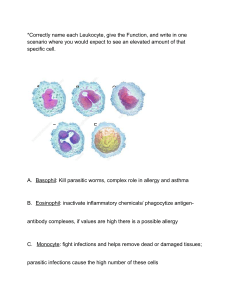
ANTIBIOTICS AMINOGLYCOSIDES Drug Treatment amikacin (Amikin) gentamicin (Garamycin) kanamycin (generic) neomycin (Mycifradin) streptomycin (generic) tobramycin (TOBI, Tobrex) serious gramnegative infections Pseudomonas infection hepatic coma and decrease GI normal flora suppression of GI normal flora tuberculosis Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Poorly absorbed in the GI tract but is rapidly absorbed after intramuscular injections, reaching peak levels of 1 hour. Half-life of 2 to 3 hours. -effects in CNS include ototoxicity, deafness, vestibular paralysis, depression, and weakness. ocular infections Clinically Important Interactions -synergistic bactericidal effects when given with penicillin or cephalosporins - avoid combining diuretics -renal toxicity - GI effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, weight loss, stomatitis, and hepatic toxicity -palpitations, hypotension, and hypertension Contraindications and Cautions contraindicated in patients with known allergy to aminoglycosides; renal or hepatic disease caution is necessary in pregnancy amikacin is very high, use only as long as necessary streptomycin is very toxic to eighth cranial nerve and kidney, to be use only in special situations CARBAPENEMS Drug doripenem (Doribax) ertapenem (Invanz) imipenemcilastatin (Primaxin) meropenem (Merrrem IV) Treatment Pharmacokinetics complicated intraabdominal infections or complicated UTIs communityacquired pneumonia, acute pelvic infections, intra-abdominal infections serious respiratory infections, septicemia, bone and joint infections endocarditis, and polymicrobic infections bacterial meningitis, complicated skin and skin infection -rapidly absorbed if given intramuscularly and reach peak levels at the end of the infusion if given intravenously -excreted unchanged in the urine -half-life of 1 to 4 hours Adverse Effects -superinfections can occur -headache, dizziness, and altered mental state -seizures are reported with combined with other drugs Clinically Important Interactions -consider alternative treatment if patient is on valproic acid Contraindication and Cautions -known allergy to carbapenem or beta-lactam CEPHALOSPORINS Drug Treatment cefadroxil (generic) cephalexin (Keflex) Pharmacokinetics UTIs, pharyngitis, and tonsilitis respiratory, skin, bone, and GU infections -well absorbed in GI tract Adverse Effects -nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia -primarily metabolized in liver Clinically Important Interactions -patients receiving this drug aminoglycoside are at risk for nephrotoxicity Contraindication and Cautions -known allergies to cephalosporins -use with caution in pregnant women -those who receive with anticoagulants are at risk for bleeding - avoid alcohol for 72 hours after discontinuation of the drug SECOND-GENERATION CEPHALOSPORINS Drug Treatment cefaclor (Ceclor) cefoxitin (generic) cefprozil (generic) cefuroxime (Zinacef) Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Clinically Important Interactions Contraindication and Cautions respiratory infections, UTIs, otitis media, typhoid fever, anthrax infection preoperative prophylaxis for cesarian section and abdominal or colorectal surgery pharyngitis. Tonsilitis and secondary bronchial infections wide range of infections THIRD-GENERATION CEPHALOSPORINS Drug Treatment cefdinir (generic; a suspension form is available for children) respiratory infections Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Clinically Important Interactions Contraindications and Cautions cefotaxime (Claforan) moderatesevere infections, peritonitis, septicemia, bone infections cefpodoxime (Vantin) gonorrhea ceftazidime (Ceptaz, Tazicef) CNS infections ceftibuten (Cedax; a suspension form is available for children) exacerbations of bronchitis ceftriaxone (Rocephin) Lyme disease FOURTH-GENERATION CEPHALOSPORINS Drug Treatment cefditoren (Spectracef) acute exacerbations of bronchitis cefepime (Maxipime) skin, urinary, and respiratory infections communityacquired pneumonia ceftaroline (Tefl aro) Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Clinically Important Interactions Contraindications and Cautions FLUOROQUINOLONES Drug ciprofloxacin (Cipro) gemifloxacin (Xtoro) Treatment wide spectrum of gramnegative bacteria otitis media absorbed from the GI tract, metabolized in the liver, and excreted most common are headache, dizziness, insomnia, and depression Clinically Important Interactions Contraindications and Cautions taken concurrently with iron salts, sucralfate, mineral supplements, or antacids, the contraindicated in patients with known allergy to any fluoroquinolone and in pregnant or lactating patients levofloxacin (Levaquin) moxifloxacin (Avelox) ofloxacin (Floxin, Ocuflox) respiratory, urinary tract, skin, and sinus infections adults with sinusitis, bronchitis, or communityacquired pneumonia f respiratory, skin, and urinary tract infections; pelvic inflammatory disease in the urine and feces. Because of its parenteral availability, it may be preferred for severe infections or for use when the patient cannot take oral drugs related to possible effects on the CNS membranes. vomiting, diarrhea, and dry mouth, related to direct drug effect on the GI tract therapeutic effect of the fl uoroquinolone is decreased are taken with drugs that increase the QTc interval or cause torsade de pointes severe-to-fatal cardiac reactions are possible not recommended for use in children younger than 18 years of ag fever, rash, and photosensitivity, a potentially serious adverse effect that can cause severe skin reactions. PENICILLINS AND PENICILLINASE-RESITANT Drug Treatment Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Clinically Important Interactions Contraindications and Cautions penicillin G benzathine (Bicillin, Permapen) Severe infections caused by sensitive organisms; treatment of syphilis and erysipeloid infections -rapidly absorbed -The major adverse effects of penicillin therapy involve the GI tract -taken concurrently patients with allergies to penicillin or cephalosporins or other allergens -Pain and inflammation at the injection site can occur with injectable forms of the drugs. Hypersensitivity reactions may include rash, fever, wheezing, and, with repeated exposure, anaphylaxis that can progress to anaphylactic shock and death -combination with penicillin G potassium (Pfizerpen) severe infections; used for several days in some cases penicillin G procaine (Wycillin) moderately severe infections penicillin V (Veetids) prophylaxis for bacterial endocarditis; Lyme disease, urinary tract infections from the GI tract, reaching peak levels in 1 hour -sensitive to the gastric acid levels in the stomach and should be taken on an empty stomach to ensure adequate absorption. with tetracyclines, a decrease in the effectiveness of the penicillin results. any of the parenteral aminoglycosides, inactivation of the aminoglycosides occurs. amoxicillin (Amoxil, Trimox) Broad spectrum of uses ampicillin (Principen) Broad spectrum of activity; Infections by penicillinaseproducing staphylococci Infections by penicillinaseproducing staphylococci nafcillin oxacillin SULFANAMIDES Drug Treatment Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects sulfadiazine (generic) sulfasalazine (Azulfidine) broad spectrum of infections -are teratogenic - given orally, are -GI effects ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease; rheumatoid arthritis cotrimoxazole (Septra, Bactrim) otitis media, bronchitis, urinary tract infections, and pneumonitis caused by P. carinii absorbed from the GI tract, metabolized in the liver, and excreted in the urine. photosensitivity and rash related to direct effects on the dermal cell effects Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Clinically Important Interactions Contraindications and Cautions taken with tolbutamide, tolazamide, glyburide, glipizide, or chlorpropamide, the risk of hypoglycemia increases. -contraindicated with Clinically Important Interactions Contraindications and Cautions penicillin G and tetracyclines are taken concurrently, the effectiveness of penicillin G decreases contraindicated in patients with known allergy to tetracyclines or to tartrazine any known allergy to any sulfonamide, to sulfonylureas, or to thiazide diuretics because crosssensitivities occur; TETRACYLINES Drug Treatment demeclocycline (generic) wide variety of infections when penicillin cannot be used traveler’s diarrhea and sexually transmitted diseases; periodontal disease doxycycline (Doryx, Vibramycin) absorbed adequately, but not completely, from the GI tract. half-life ranging from 12-25 hours administered on an empty stomach 1 hour before or 2 direct irritation of the GI tract Fatal hepatotoxicity related to the drug’s irritating effect on the liver has also been reported. oral contraceptives are taken with tetracyclines, the effectiveness of the contraceptives should be used with caution in children younger than 8 years of age minocycline (Arestin, Minocin) meningococcal carriers and of various uncomplicated genitourinary and gynecological infections acne vulgaris and minor skin infections caused by susceptible organisms tetracycline (generic) to 3 hours after any meal or other medication decreases, and patients who take oral contraceptives should be advised to use an additional form of birth control while receiving the tetracycline ANTIMYCOBACTERIALS Drug Treatment Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Clinically Important Interactions Contraindications and Cautions ethambutol (Myambutol) isoniazid (Nydrazid) pyrazinamide (generic) rifampin (Rifadin, Rimactane) M. tuberculosis contraindicated for patients with any known allergy to these agents; in those with severe renal or hepatic failure M. tuberculosis neuritis, dizziness, headache, malaise, drowsiness, and hallucinations, are often reported and are related to direct effects of the drugs on neurons. rifampin and INH are used in combination, the possibility of toxic liver reactions increases rifapentine (Priftin) Streptomycin (generic) cycloserine (Seromycin) capreomycin (Capastat) ethionamide (Trecator-SC) rifabutin (Mycobutin) dapsone (generic) M. tuberculosis generally, well absorbed from the GI tract. These drugs, given orally, are metabolized in the liver and excreted in the urine; they cross the placenta and enter breast milk, placing the fetus or child at risk for adverse reactions M. tuberculosis M. tuberculosis M. tuberculosis M. tuberculosis M. tuberculosis M. tuberculosis M. tuberculosis leprosy, P. carinii pneumonia in AIDS patients cause discoloration of body fluids from urine to sweat and tears. KETOLIDE Drug Treatment telithromycin (Ketek) mild to moderate communityacquired pneumonia caused by susceptible bacteria Pharmacokinetics rapidly absorbed through the GI tract, reaching peak levels in 1 hour. Adverse Effects Clinically Important Interactions Contraindications and Cautions half-life of 10 hours nausea, vomiting, taste alterations, and the potential for pseudomembranous colitis. risk of increased serum levels of telithromycin and potentially serious adverse effects if it is combined with pimozide, simvastatin, lovastatin, or atorvastatin contraindicated with known allergy to any component of the drug or to macrolide, with known congenital prolonged QT interval, bradycardia, or any proarrhythmic condition such as hypokalemia Clinically Important Interactions Contraindications and Cautions LINCOSAMIDES Drug Treatment Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects clindamycin (Cleocin) severe infections lincomycin (Lincocin) severe infections rapidly absorbed from the GI tract or from IM injections and are metabolized in the liver and excreted in the urine and feces. Severe GI reactions, including fatal pseudomembranous colitis, have occurred, limiting the usefulness of lincosamides caution in patients with hepatic or renal impairment, which could interfere with the metabolism and excretion of the drug. Use during pregnancy and lactation only if the benefi t clearly outweighs the risk to the fetus or neonate LIPOGLYCOPEPTIDES Drug Treatment Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Clinically Important Interactions Contraindications and Cautions televancin (Vibativ) complicated skin and skinstructure infections It is rapidly absorbed with peak levels occurring at the end of the infusion toxic effects on the GI tract increased risk of prolonged QT interval and resultant arrhythmias if telavancin is combined with other drugs known to prolong the QT interval; contraindicated with known allergy to any component of the drug oritavancin (Orbitiv) telavancin (Vibativ) complicated skin and skinstructure infections complicated skin and skinstructure infections half-life of 8 to 9 hours A transfusion reaction called red man syndrome with flushing, sweating, and hypotension can occur with rapid infusion OXAZOLIDIZONES Drug Treatment linezolid (Zyvox) pneumonia tedizolid (Sivextro) acute skin infections Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Clinically Important Interactions available in oral or IV use. Tedizolid has a half-life of 12 hours, linezolid has 5 hours CNS effects, thrombocytopenia risk for hypertension increased risk of bleeding when combined with NSAIDs Contraindications and Cautions contraindicated with known allergy to the drug components, with PKU avoid foods containing tyramine MACROLIDES Drug Treatment azithromycin (Zithromax) clarithromycin (Biaxin) erythromycin (Ery-Tab, Eryc) mild to moderate respiratory infections various respiratory, skin, sinus, and maxillary infections Pharmacokinetics widely distributed throughout the body treatment of Legionnaire’s disease Adverse Effects most frequent ones, which involve the direct effects of the drug on the GI tract, are often uncomfortable enough to limit the use of the drug. Clinically Important Interactions Contraindications and Cautions increased serum levels of digoxin occur when digoxin is taken concurrently with macrolides contraindicated in patients with a known allergy to any macrolide should be taken on an empty stomach with a full, 8-oz glass of water 1 hour before or at least 2 to 3 hours after meals MONOBACTAM Drug aztreonam (Azactam) Treatment gram-negative enterobacterial infections Pharmacokinetics Adverse Effects Clinically Important Interactions Contraindications and Cautions available for IV and IM use only and reaches peak effect levels in 1 to 1.5 hours. Its halflife is 1.5 to 2 hours GI effects include nausea, GI upset, vomiting, and diarrhea. Aztreonam is incompatible in solution with nafcillin, cephradine, and metronidazole. contraindicated with any known allergy to aztreonam