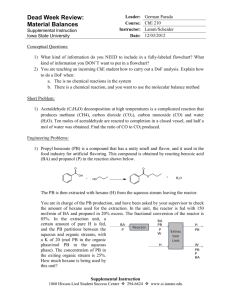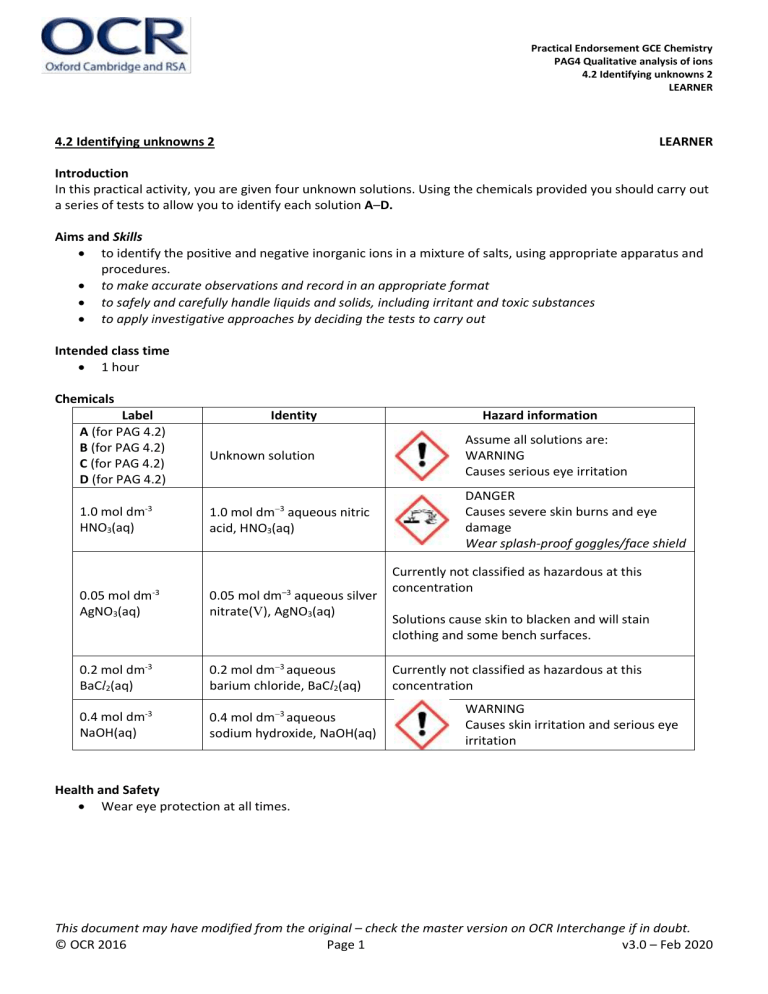
Practical Endorsement GCE Chemistry PAG4 Qualitative analysis of ions 4.2 Identifying unknowns 2 LEARNER 4.2 Identifying unknowns 2 LEARNER Introduction In this practical activity, you are given four unknown solutions. Using the chemicals provided you should carry out a series of tests to allow you to identify each solution A–D. Aims and Skills to identify the positive and negative inorganic ions in a mixture of salts, using appropriate apparatus and procedures. to make accurate observations and record in an appropriate format to safely and carefully handle liquids and solids, including irritant and toxic substances to apply investigative approaches by deciding the tests to carry out Intended class time 1 hour Chemicals Label A (for PAG 4.2) B (for PAG 4.2) C (for PAG 4.2) D (for PAG 4.2) -3 1.0 mol dm HNO3(aq) Identity Unknown solution 3 1.0 mol dm aqueous nitric acid, HNO3(aq) 0.05 mol dm-3 AgNO3(aq) 0.05 mol dm–3 aqueous silver nitrate(V), AgNO3(aq) 0.2 mol dm-3 BaCl2(aq) 0.2 mol dm3 aqueous barium chloride, BaCl2(aq) 0.4 mol dm-3 NaOH(aq) 0.4 mol dm3 aqueous sodium hydroxide, NaOH(aq) Hazard information Assume all solutions are: WARNING Causes serious eye irritation DANGER Causes severe skin burns and eye damage Wear splash-proof goggles/face shield Currently not classified as hazardous at this concentration Solutions cause skin to blacken and will stain clothing and some bench surfaces. Currently not classified as hazardous at this concentration WARNING Causes skin irritation and serious eye irritation Health and Safety Wear eye protection at all times. This document may have modified from the original – check the master version on OCR Interchange if in doubt. © OCR 2016 Page 1 v3.0 – Feb 2020 Practical Endorsement GCE Chemistry PAG4 Qualitative analysis of ions 4.2 Identifying unknowns 2 LEARNER Equipment splash-proof goggles pH indicator paper wash bottle containing distilled (or de-ionised) water measuring cylinder (25 cm3) beaker (100 cm3) glass rod conical flask (100 cm3) test-tube rack four test tubes dropping pipettes spatula Bunsen burner test-tube holder Procedure Before starting your practical work, read the information below. Decide how you will organise your practical work and make a note of this. Decide which observations you need to make and/or which measurements you need to take. Ensure that you record all of your results in a suitable format. The identities of the solutions A–D are listed below in no particular order: aqueous ammonium chloride, NH4Cl(aq) aqueous sodium chloride, NaCl(aq) aqueous sodium carbonate , Na2CO3(aq) aqueous sodium sulfate, Na2SO4(aq) 1. Plan and carry out a series of tests that would allow you to identify each solution A–D. 2. You should carry out the minimum number of tests required. Each test should produce a positive result for at least one of the solutions A–D. You can use any of the chemicals supplied. 3. Record the tests you carried out. 4. Record all the observations for your tests on solutions A–D. Analysis of results 1. Record your conclusions for each test. 2. Record the identity of each solution. Extension opportunities 1. Write the equations for the reactions that you have observed. 2. Write the methods for the experiments that you have carried out. Records As evidence for the Practical Endorsement, you should have recorded evidence of your methods, and all of your observations and measurements in a suitable format. All work should be clearly dated. In addition, in preparation for the assessment of practical work in the written examinations and to help you develop your understanding of the underlying chemical theory, you should complete the questions in the Analysis and Extension Opportunities sections. For calculations, you should show full workings and give final answers to the appropriate number of significant figures. This document may have modified from the original – check the master version on OCR Interchange if in doubt. © OCR 2016 Page 2 v3.0 – Feb 2020