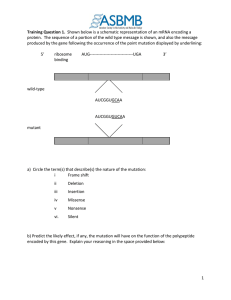
What is the function of the start codon? The start codon is a crucial component of the genetic code that signals the beginning of protein synthesis. The start codon is responsible for initiating the translation process by providing the necessary information for the ribosome to locate the correct reading frame for the mRNA transcript. The most common start codon in the genetic code is AUG, which codes for methionine. Other start codons, such as GUG and UUG, exist in some organisms, but AUG is the most prevalent. After recognizing the start codon, the ribosome joins the two subunits and begins the process of protein synthesis. The tRNA molecule carrying the amino acid methionine enters the ribosome and is positioned at the start codon. The ribosome then moves along the mRNA transcript, reading the codons and synthesizing the protein based on the sequence of nucleotides. In summary, the start codon plays a critical role in the process of protein synthesis by initiating the translation process and ensuring that the ribosome starts at the correct location on the mRNA transcript. References: 1. Alberts, B., Johnson, A., Lewis, J. et al. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 4th edition. New York: Garland Science; 2002. 2. Lodish, H., Berk, A., Zipursky, S.L. et al. Molecular Cell Biology. 4th edition. New York: W. H. Freeman; 2000.