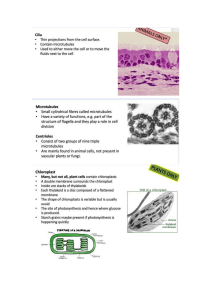
What are the two major portions of mitochondria called? Mitochondria are double-membrane organelles found in eukaryotic cells that are responsible for generating most of the cell's energy. These organelles are considered as the powerhouse of the cell since they produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the molecule that carries energy for all cellular activities. The unique structure of mitochondria allows them to perform several essential functions, including oxidative phosphorylation, fatty-acid oxidation, and the synthesis of several important biomolecules. Mitochondria vary in size and shape based on the specific needs of the cell. Generally, they are around 1-10 micrometers in length and have a spherical or rodlike shape. Moreover, the size and shape of mitochondria can fluctuate in response to the metabolic needs of the cell. The two major portions of mitochondria include the outer membrane and the inner membrane. The outer membrane is a lipid bilayer that separates the mitochondria from the cytoplasm. In contrast, the inner membrane is highly folded into cristae, which provide an enormous surface area for various reactions occurring in the organelle. The spaces between the cristae are filled with the matrix, which contains several enzymes involved in the synthesis of ATP. In conclusion, mitochondria are essential organelles that play a vital role in cellular energy production. Their unique structure and the presence of specific biomolecules allow them to carry out various metabolic processes that are essential for the proper functioning of the cell. References: 1. Alberts, B. et al. (2002). Molecular Biology of the Cell. New York: Garland Science. 2. Lodish, H. et al. (2016). Molecular Cell Biology. New York: W. H. Freeman and Company.