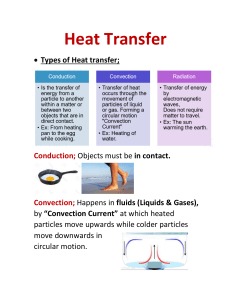
What is convection and how does it affect the movement of air? Answer: Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of a fluid or gas, such as air. When a fluid or gas is heated, it becomes less dense and rises, while cooler, denser fluid or gas sinks to take its place. This creates a circular motion known as a convection current. In the case of air, warmer air rises, creating a low-pressure system, while cooler air sinks, creating a highpressure system. This movement of air can lead to changes in weather patterns and the distribution of heat across the earth's surface. Convection is an important process in the atmosphere, as it helps to distribute heat from the equator towards the poles, as well as to transport moisture and pollutants. It is also the driving force behind many of the earth's natural phenomena, such as thunderstorms, hurricanes, and tornadoes. References: - Encyclopaedia Britannica. (2021). Convection. https://www.britannica.com/science/convection - National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. (n.d.). Convection. https://www.weather.gov/jetstream/convection