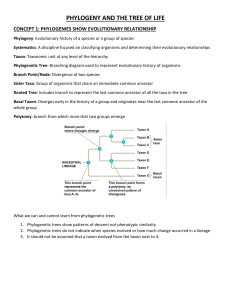
Phylogenetic trees are also called? Phylogenetic trees are also called evolutionary trees, and are used to display the evolutionary relationships among species or groups of species (clades). These trees can provide insights into the history of life on earth, and how different species are related to each other through common ancestry. Phylogenetic trees are constructed using various types of data, such as DNA sequences, morphological traits, or behavioral characteristics, which are used to infer the evolutionary relationships among the different taxa. The tree is usually rooted at a common ancestor of all the taxa being studied, and the branching pattern represents the hypothesized sequence of speciation events that led to the current diversity of life. The branches of the tree are also labeled with measures of evolutionary distance or time, which can be used to compare the rates of evolution among different lineages, or to investigate patterns of diversification or extinction over time. Phylogenetic trees have been used extensively in evolutionary biology to study a wide range of topics, from the origin of life to the diversification of modern species. They are also applied in other fields such as epidemiology, ecology, and even linguistics to study the evolution and spread of diseases, species interactions, and the evolution of languages, among others. References: - Felsenstein, J. (2004). Inferring phylogenies. Sinauer Associates. - Hillis, D. M., & Bull, J. J. (1993). An empirical test of bootstrapping as a method for assessing confidence in phylogenetic analysis. Systematic Biology, 42(2), 182-192. - Darwin, C. (1859). On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life. John Murray.