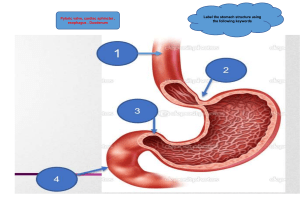
Name ID A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Larynx Trachea Lung Liver spleen Esophagus Lesser omentum Espohagus Gallbladder Colon Primary bronchi Pancreas Jejunum Cecum Stomach Jejunum Duodenum Pseudostratified columnar epithelia Brush border microvilli Simle squamous Air sacs of ling tissue Stratified squamous Basal Simple columnar Multiple Choice: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 B D A A A A C C C True/False 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 True False True True True False No question 7 provided Short Answer 1. The alveoli are highly vascularized to take up O2 breathed in and release CO2 to breathe out as efficiently as possible in the lungs. 2. Hyaline cartilage is found in the trachea. 3. Mucous in the stomach is produced to protect the epithelium and to facilitate movement of food particles. 4.Villi in small intestine increase surface area to volume ratio to aid in absorption of nutrients. 5. An inflamed appendix that ruptures can spread bacteria into the abdominal cavity. Essay: 1. In respiration/ blood-tissue interface, CO2 from respiring tissue is brought into the capillary blood and dissolved and broken into CO2 + plasma protein to carbamino compounds. CO2 and hemoglobin combine to create carbaminohemoglobin and a chloride shift in the red blood cells occurs. CO2 and H2o are catalyzed into H2CO3 and broken down to HCO3- and H+ then converted to HbO2 and H+ in the red blood cell and coverted to O2 + HHb and released from the RBC to the respiring tissue outside the capillary blood. 2. Digestive enzymes are regulated by hormones that control digestion activity such as cholecystokinin, secretin, and gastrin. The activity of these hormones controls the production or inhibition of digestive enzymes. Gastrin in the stomach stimulates the release of stomach acid to begin to digest proteins. Secretin stimulates the pancreas to produce bicarbonate to send to the duodenum along with CCK as pancreatic juices for digestion and to release bile for fat digestion.