 2015 Cash dividend - 2015 (40% r. 1,000,000) Carrying amount - December 31, 2015 5,000,000 692,000 (320,000) 5,372,000 5,372,000 748,000 ( 400,000) 5,720,000 88. Answer is (A). The stock dividend from Parr Company is not an income. The cash dividend from Lark Company is not also an income because the interest is 25% and therefore the equity method is used. 89. Answer is (A). Cash dividend from Rock = P15,000 90. Answer is (A). Cash dividend from Bow Company (2% x 2,000,000) Answer Explanation & Solutions 40,000 Page 71 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING The cash dividend from Seco and the liquidating dividend from King are not income but reduction of the investment account. 91. Answer is (A). Cash dividend of P80,000 from Rain Company. 92. Answer is (A). Dividend income 93. Answer is (C). Sun Star Total income from investments Answer Explanation & Solutions (2,000,000 x 2%) 40,000 P2,000,000 x 10% P4,000,000 x 30% 200,000 1,200,000 1,400,000 Page 72