Circulatory System Basics Notes
advertisement

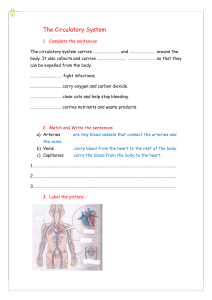
Notes: Circulatory System Basics Theme of the Unit: What Role Does the Circulatory System Have in Helping the Body Maintain Homeostasis? We want you to: 1. Identify and describe the primary function and organs of the circulatory system 2. Describe the difference between the structure & function of each blood vessel Functions of the Circulatory System AKA: Cardiovascular System Circulate blood to TRANSPORT: 1. Oxygen TO cells AND CO2 AWAY from cells 2. Nutrients (glucose) to cells and wastes AWAY 3. Immune system components (WBCs, antibodies) 4. Hormones Circulatory System Organs 1.Blood (last unit) 2.Heart 3.Blood vessels Blood (Review) • Fluid tissue that transports: blood cells, nutrients, gasses oxygen/carbon dioxide, & waste Heart Basics 1. Function: Pump blood through the body 2. Structure: mainly made of cardiac muscle 3. Details: has 4 chambers: – Left & right ventricles – Left & right atriums Blood Vessels • Tubes that transport blood from heart to all cells in the body • 3 types: arteries, veins, capillaries • Each type has a different function Memory Tool to Remember Veins & Arteries VeINs 1. Function: carry blood INto the heart FROM body 2. Structure: THINNER than arteries 3. Details: – Blood here is under LOWER pressure than in arteries – Contain muscular valves to help push blood back INTO to the heart (usually against gravity) Capillaries 1. Function: where exchange of nutrients & oxygen TO cells & waste/CO2 AWAY from cells occurs 2. Structure: tiniest AND thinnest blood vessel - only one cell thick! 3. Details: Connect arteries to veins Memory Tool to Remember Capillaries Connect