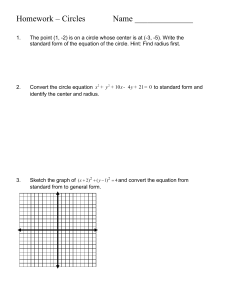
QUALITY CIRCLES Presented By Veena Peter What is a Quality Circle(QC) ?? A quality circle is a small group between three and twelve people who do similar work, voluntarily meeting together regularly for about an hour per week in paid time, who are trained to identify, analyze and solve some of the problems in their work, presenting solutions to management, and where possible, implementing the solutions themselves’ Nature of a Quality Circle… Quality Circles are (informal) groups of employees. Usually the members of a particular team (quality circle) should be from the same work area or who do similar work. The number of members in a quality circle can vary. Other Names of Quality Circles… Small Groups Action Circles Excellence Circles Human Resources Circles Productivity Circles What type of org can use it?? Every organization offering goods or services needs Quality circles to involve its people in Quality consciousness. QCs’ are now used in such diverse industries as : - Engineering industries, - Merchandising, - Hospital, - Canteen, - Insurance and many more. How about Meetings?? For the purpose of continuity and effectiveness it is advisable to hold meeting : Meetings are important part of quality circle's working. Meetings are attended by all the members of the quality circle. In general, meetings take place once a week or once in a fortnight. Each meeting lasts for approximately one hour, though variations are possible. Objectives of QC’s… Change in Attitude From "I don't care" to "I do care”. Continuous improvement in quality of work life through humanization of work. Self Development Bring out the hidden potential of people. People get to learn additional skills. Development of team spirit "I could not do but we did it“. Eliminate inter departmental conflicts. Improved Organizational Culture Positive working environment Total involvement of people at all levels Higher motivational level Participate Management process. Promote job involvement Create problem solving capability Improve communication Promote leadership qualities Promote personal development Develop a greater awareness for cleanliness Develop greater awareness for safety Reduce errors Enhance quality Inspire more effective team work Build an attitude of problem prevention Promote cost reduction Develop harmonious manager, supervisor and worker relationship Improve productivity Increase employee motivation What Quality Circles are Not?? (Misconcepts) QC’s do not tackle just quality problems QC is not a substitute or replacement for task forces, product committees, joint plant councils or works committees, quality assurance department, suggestion schemes. QC’s do not change the existing organizational structure or the chain of command. QC’s are not a forum for grievances or a spring board for demands QC’s are not a means for the management to unload all their problems. QC’s are not just another technique. QC’s are not a panacea for all ills. Structure of QC Program… Top Management Steering Committee Co-ordinator Facilitator Leader Members Roles Played by them… Top Management The success of the QC’s depends solely on the attitude of the Top management and plays an important role to ensure the success of implementation of QC’s. Steering Committee It is called middle management which consists of chief executive heads of different divisions or a coordinator plays a positive role in quality circle activities for the success of the efforts. The meetings are conveyed at least once in one to two months interval Co-ordinator They also act as facilitators, is an individual responsible for coordinating and directing the QC’s activities within an organization and carries out such functions as would make the operations of QC’s smooth, effective and self-sustainable. Facilitator Communicating with all levels of management and obtaining their support and assistance Providing training to QC leaders and assisting in training of QC members where required Maintaining an open and supportive environment Ensuring QC members direct their activities to work- related problems As a mediator in problem-solving As a resource person to the Circle Evaluating the costs and benefits of the QC program and reporting to the Management. Leader Leader of the quality circles is chosen by the members among themselves . Responsible for the smooth operation of QC activities and fostering the spirit of cooperation and harmony among members; Assisting the Circle members in record keeping and in the preparation of management presentations Conducting meetings in an orderly and effective manner Showing interest and support to the Circle Encouraging other workers to become members Assisting members in problem-solving and Enforcing team discipline. Members Members of the quality circles are the small group of people from the same work area or doing similar type of work whereas non-members are those who are not members of the quality circle but may be involved in the circle recommendation. Attending meetings regularly Directing their efforts towards solving work-related problems Identifying problems, contributing ideas, undertaking research and investigation (where necessary) and assisting the QC in problemsolving. Participating in management presentations. How Do Quality Circles Operate? Appointment of a steering committee, facilitator and QC team leaders. Formation of QCs by nomination/voluntary enrolment of QC members. Training of all QC members (by an expert consultant). Training of non-participating employees (by an expert consultant). Problem data bank and identification of problems for QC work. Presentation of QC solutions to management. Evaluation of award/recognition. PROCESS OF OPERATION Problem identification: Identify a number of problems Problem selection : Decide the priority and select the problem to be taken up first. Problem Analysis : Problem is clarified and analyzed by basic problem solving methods Generate alternative solutions : Identify and evaluate causes and generate number of possible alternative solutions Select the most appropriate solution : Discuss and evaluate the alternative solutions by comparison in terms of investment and return from the investment. Prepare plan of action : Prepare plan of action for converting the solution into reality which includes the considerations "who, what, when, where, why and how" of solving problems. Present solution to management circle members present solution to management fore approval. Implementation of solution : The management evaluates the recommended solution. Then it is tested and if successful, implemented on a full scale. Benefits of QC Self development. Promotes leadership qualities among participants. Recognition. Achievement satisfaction. Promotes group/team working. Serves as cementing force between management/non- management groups. Promotes continuous improvement in products and services. Brings about a change in environment of more productivity, better quality, reduced costs, safety and Pitfalls and Problems Lack of faith in and support to Quality Circle activities among management personnel Lack of interest or incompetence of leaders/facilitator Apathy, fear and misunderstanding among middle level executives Delay or non-implementation of Circle recommendations Irregularity of Quality Circle activities Non-application of simple techniques for problem solving Lack of or non-participation by some members in the Circle activities Circles running out of problems Antagonism of non-members towards Quality Circle operations Inadequate visibility of management support Complexity of problems taken up Non-maintenance of Quality Circle records Too much facilitation or too little Language difficulty in communication Communication gap between Circles and departmental head Change of management Confusing Quality Circle for another technique Resistance from trade unions Approach to problems With positive attitude instead of tendency to shrug off problems. Open discussion and Brain storming with every one participating and a positive and cooperative manner will shed new light on the problem. Knowledge and training imparted in application of quality management techniques, circles should approach with confidence to find solutions. BASIC PROBLEM SOLVING TECHNIQUES These are called the old QC tools: Brainstorming Pareto analysis Cause and effect diagram /fish bone diagram /Ishikawa diagram Histogram Scatter diagram Stratification Check sheet Control charts and graphs New QC Tools Quality circles started using additional seven tools as they started maturing: Relations diagram Affinity diagram Systematic diagram or Tree diagram Matrix diagram Matrix data analysis diagram PDPC (Process Decision Program Chart) Arrow diagram APPLICABILITY IN GOVERNMENT ORGANISATIONS The Public Works Department of Government of Maharashtra is responsible for the construction and maintenance of about 2.00 lakhs km. of road net work in the state and a large number of Government-owned buildings spread all over the state. The sub-ordinate officers and staff working in the field and who are well-acquainted with the day-to-day problems in their work areas, are the best judges to decide upon the line of action. The top management in Maharashtra P.W.D. realized this need of the time and introduced the concept of Quality Circle as employee participation method in the organization. The concept of Quality Circle was launched in the Public Works Department of Govt. of Maharashtra on 18-11-1997. Some of the problems solved by the Quality Circles in P.W.D. of Maharashtra are as follows: Eliminating delay in issuing observation memos after inspection of site. Preventing accidents on highways. Reducing electricity bill in office. Avoiding duplication of work. Removal of encroachment from Govt. land. Speeding up pot-hole filling on roads during monsoon. Up keeping of service records of employees Maintaining Govt. offices clean. Stream-lining reservation system of Govt. rest houses. Improvement in maintenance of Govt. Hospital at Sholapur To Conclude With… Quality circles are easily introduced, are simple, and after taking root they can help to create a participatory management culture in organizations. They have considerable potential for altering organizational cultures from topdown, hierarchical, role -bound ones to more participatory, open and experimental ones in development agencies.