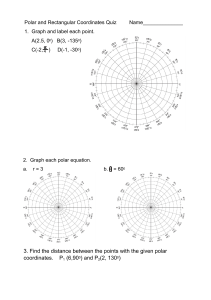
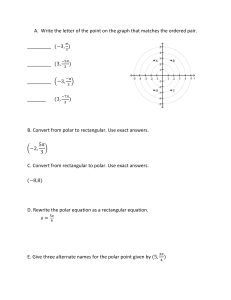
Lesson 9-2 Polar Graphs Plotting points in polar form 1. Use the polar grid to plot these polar points / -\ A 13.+ \ o/ B (4,r) I c' l-r. \ _:: 6/ D (-'.*) I Point conversions 2. Write the rectangular point ( a. r)0, 0>0 3. Change the point 1 ,.6) in polar fonn such that: b. r>A. 0<0 (Z,r) to rectangular form. 4" Change the point to polar lorm. c. r(0, 0>0 (-:,:) d. r(0, Conversion Equations x? +y'= tan9: x= y - 0<A 231 Equation conversions (rectanguiar to polar) -t. -i,=:i 6.3x-y+?=6 Iiquation conr.ersions (polar to rectangular) 8. t'- 2 9. r:3cos0 10. r =? csc0 Sketching polar graphs (use a calculator on those in bold) 11. Circles 12. Rose petalcurves a. r:2cos9 i3. b. r:Ssin?' Linraqons a. r=2*3cosd a. y=Scas(27) b" r':4sin (:e) 14. Lemniscate b. r :3+3sin0 ,'=lsin(Z?) 232 Sketching polar graphs: Circles: r = dqs9 (x-axis symmetry) r = dsin9 @-axis symmetry) Rose petai cur\/es: r: acos(n7) r' Limaqons: r = : l d is the diameter a sin (n0) 11.-axis symmetrl.; a*bcos0 r: atbsin? (x-axis symmetry) (y-axis symmetry) at w-hich the graph I is the maximum r n petals if n is odd, 2n petaTs if r is even may harre inner loop ) Tangent lines I 5' Find an equation of the tansent line to the graph 16' Find the points a (x-axis symmetry) may or may not include the pole of r = z (t *-sin 0) at thepoint i:. o) of r : 2-2cos0 hashorizontal tansenls. 1) Tangent Iines at the pole 17. Find the equations of the ri,es rangent to r:4sin(3d) at the pore l . 4) 21