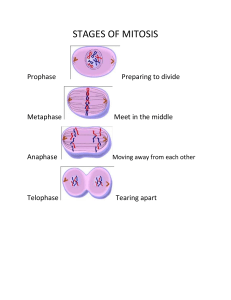
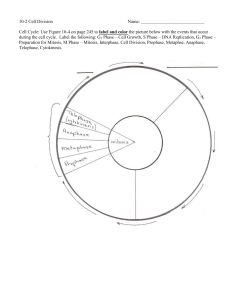
MARCIAL O. RAÑOLA MEMORIAL SCHOOL Guinobatan, Albay LESSON PLAN IN SCIENCE 8 For Demonstration Teaching School Year 2016-2017 D ate: January 27, 2017 I. OBJECTIVES/ INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOMES At the end of the lesson the students are expected to; Identify and describe the stages of mitosis; Differentiate cytokinesis in animal cell and plant cell; Apply the importance of mitosis in everyday life. II. SUBJECT MATTER A. TOPIC: Mitosis B. REFERENCES: Grade 8 Learners Module 5 Unit 4, Pages 321-322 Grade 8 Teachers Guide Module 5 Unit 4, Pages 323-324 Biology Prentice Hall by Miller and Levine, Teachers Edition, Pages 246-248 Biology 9th Edition by Raven, Pages 194-197 C. SCIENCE CONCEPTS Chromosomes are made up of DNA which carries the cells coded genetic information and proteins. Spindle fibers form a protein structure that divides the genetic material in a cell. Centrioles a minute cylindrical organelle near the nucleus in animal cells, occurring in pairs and involved in the development of spindle fibers in cell division. Mitosis is nuclear division plus cytokinesis, and produces two identical daughter cells during prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Prophase is when the chromatin condenses into two rod-shaped structures called chromosomes in which the chromatin becomes visible. Metaphase the second stage of cell division, between prophase and anaphase, during which the chromosomes become attached to the spindle fibers. Anaphase the stage of meiotic or mitotic cell division in which the chromosomes move away from one another to opposite poles of the spindle. Telophase where chromosomes are clustered at opposite poles and condense. Nuclear envelopes re-form around chromosomes and Golgi complex and ER re-form. Cytokinesis is the physical process of cell division, which divides the cytoplasm of a parental cell into two daughter cells. Cleavage furrow is the formation and ingression during animal cytokinesis Cell plate a plate that develops at the midpoint between the two groups of chromosomes in a dividing cell and that is This study source was downloaded by 100000863535798 from CourseHero.com on 03-10-2023 23:53:28 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/31605322/DLP-Mitosis-DEMO-TEACHINGdocx/ involved in forming the wall between the two new daughter cells. Karyokinesis is nuclear division Diploid cells having a complete set of chromosome. D. SCIENCE PROCESSES: Inquiry, differentiating, observing and identifying E. MATERIALS: Laptop, LCD projector, references, pictures, Power point, Mitosis models and visual aids. TEACHERS ACTIVITY III. PRELIMINARY ACTIVITY “Good morning students” STUDENTS ACTIVITY “Good morning Ma’am” Cleaning of assigned areas. “Are all the areas clean?” “Yes Ma’am” “Very good. Before we start let us Students will pray. pray first. Christine please lead the prayer” “Okay class you may take your seats” “None Ma’am” “Class monitor who is absent today” “Very good I’m glad that everyone is present. Check your areas if it’s already clean. Don’t forget to pick up the pieces of paper.” “Yes Ma’am” “Are you excited to learn a new topic this morning?” “Before we proceed to our next “The cell cycle and parts of a discussion lets first have a recap. chromosome” What was our lesson yesterday?” “Very good. We are already done discussing the Cell cycle. Today we will proceed to the next topic. Let’s try to explore how cells present in our body divides and multiply.” IV. LESSON PROPER ELICIT (3 minutes) “Do you believe that we are made up “Yes Ma’am” of cells?” “Did you know that there are two general types of cells that exist in the body of organisms. What do we call “Somatic cells and germ cells” This study source was downloaded by 100000863535798 from CourseHero.com on 03-10-2023 23:53:28 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/31605322/DLP-Mitosis-DEMO-TEACHINGdocx/ these two cells?” “That’s right! What is the difference “Somatic cells are cells that do not between somatic cells and germ participate directly in sexual cells?” reproduction while germ cells are reproductive cells” “Blood cells, epithelial cells, bone “Can you give examples of somatic cells and other differentiated cells cells and germ cells?” are example of somatic cells while sperm and ovum are examples of germ cells” “Very good! Today we will focus on somatic cells.” ENGAGE (3 minutes) Presentation of Pictures “Have you had a really big cut on your “Yes Ma’am” skin?” “It’s no longer present Ma’am” “What happens to your wound after a few days?” “What do you think happened? Why Students will share their ideas. do our wounds heal?” “Okay, how about when you cut your nails and hair? Why do you think that after several days you notice that it’s a “It’s because our cells divide to produce new cells” lot longer from the last time you cut it?” “We will not grow, develop and repair damage tissues” “Yes, that’s right! What do you think will happen if all of our cells stops to divide?” “Mitosis” “Very good your idea is right! What do we call this process that makes “Mitosis is a part of the cell cycle growth, development and repair of when replicated chromosomes are tissues possible?” separated into two new nuclei.” “Right! It is termed as Mitosis. Who can define mitosis?” This study source was downloaded by 100000863535798 from CourseHero.com on 03-10-2023 23:53:28 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/31605322/DLP-Mitosis-DEMO-TEACHINGdocx/ “Correct!” “Very good! Today we are going to investigate the process by which cells make exact copies of themselves. Bone cells repair bone cells, hair cells cause your hair to grow, and new fingernails grow to replace broken ones. Practically every cell in your body is capable of making a copy of itself through the process of mitosis.” EXPLORE (15 minutes) The class will be divided into 5 The students will identify and groups. Each group will be given a describe what happens in the stage of mitosis assigned to them. model of one stage of mitosis. By using the model given they will brainstorm about the important events that occur in each stage. EXPLAIN (10 minutes) After the activity, the teacher will let Each group will describe in front of the class the important events each group present their work. that happens in each phase of mitosis. ELABORATE (19 minutes) “If you can recall the previous topic we discussed about the cell cycle. What is longer interphase or M “Interphase” phase?” “Cells grow” “Very good. What happens in “Cells divide” interphase?” “What happens in mitosis?” “Very good. In order to develop and regenerate new cells mitosis occurs. “Prophase, Biologist divided the events of mitosis metaphase, into four phases. What are these telophase” phases?” prometaphase, anaphase and “In prophase chromosomes “Who can explain the things that condense and become visible. This study source was downloaded by 100000863535798 from CourseHero.com on 03-10-2023 23:53:28 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/31605322/DLP-Mitosis-DEMO-TEACHINGdocx/ happen in prophase?” Chromosomes appear as two sister chromatids held together at the centromere. Cytoskeleton is disassembled; spindle begins to form. Golgi and ER are dispersed and nuclear envelope breaks down.” “Cohesin proteins” “What holds the sister chromatids together?” “Prometaphase” “Very good. follows?” After “What are the prometaphase?” prophase, changes what “Chromosomes attach to during microtubules at the kinetochores. Each chromosome is oriented such that the kinetochores of sister chromatid are attached to microtubules from opposite poles. Chromosomes move to equator of the cell.” “What is the difference prometaphase to metaphase?” “All chromosomes are aligned at of the equator of the cell, called the metaphase plate. Chromosomes are attached to opposite poles and are under tension.” “What do we mean by metaphase “An imaginary line perpendicular plate?” to the spindle fiber.” “Very good.” “After the chromosomes are aligned at “Proteins holding centromeres of the center. What happens in the sister chromatids are degraded, anaphase?” freeing individual chromosomes. Chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles and spindle poles move apart.” “Right! What do you think happens in “The spindle shortens” the spindle fiber during anaphase?” “Yes, that’s why sister chromatids are pulled on the opposite poles.” “After the chromosomes moved in “Telophase where chromosomes each pole. What is the next phase?” are clustered at opposite poles and decondense. Nuclear envelopes re-form around chromosomes and Golgi complex and ER re-form.” “Does cell division end there?” “Yes Ma’am” This study source was downloaded by 100000863535798 from CourseHero.com on 03-10-2023 23:53:28 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/31605322/DLP-Mitosis-DEMO-TEACHINGdocx/ “Not yet. Do you think the cell are divided completely?” “Not yet. The cell still needs to undergo cytokinesis.” “Very good. What is cytokines?” “Cell division” “Right! Cytokinesis occurs in animal cells and plants cells completely. How cytokinesis occurs in animal cells?” “In animal cells, cleavage furrow forms to divide the cells.” “Very good! How about in plants “In plant cells, cell plate forms to cells?” divide the cells.” “Correct!” “After the end of cytokinesis what type “Diploid cells” of cells are produced?” “Very good!” The teacher will use a hand technique that illustrate how mitosis occurs. She The students will apply what they will also ask her students to follow learn during discussion. what she is doing. “To sum up our discussion this morning why does mitosis play a significant role to our lives?” EVALUATE (10 minutes) I. Match the pictures to each The students will answer the following questions and identify stage of Mitosis each phase of mitosis. A B C D E This study source was downloaded by 100000863535798 from CourseHero.com on 03-10-2023 23:53:28 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/31605322/DLP-Mitosis-DEMO-TEACHINGdocx/ Which of the drawings A-E shows? 1. Prophase ______ (chromosomes become visible and spindle fiber forms) 2. Prometaphase _____ (chromosomes connect to the spindle fiber) 3. Metaphase _____ (Chromosomes align at the equator) 4. Anaphase _____ (Sister chromatids separate) 5. Telophase _____ (new nucleus forms at each end) II. Differentiate Cytokinesis in Plant cell and animal cell III. Give one importance mitosis to our life. of EXTEND Answer the following questions: 1. What is Meiosis? 2. What happens during each stage of Meiosis? 3. What is the difference between mitosis from meiosis? 4. What types of cells undergo Meiosis? 5. Does Meiosis produce diploid or haploid cells? Why? 6. Why is Meiosis important? Reference material: Grade 8 Learners Module 5 Unit 4, Pages 324-327 Prepared by: MA. SHARYLN A. NAVIA Student Teacher This study source was downloaded by 100000863535798 from CourseHero.com on 03-10-2023 23:53:28 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/31605322/DLP-Mitosis-DEMO-TEACHINGdocx/ Noted: GLENDA D. DE LA TORRE Cooperating Teacher Approved: LEA R. PALIANGAYAN Head Teacher III, Science Department This study source was downloaded by 100000863535798 from CourseHero.com on 03-10-2023 23:53:28 GMT -06:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/31605322/DLP-Mitosis-DEMO-TEACHINGdocx/ Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)