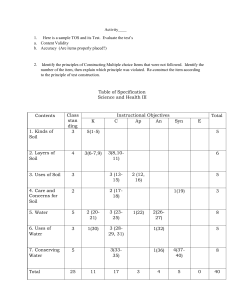
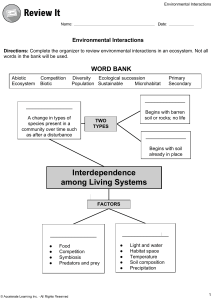
Geotechnical Engineering Sample Examination Reviewer 1. It was originally proposed by the Highway Research Board’s Committee on Classification of Materials for Subgrades and Granular Type Road. According to the present form of the system, soil can be classified according to eight major groups, A-1 through A-8, based on the grain size distribution, liquid limit and plasticity indices. a. AASHTO System c. USDA System b. USCS System d. MIT System 2. It is a soil classification system used in engineering and geology to describe the texture and grain size of a soil. The classification system can be applied to most unconsolidated materials and is represented by a two-letter symbol. a. AASHTO System c. USDA System b. USCS System d. MIT System 3. It is also called as Textural classification system. a. AASHTO System b. USCS System c. USDA System d. MIT System 4. Provides a means of describing the degree and kind of cohesion and adhesion between the soil particles as related to the resistance of the soil to deform or rupture. a. Soil Consistence b. Soil Firmness c. Soil Stability d. Soil Index 5. It is defined as the relative ease with which a soil can be deformed. use the terms of soft, firm, or hard. a. Rupture Consistence b. Soil Consistency c. Rupture Resistance d. Rupture Index 6. Is the attraction of one water molecule to another resulting from hydrogen bonding (water-water bond). a. Cohesion b. Adhesion c. Stickiness d. Plasticity 7. It involves the attraction of a water molecule to a non-water molecule (water-solid bond). a. Cohesion b. Adhesion c. Stickiness d. Plasticity 8. The capacity of soil to adhere to other objects. It is estimated at moisture content that displays maximum adherence between thumb and forefinger. a. Cohesion b. Adhesion c. Stickiness d. Plasticity 9. It is a degree that a soil can be molded or reworked causing permanent deformation without rupturing. a. Cohesion b. Adhesion c. Stickiness d. Plasticity 10. These are the limits of water content used to define soil behavior. a. Atterberg’s Limits b. Liquid Limits c. Soil Limits d. Shrinkage Limits 11. It is a line along which the potential head at all points are equal. a. Flow line b. Energy line c. Equipotential line d. Datum line 12. It is a line along which water particle will travel from upstream to the downstream side in the permeable soil medium. a. Flow line b. Energy line c. Equipotential line d. Datum line