Concept of Life: Experiments & Theories - High School Biology
advertisement
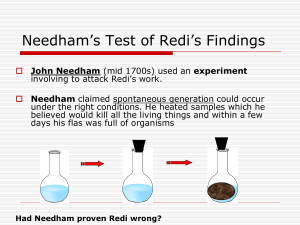
THE CONCEPT OF LIFE GRADE 11 TVL- GROUP 1 Content 01 REDI'S EXPERIMENT 02 NEEDHAM'S EXPERIMENT 03 SPALLANZANI'S EXPERIMENT 04 PASTEUR'S EXPERIMENT REDI'S EXPERIMENT • Francesco Redi, an Italian physician, conducted an experiment that questioned the idea of spontaneous generation in 1668. His experiment involved using maggots that arose in decaying meat to disprove spontaneous generation. He performed the experiment using two sets of identical jars, one with a gauze covering and the other without. REDI'S EXPERIMENT • Redi went on to demonstrate that dead maggots or flies would not generate new flies when placed on rotting meat in a sealed jar, whereas live maggots or flies would. This disproved both the existence of some essential component in once-living organisms, and the necessity of fresh air to generate life. NEEDHAM'S EXPERIMENT • John Needham, an English priest, challenged Redi's experiment in 1748. It was widespread known at that time that boiling could kill microorganisms. His experiment tested whether or not microorganisms can appear spontaneously after boiling. He placed and heated a solution of boiled mutton broth in a container. The flask was then sealed with corks to keep anything from the environment from entering and causing life to grow. MICROORGANISM/MICROBES - Microbes are tiny living things that are found all around us and are too small to be seen by the naked eye. They live in water, soil, and in the air. -A microorganism is defined as a living thing that is so small it must be viewed with a microscope. SPALLANZANI'S EXPERIMENT Lazzaro Spallanzani, an Italian scientist, challenged Needham's experiment in 1767. Spallanzani boiled a broth containing meat and vegetables placed in clean glass containers. Although both containers were boiled, one setup was not sealed, enabling air to enter the flask. After several days, the open flask was filled with a colony of microorganisms, but the sealed container remained sterile. He concluded that life arose from something that entered the open flask and was responsible for life to grow. PASTEUR'S EXPERIMENT • Pasteur designed an experiment to test the idea that a vital element from air was essential for life to exist. In flasks with long neck, he boiled sugar solution with yeasts. The flasks were left open to allow the vital element in air to enter, but no organisms developed in the mixture. It was because the microorganism settled on the bottom of the curved neck of the flask and could not reach the mixture. This experiment supported the theory of biogenesis and disproved spontaneous generation. This evidence suggests that new bacteria appear only when they are produced by 1 . 3 Primodial Soup Theory Penspermia 2 4 Miller-Urey Experiment Early Forms of Life PRIMORDIAL SOUP THEORY • The first idea to capture scientists' attention was the “primordial soup”: the notion that when Earth was young, the oceans were filled with simple chemicals important for life. These would eventually self-assemble into simple living cells. • This was proposed by Alexander Oparin and John Haldane. According to this theory, life started in a primordial soup of organic molecules. This hypothesis deals with the primordial soup that complex biological compounds were randomly assembled by chance in an organic broth on Earth's early surface. Some form of energy from lightning and chemicals from the atmosphere combined to make amino acids, the building blocks of protein. • The theory states that if energy is added to the gases that made up Earth's early atmosphere, the building blocks of life would be created. MILLER-UREY EXPERIMENT • Stanley L. Muller and Harold C. Urey performed an experiment to describe the origin of life on earth. They were of the idea that the early earth’s atmosphere was able to produce amino acids from inorganic matter. The two biologists made use of methane, water, hydrogen, and ammonia which they considered were found in the early earth’s atmosphere. PANSPERMIA • Panspermia supports the idea that a meteor or cosmic dust may have carried to Earth significant amounts of organic molecules, which started the evolution of life. A meteorite found in Antarctica in 1966 suggested that it had been ejected from Mars possibly as a result of a collision with an asteroid. The meteorite contained presence of complex organic molecules and small globules that resemble those found on Earth. • The panspermia hypothesis suggests life began on Earth when the "seeds" of life, already present in the universe, arrived here from space • The panspermia hypothesis suggests life began on Earth when the "seeds" of life, already present in the universe, arrived here from space. EARLY FORMS OF LIFE • About 3.5 billion years ago, the first form of life is believed to have appeared. The first evidence of life is found and seen in microfossils (microscopic fossils). These are fossils that contain the remains of tiny plants and animals. These are very small and can be measured in millimeters. Some could only be identified under a microscope. • The fossils are known as stromatolites and are the evidence of ancient water-based bacterial colonies, which cemented sediments together into distinctive layers with carbonate. Before this new discover, the oldest known fossils were 3.48-billionyear old stromatolites found in Western Australia • PROKARYOTES - organism that do not have a nucleus, such as bacteria and archea. Prokaryotes are small, consist entirely of single cells, have little internal structure, and are known to be the earliest forms of life. • The first photosynthetic organisms to form are the cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae). Cyanobacteria are not actually algae, they are prokaryotic life forms which are normally present in bodies of water. Their microfossils are among the easiest to identify. • Eukaryotes include all complex life on Earth, including every animal, plant, fungus and algae. Their cells are large, structured, and filled with many internal compartments. These include the nucleus, where DNA is stored, and the mitochondria, which act as tiny powerhouses, and other organelles. The first eukaryotes were protists, and the oldest eukaryotic fossils are a type of red algae. ANSWERS ONLY MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following individuals is credited for definitively refuting the theory of spontaneous ganeration using broth in swan-neck flask? A. Aristotle B. Jan Baptista Van Helmot C. John Needham D. Louis Pasteur 2. What was the problem in Redi's experiment? A. How do maggots appear in meat? B. How do worms appear in wood? C. Is spontaneous generation a valid explanation for maggots in meats? D. All of the above 3. What was the variable in his experiment? A. Covering both jars. B. Covering one jar and leaving the other uncovered C. Leaving both jars uncovered. D. There was no variables in his experiment 4. What did the Miller-Urey experiment prove? A. That life arose on earth through abiogenesis B. That life could have arisen on earth through abiogenesis C.That life on earth did not arisen through abiogenesis D. It proved none of these 5. What does the theory of panspermia suggest? A. Life existed in outer space and was transported by meteorites asteroids, or comets to a receptive earth. B. He coined the term panspermia to describe the concepts of life traveling between planet and seed. C. To terraform a planet so that Humanity could extensively then settle it D. A theory that life did not originate on earth but arrived in the form of bacterial spores or viruses. ARRANGE THE JUMBLED LETTERS 6. AHMEEDN - He is an English priest, challenge Redi's experiment in 1748 7. LIADROMIP - According to this theory, life started in a primordial soup of organic molecules 8. TENMIREPEX - Perform a scientific procedure, specially in a labaratory to determine something 9. LASZANLANIP - he challenged Needham's experiment in 1767. 10. YOKATESEUR - It include all complex life on Earth, including every animal, plant fungus ang algae IDENTIFICATION 11. They are prokaryotic life forms which are normally present in bodies of water. 12. The fossils are known as what? 13. Some of the remains of organism do not have a nucleus, so they were called as? 14. These are very small and can be measured in millimetres. 15. Cyanobacteria is also known as what algae? Thanks You!