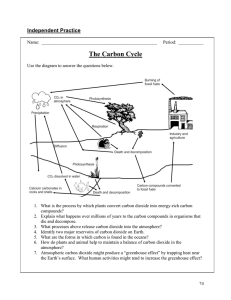
Which process is part of the carbon cycle? Answer: The carbon cycle is the cycle of carbon through the Earth's atmosphere, oceans, and land, and it consists of various processes that move carbon from one reservoir to another. One of the important processes in the carbon cycle involves the exchange of carbon dioxide (CO2) between the atmosphere and the oceans through physical and biological processes. The oceans absorb around 25 percent of the total carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere, and through this process, they help regulate the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. During photosynthesis, plants use carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to produce organic compounds such as sugars, which are then used for energy or stored in tissues. It is a significant biological process that removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and it happens in all plants and other photosynthetic organisms. Another process in the carbon cycle is the decomposition of dead organic matter by fungi, bacteria, and other organisms. This process releases carbon dioxide back into the air or soil as the organic matter is broken down into simpler compounds. Additionally, the burning of fossil fuels by human activities is also a critical process in the carbon cycle. The burning of these fuels releases large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to the current buildup of greenhouse gases that are causing global climate change. References: - IPCC. (2014). Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. - Houghton, R. A. (2007). Balancing the global carbon budget. Annual review of Earth and planetary sciences, 35, 313-347. - NASA. (n.d.). The Carbon Cycle. Retrieved from https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/oco/CarbonCycle-main.html