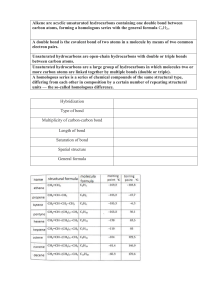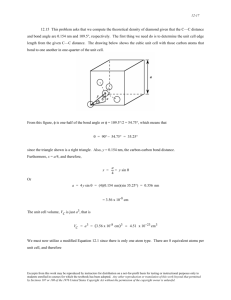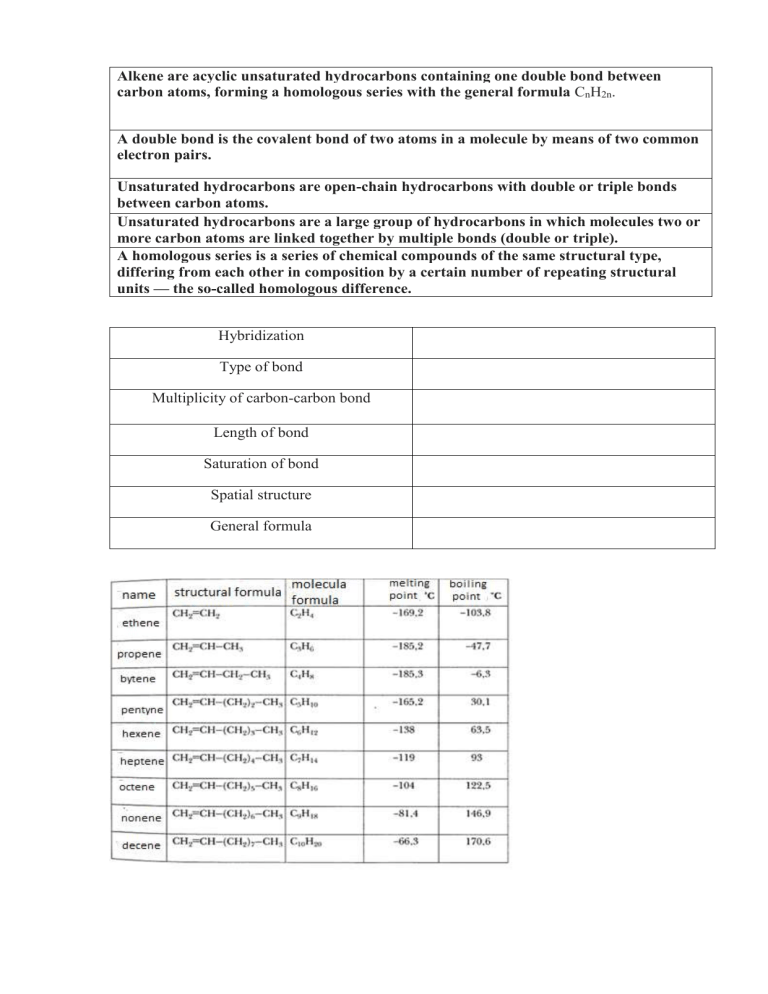
Alkene are acyclic unsaturated hydrocarbons containing one double bond between carbon atoms, forming a homologous series with the general formula CnH2n. A double bond is the covalent bond of two atoms in a molecule by means of two common electron pairs. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are open-chain hydrocarbons with double or triple bonds between carbon atoms. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are a large group of hydrocarbons in which molecules two or more carbon atoms are linked together by multiple bonds (double or triple). A homologous series is a series of chemical compounds of the same structural type, differing from each other in composition by a certain number of repeating structural units — the so-called homologous difference. Hybridization Type of bond Multiplicity of carbon-carbon bond Length of bond Saturation of bond Spatial structure General formula