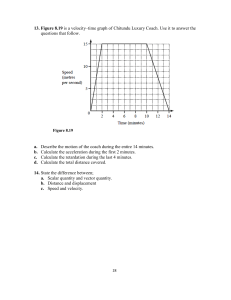
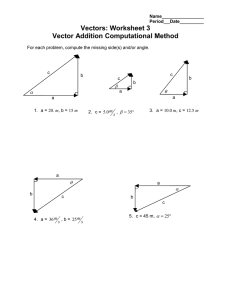
Answers to Exam-style questions 1 Kinematics – describing motion 1 a Distance in a (particular) direction b When athlete returns to his original position/the start (direct) distance from original position is zero. 2 [1] [1] [1] boy s / m 40 38 3635 4 a Vector quantities have direction and scalar quantities do not. One example of a vector, e.g. velocity, acceleration, displacement, force One example of a scalar, e.g. speed, time, mass, pressure [1] [1] [1] 100 km h–1 girl 30 25 N 20 15 10 500 km h–1 resultant 5 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 t/s a straight line from t = 0, s = 0 to t = 12, s = 36 b straight line from t = 0, s = 0 to t = 5, s = 10 straight line from t = 5, s = 10 to t = 12, s = 38 c 10 s 3 a Each second it travels a constant distance At least two examples: 108 − 84 = 24 cm, 84 − 60 = 24 cm, 60 − 36 = 24 cm b speed = d = 24 t 0.1 speed = 240 cm s−1 c 108 + 2 × 24 156 cm [1] [1] [1] [1] b Correct vectors drawn and labelled Scale stated and diagram of sufficient size Resultant velocity 510 (±5) km h−1 11° W of N or a bearing of 349° (±3°) c 0.25 × 510 = 128 ≈ 130 km 11° W of N 5 a velocity of aircraft B [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] 7.5 m s–1 15 m s–1 [1] [1] [1] [1] A Correct vector diagram Velocity of aircraft in still air in easterly direction or calculation b tout = 5000 = 333 s and treturn = 5000 15 13.5 = 370 s [1] [1] [1] total time = 703 or 704 s or 703.7 s average speed = 10000 = 14.2 m s−1 703.7 AS and A Level Physics © Cambridge University Press Chapter 1: Answers to exam-style questions [1] [1] 1