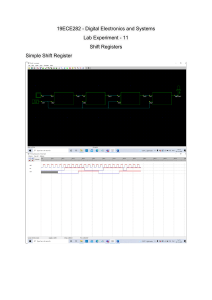
TOPIC 2: CULTURAL DIFFERENCES: INCLUDING REGISTERS AND LANGUAGE VARIETIES CULTURAL DIFFERENCES: INCLUDING REGISTERS AND LANGUAGE VARIETIES SOME CULTURAL DIFFERENCES (SUMMARY OF TERMS) -CONTEXTUAL DIFFERENCES (Communication Style) -SOCIAL DIFFERENCES 1. Concept of time 2. Time Orientation 3. Manners 4. Roles and Status 5. Attitudes towards work and success 6. Openness and Inclusiveness -NONVERBAL DIFFERENCES -AGE DIFFERENCES -LANGUAGE DIFFERENCES 1. Level of Formality or Register 2. Features of Language, e.g. spelling & vocabulary STOP AND THINK 1. The fast food giant McDonald’s spent thousands on a new TV ad to target the Chinese consumers. The ad showed a Chinese man kneeling before a McDonald’s vendor begging him to accept his expired discount coupon. The ads was eventually pulled out. Why do you think it was pulled out? 2. A golf-ball manufacturing company packaged golf balls in packs of four for convenient purchase in Japan. Unfortunately, they did not sell. The company had to repackage the product. Why do you think the balls in the original packaging did not sell? CULTURAL DIVERSITY Cultural Diversity is the existence of a variety of cultural groups within a society. The diversity ranges from ethnicity, race, religion, language, values, traditions, beliefs, behaviors , rules of conduct, etc. People can have better interpersonal dialogue and communicate more on a personal level when they know about the different cultural backgrounds of others (Shah, 2017). CONTEXTUAL DIFFERENCES This relates to communication styles usually evident in the way business people approach decision-making, problemsolving, negotiations, interactions within an organization, and socializing outside the workplace. E.g. People in low-context cultures tend to be more direct in communicating, focused on results, and dependent on facts in making decisions. Meanwhile, those from high-context are more indirect, may give more emphasis on building and protecting relationships, and will likely use feelings in making decisions. SOCIAL DIFFERENCES 1. Concept of Time -E.g. Americans are time conscious; Indians and Filipinos have this norm of arriving late. 2. Time Orientation (preference towards past, present, or future) -E.g. Future-oriented cultures, such as the US are more invested in long-term goals, compared to present-oriented cultures like India and China. SOCIAL DIFFERENCES 3. Manners -E.g. Winking and whistling in public are normal in the Philippines but inappropriate in India. 4. Roles and Status -E.g. People in China are addressed according to their official titles, e.g. Manager, but in the US respect towards top managers is shown by addressing them as Mr./Ms. Roberts. SOCIAL DIFFERENCES 5. Attitudes towards Work -E.g. East Asian workers are happier and more successful when they have a good relationship with colleagues and supervisors, while North Americans thrive when they enjoy gratifying job assignments and organizational policies. 6. Openness and Inclusiveness -E.g. Filipinos, known for their hospitality, welcome foreigners while some Hong Kongers tend to show biases and racial discrimination against other cultures. NONVERBAL DIFFERENCES •Placing hands in pocket is disrespectful in Turkey while bowing shows rank in Japan. •Distant cultures such as Northern Europe, the US, and other western cultures tend to keep more personal space. •Warm cultures such as the Middle East and South American welcome and accept close proximity. AGE DIFFERENCES Some countries like the United States support their youth which signifies vibrancy, strength, energy, potential, and innovative ideas. On the other hand, other cultures such as Singapore value age and seniority which earns more respect and freedom. LANGUAGE DIFFERENCES Different varieties of English are used in various parts of the world. American English (AmE) is spoken by about two-thirds of Americans who live in the United States. British English (BrE) is spoken mainly in the United Kingdom. Australian English (AuE) is used in Australia. Also, Philippine English (PE) is a variety of English “nativized legitimately” in the Philippines. It is used by Filipinos in different fields, such as science and technology, judiciary and legislature, bureaucracy, and scholarly discourse (Dayag, 2012). Each variety has a distinct vocabulary, grammar, and registers. LANGUAGE DIFFERENCES: VARIETIES (FOR FYI PURPOSES) Kachru’s 3 Concentric Circles: The Expansion of English Braj Kachru (1932-2016) coined the term ‘World Englishes’ to refer to varieties of 'global' English. VARIETIES OF ENGLISH – WORLD ENGLISHES (FYI PURPOSES) •The global spread of English has led to the development of many different varieties of English, such as ‘Canadian English’, ‘Indian English (Hindi English/Hinglish)’, and Singapore English (Singlish), which have developed to meet the linguistic needs of those populations. These varieties of English (called World Englishes) are slightly different from each other in word choice, grammar, semantics etc. yet they can all be understood by English speakers. There may be hundreds of World Englishes; however, as there is no set definition for what constitutes an official variety of a language it is not possible to state how many. 1. LEVEL OF FORMALITY OR REGISTERS - Registers refer to the level and style of speaking and writing appropriate for different situations. Registers are determined by social occasion, relationships, context, context, purpose, and audience. -There are 5 established registers based on the English language. a. Frozen/Static – Language does not change, e.g. National Anthem b. Formal – Language follows accepted & prescribed format, e.g. business meetings, academic papers, lectures c. Consultative – Language is less formal and the context involves one with specialized knowledge or an expert who is consulted or can give advice. d. Casual – Language is conversational – may be informal with slang and contractions, e.g. chit-chat & text messages between friends e. Intimate - Language is for private communication used between lovers or very close family and friends, e.g. inside pet names, inside jokes, terms of endearment. -* Not all languages in different cultures may have these 5 registers. For instance, the Korean language seems to have 4 speech levels: Formal and Polite, Formal and Casual, Informal and Polite, Informal and Casual [*Honorific speech and speech levels in Korean. (2018) Retrieved from https://www.sayjack.com/korean/learn-korean/honorific-speech-and-speech-levels-in-korean/] 2. LANGUAGE VARIETY: FEATURES OF LANGUAGE Language varieties include vocabulary, pronunciation, spelling, and even grammatical structures. The following are some differences in terms of vocabulary and spelling. Spelling -E.g. centre, mould (British English) – center, mold (American English) Vocabulary -E.g. estafa (Phil. English meaning criminal deception intended to result in financial or personal gain) – swindle or fraud (American English) -E.g. booze (Australian English) – alcohol (British English) -E.g. line (American English) – queue (British English) SOME ENGLISH WORDS used DIFFERENTLY IN THE PHILIPPINES (FYI only) Word SALVAGE Intended Meaning rescue Meaning in the Philippine Context murder OVERPASS a bridge by which a road or railroad passes A structure referring to a bridge made from over another. cement or steel that people can use to get to the other side of the street VULCANIZING SHOP tire repair shop - DOUBLE DECK bunk bed - BEDSPACE; BEDSPACER bed space (a space in the bed) Not limited to the space in the bed; one who rents EAT-ALL-YOU-CAN all-you-can-eat buffet or restaurant COMFORT ROOM restroom; toilet CHANCING sexual advances LIVE-IN living in one’s place of employment BOODLE FIGHT communal eating (?) military style of eating where long tables are prepared and food are on top of the banana leaves References 1. Purposive Communication book 2. Rosado, C. (2010). What makes a school multicultural? from Retrieved from https://www.purdueglobal.edu/blog/humanservices/what-is-cultural-diversity/ 3. Kachru's three concentric circles: the expansion of English. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.studysmarter.us/explanations/english/international-english/kachrus-3-concentric-circles/