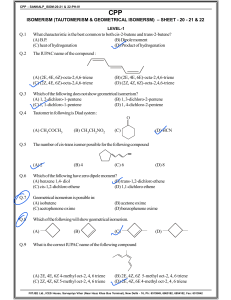
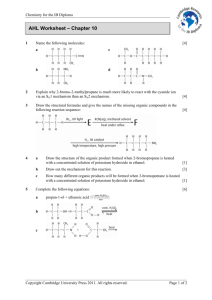
STEREOISOMERISM Molecules have the SAME MOLECULAR FORMULA but the atoms are joined to each other in a DIFFERENT SPACIAL ARRANGEMENT - they occupy a different position in 3-dimensional space. There are two types... • GEOMETRICAL ISOMERISM • OPTICAL ISOMERISM GEOMETRICAL ISOMERISM IN ALKENES Introduction GEOMETRIC ISOMERS •occurs due to the RESTRICTED ROTATION OF C=C bonds • get two forms... CIS (Z) Groups/atoms are on the SAME SIDE across the double bond (E) but-2-ene Or Trans-but-2-ene E entgegen (opposite) TRANS (E) Groups/atoms are on OPPOSITE SIDES across the double bond (Z) but-2-ene Or Cis-but-2-ene Z zusammen (together) GEOMETRICAL ISOMERISM IN ALKENES RESTRICTED ROTATION OF C=C BONDS Single covalent bonds can easily rotate. What appears to be a different structure is REALLY the same. ALL THESE STRUCTURES ARE THE SAME BECAUSE C-C BONDS HAVE ‘FREE’ ROTATION GEOMETRICAL ISOMERISM IN ALKENES RESTRICTED ROTATION OF C=C BONDS C=C bonds have restricted rotation so the groups on either end of the bond are ‘frozen’ in one position; it isn’t easy to flip between the two. Animation doesn’t work in old versions of Powerpoint This produces two possibilities. The two structures cannot interchange easily so the atoms in the two molecules occupy different positions in space. GEOMETRICAL ISOMERISM IN ALKENES Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIG) Priority Rules PRIORITY: H < CH3 < CH2CH3 Look at HIGHEST atomic numbers of atoms attached to C=C Highest values opposite = E (like trans) Highest values together = Z “zame zide” (like cis) 9 6 35 6 Z 2-bromo-3-fluorobut-2-ene 1 6 6 6 6 1 E 3-methylpent-2-ene GEOMETRICAL ISOMERISM IN ALKENES Rule For Naming with E and Z Compare the atomic number (Z) of the atoms directly attached to the stereocentre (double bond); the group having the atom of higher atomic number receives higher priority. GEOMETRICAL ISOMERISM IN ALKENES Next Let us Try 2 stereoisomers of: 1-bromo - 2-chloro - 2-iodoethene and draw the structures of them, then name them. GEOMETRICAL ISOMERISM IN ALKENES Answer • • • • • Priority 1 I 2 Br 3 Cl 4 H E isomer E- 1-bromo-2-chloro - 2-iodoethene I and Br have the higher atomic numbers So I and Br have highest priority to determine POSITION. Then just go alphabetically Z isomer Z- 1-bromo -2-chloro-2-iodoethene GEOMETRICAL ISOMERISM IN ALKENES CH3 H C CH3 C H CH3 C CH3 C H H trans but-2-ene cis but-2-ene (E) but-2-ene (Z) but-2-ene ATOMS OF C=C MUST HAVE TWO DIFFERENT GROUPS TASK : Is this a Geometric Isomer? CH3 H C NO C CH3 H methylpropene H H C CH3 H C C Z Cl Cl 1-chloropropene CH3 YES C E H TASK : Is this a Geometric Isomer? CH2 CH3 C CH3 NO C H CH3 2-methylpent-2-ene H CH2 C H CH2 CH3 NO C CH2 2-ethylpent-1-ene CH3 GEOMETRICAL ISOMERISM IN ALKENES Isomerism in butene Here are some structural isomers of C4H8 that are alkenes. Of these which exhibits geometrical isomerism. but-1-ene cis but-2-ene (Z) but-2-ene trans but-2-ene (E) but-2-ene 2-methylpropene GEOMETRICAL ISOMERISM IN ALKENES How to tell if it exists Two different groups attached Two different groups attached Two similar groups attached to same end Two similar groups attached to same end Two similar groups attached to Same end Two different groups attached Two different groups attached Two different groups attached GEOMETRICAL ISOMERISM Once you get two similar atoms/groups attached to one end of a C=C, you cannot have geometrical isomerism GEOMETRICAL ISOMERISM