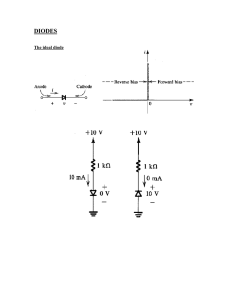
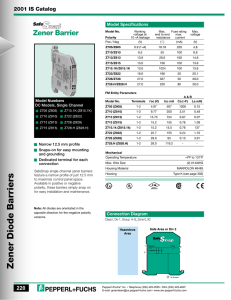
Electronic Devices 10th ed. Chapter 3 Special-Purpose Diodes Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices 10th ed. Objectives: ◆ Describe the characteristics of a zener diode and analyze its operation ◆Apply a zener diode in voltage regulation ◆ Describe the varactor diode characteristic and analyze its operation ◆ Discuss the characteristics, operation, and applications of LEDs, quantum dots, and photodiodes ◆ Explain the basic operation of a solar cell ◆ Discuss the basic characteristics of several types of diodes ◆ Troubleshoot zener diode regulators Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices The Zener Diode The zener diode is designed to operate in the reverse breakdown region. I F Cathode (K) Breakdown VR Anode (A) VZ VF Reversebreakdown region Symbol IR Characteristic curve Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices The Zener Diode The zener diode is designed to operate in the reverse breakdown region. I F Cathode (K) Anode (A) Symbol Ideally, the reverse breakdown has a constant breakdown voltage. This makes it useful as a voltage reference, which is its primary application. Breakdown VR VZ VF Reversebreakdown region IR Characteristic curve Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices The Zener Diode + The zener impedance, ZZ, is the ratio of a change in voltage in the breakdown region to the corresponding change in current: ZZ = Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved VZ I Z ZZ + – VZ – Practical model Electronic Devices The Zener Diode + The zener impedance, ZZ, is the ratio of a change in voltage in the breakdown region to the corresponding change in current: ZZ = VZ I Z ZZ + – VZ – Practical model What is the zener impedance if the zener diode voltage changes from 4.79 V to 4.94 V when the current changes from 5.00 mA to 10.0 mA? Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices The Zener Diode + The zener impedance, ZZ, is the ratio of a change in voltage in the breakdown region to the corresponding change in current: ZZ = VZ I Z ZZ + – VZ – Practical model What is the zener impedance if the zener diode voltage changes from 4.79 V to 4.94 V when the current changes from 5.00 mA to 10.0 mA? ZZ = Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved VZ 0.15 V = = I Z 5.0 mA Electronic Devices The Zener Diode + The zener impedance, ZZ, is the ratio of a change in voltage in the breakdown region to the corresponding change in current: ZZ = VZ I Z ZZ + – VZ – Practical model What is the zener impedance if the zener diode voltage changes from 4.79 V to 4.94 V when the current changes from 5.00 mA to 10.0 mA? ZZ = Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved VZ 0.15 V = = 30 W I Z 5.0 mA Electronic Devices The Zener Diode The temperature coefficient of a zener diode can be specified as the percent change in zener voltage for each degree Celsius change in temperature: VZ TC = VZ T where TC has units of %/oC. Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices The Zener Diode The temperature coefficient of a zener diode can be specified as the percent change in zener voltage for each degree Celsius change in temperature: VZ TC = VZ T where TC has units of %/oC. Alternatively, it can be specified in terms of change in voltage per degree Celsius change in temperature. TC = VZ T where TC has units of mV/oC. Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices The Zener Diode The temperature coefficient can be positive or negative, depending on the zener voltage. Above 5.6 V, zeners generally have a positive temperature coefficient; below about 5.6 V, they have a negative temperature coefficient. Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices The Zener Diode - Example The temperature coefficient can be positive or negative, depending on the zener voltage. Above 5.6 V, zeners generally have a positive temperature coefficient; below about 5.6 V, they have a negative temperature coefficient. A 1N756 is an 8.2 V zener diode (8.2 V at 25o C) with a positive temperature coefficient of 5.4 mV/oC. What is the output voltage if the temperature rises to 50o C? Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices The Zener Diode - Example The temperature coefficient can be positive or negative, depending on the zener voltage. Above 5.6 V, zeners generally have a positive temperature coefficient; below about 5.6 V, they have a negative temperature coefficient. A 1N756 is an 8.2 V zener diode (8.2 V at 25o C) with a positive temperature coefficient of 5.4 mV/oC. What is the output voltage if the temperature rises to 50o C? VZ = TC T = ( 5.4 mV ) ( 25o C ) = 189 mV VZ = 8.2 V + 0.189 V = Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices The Zener Diode - Example The temperature coefficient can be positive or negative, depending on the zener voltage. Above 5.6 V, zeners generally have a positive temperature coefficient; below about 5.6 V, they have a negative temperature coefficient. A 1N756 is an 8.2 V zener diode (8.2 V at 25o C) with a positive temperature coefficient of 5.4 mV/oC. What is the output voltage if the temperature rises to 50o C? VZ = TC T = ( 5.4 mV ) ( 25o C ) = 189 mV VZ = 8.2 V + 0.189 V = 8.389 V Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices The Zener Diode - Application In low current applications, a zener diode can be used as a basic regulator. Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices The Zener Diode - Application In low current applications, a zener diode can be used as a basic regulator. R A 1N756 (8.2 V at 25o C) is used as an 8.2 V regulator in the circuit shown. What is the smallest load resistor that can be used before losing regulation? Assume an ideal zener diode model. Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 1.0 kW + VIN 18 V – 1N756 8.2 V RL Electronic Devices The Zener Diode - Application In low current applications, a zener diode can be used as a basic regulator. R A 1N756 (8.2 V at 25o C) is used as an 8.2 V regulator in the circuit shown. What is the smallest load resistor that can be used before losing regulation? Assume an ideal zener diode model. The no load zener current is I NL = 1.0 kW + VIN 18 V – 1N756 8.2 V VIN − VZ 18 V − 8.2 V = = 9.8 mA R 1.0 kW This is the maximum load current in regulation. Therefore, RL = Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved 8.2 V = 9.8 mA RL Electronic Devices The Zener Diode - Application In low current applications, a zener diode can be used as a basic regulator. R A 1N756 (8.2 V at 25o C) is used as an 8.2 V regulator in the circuit shown. What is the smallest load resistor that can be used before losing regulation? Assume an ideal zener diode model. The no load zener current is I NL = 1.0 kW + VIN 18 V – 1N756 8.2 V VIN − VZ 18 V − 8.2 V = = 9.8 mA R 1.0 kW This is the maximum load current in regulation. Therefore, RL = Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved RL 8.2 V = 837 W 9.8 mA Electronic Devices Zener Diode Application Zeners are embedded in three-terminal regulators to establish a reference voltage. These circuits are capable of much larger load currents than the basic zener regulator shown previously. Control element VIN Ref VIN Voltage regulator Reference ground Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved VOUT Error amplifier VOUT Feedback element Electronic Devices Zener Diode Application Zeners can also be used as limiters. The back-to-back zeners in this circuit limit the output to the breakdown voltage plus one diode drop. R Vin D1 D2 +VZ1 + 0.7 V 0 –VZ1 – 0.7 V Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices Zener Diode Application Zeners can also be used as limiters. The back-to-back zeners in this circuit limit the output to the breakdown voltage plus one diode drop. R What are the maximum positive and negative voltages if the zener breakdown voltage is 5.6 V? Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Vin D1 D2 +VZ1 + 0.7 V 0 –VZ1 – 0.7 V Electronic Devices Zener Diode Application Zeners can also be used as limiters. The back-to-back zeners in this circuit limit the output to the breakdown voltage plus one diode drop. R What are the maximum positive and negative voltages if the zener breakdown voltage is 5.6 V? ± 6.3 V Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Vin D1 D2 +VZ1 + 0.7 V 0 –VZ1 – 0.7 V Electronic Devices Varactor Diodes A varactor diode is a special purpose diode operated in reverse-bias to form a voltage-controlled capacitor. The width of the depletion region increases with reverse-bias. p n Plate Plate Dielectric – VBIAS + Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices Varactor Diodes A varactor diode is a special purpose diode operated in reverse-bias to form a voltage-controlled capacitor. The width of the depletion region increases with reverse-bias. If the depletion widens, does the capacitance increase or decrease? p n Plate Plate Dielectric – VBIAS + Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices Varactor Diodes A varactor diode is a special purpose diode operated in reverse-bias to form a voltage-controlled capacitor. The width of the depletion region increases with reverse-bias. If the depletion widens, does the capacitance increase or decrease? A Hint: C = d p n Plate Plate Dielectric – VBIAS + Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices Varactor Diodes A varactor diode is a special purpose diode operated in reverse-bias to form a voltage-controlled capacitor. The width of the depletion region increases with reverse-bias. If the depletion widens, does the capacitance increase or decrease? A Hint: C = d Notice that as the effective plate separation widens, the capacitance will decrease. Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved p n Plate Plate Dielectric – VBIAS + Electronic Devices Varactor Diodes C T, diode capacitance (pF) Capacitance tolerance range are the range of values of capacitance for a given varactor. The data sheet will show the minimum nominal and maximum values, which are often plotted on a graph. 100 70 50 30 10 7 5 1N5148 1N5144 1N5139 3 1 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved TA = 25 °C f = 1 MHz 1.0 3.0 5.0 7.0 10 VR , reverse voltage (V) 30 50 60 Electronic Devices Varactor Diodes For example, you can use this graph to read the capacitance as a function of reverse voltage for various diodes. C T, diode capacitance (pF) Capacitance tolerance range are the range of values of capacitance for a given varactor. The data sheet will show the minimum nominal and maximum values, which are often plotted on a graph. 100 70 50 30 10 7 5 1N5148 1N5144 1N5139 3 1 Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved TA = 25 °C f = 1 MHz 1.0 3.0 5.0 7.0 10 VR , reverse voltage (V) 30 50 60 Electronic Devices Varactor Diodes The capacitance ratio is the ratio of the diode’s capacitance at the minimum reverse voltage (largest C) to the diode’s capacitance at the maximum reverse voltage (smallest C). Maximum Ratings (TC = 25°C unless otherwise noted) Rating Symbol Value Unit Reverse voltage VR 60 Volts Forward current IF 250 mA RF power input* Pin 5.0 Watts Device dissipation @ TA = 25 °C Derate above 25°C PD 400 2.67 mW mW/° C Device dissipation @ TC = 25°C Derate above 25°C PC 2.0 13.3 Watts mW/° C TJ +175 °C T stg –65 to +200 °C Junction temperature Storage temperature range *The RF power input rating assumes that an adequate heat sink is provided Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices Varactor Diodes The capacitance ratio is the ratio of the diode’s capacitance at the minimum reverse voltage (largest C) to the diode’s capacitance at the maximum reverse voltage (smallest C). Maximum Ratings (TC = 25°C unless otherwise noted) Data sheets also include parameters such as maximum ratings for current, power and temperature. Rating Symbol Value Unit Reverse voltage VR 60 Volts Forward current IF 250 mA RF power input* Pin 5.0 Watts Device dissipation @ TA = 25 °C Derate above 25°C PD 400 2.67 mW mW/° C Device dissipation @ TC = 25°C Derate above 25°C PC 2.0 13.3 Watts mW/° C TJ +175 °C T stg –65 to +200 °C Junction temperature Storage temperature range *The RF power input rating assumes that an adequate heat sink is provided Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices Varactor Diodes Varactor diodes are used in tuning applications. The applied voltage controls the capacitance and hence the resonant frequency. + – VBIAS R2 C1 R1 R3 C2 Vin Vout L Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved D Electronic Devices Varactor Diodes Varactor diodes are used in tuning applications. The applied voltage controls the capacitance and hence the resonant frequency. + By varying R2, the reverse bias on D is changed. This changes the capacitance, and hence the resonant frequency. Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved – VBIAS R2 C1 R1 R3 C2 Vin Vout L D Electronic Devices Diode Symbols Some common diode symbols are shown: Zener Varactor PIN Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Light-emitting Laser Tunnel Photo Schottky Current-regulator Electronic Devices Selected Key Terms-1 Zener diode Varactor Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices Selected Key Terms-1 Zener diode A diode designed for limiting the voltage across its terminals in reverse bias. Varactor Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved Electronic Devices Selected Key Terms-1 Zener diode A diode designed for limiting the voltage across its terminals in reverse bias. Varactor A variable capacitance diode. Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved