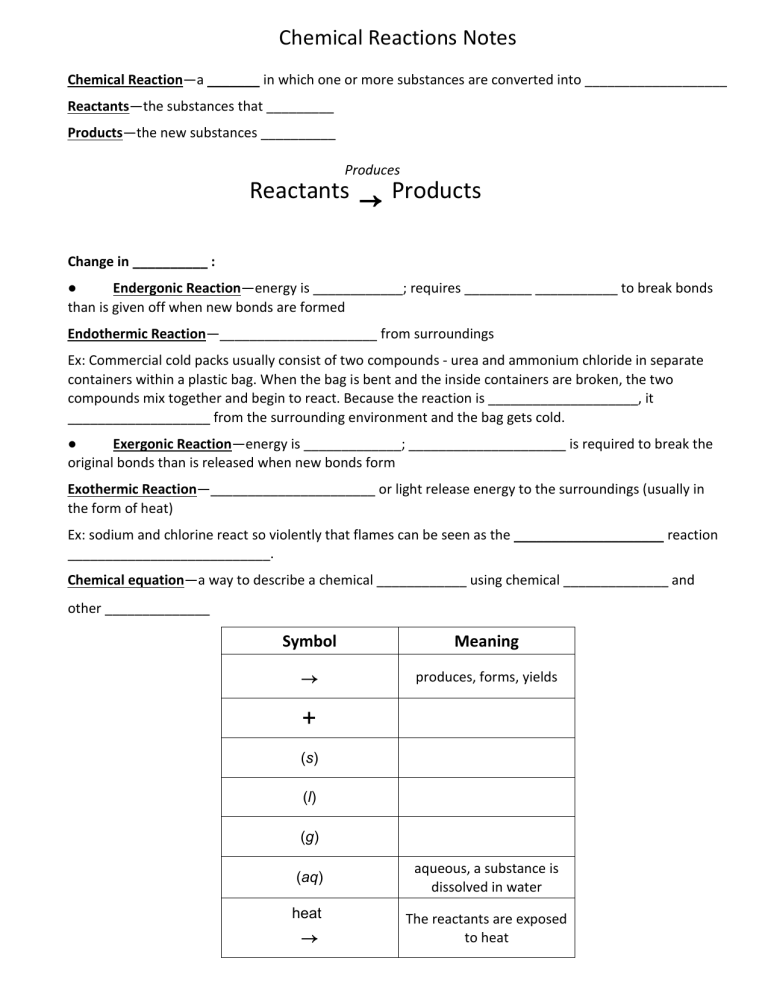
Chemical Reactions Notes Chemical Reaction—a _______ in which one or more substances are converted into ___________________ Reactants—the substances that _________ Products—the new substances __________ Produces Reactants → Products Change in __________ : ● Endergonic Reaction—energy is ____________; requires _________ ___________ to break bonds than is given off when new bonds are formed Endothermic Reaction—_____________________ from surroundings Ex: Commercial cold packs usually consist of two compounds - urea and ammonium chloride in separate containers within a plastic bag. When the bag is bent and the inside containers are broken, the two compounds mix together and begin to react. Because the reaction is ____________________, it ___________________ from the surrounding environment and the bag gets cold. ● Exergonic Reaction—energy is _____________; _____________________ is required to break the original bonds than is released when new bonds form Exothermic Reaction—______________________ or light release energy to the surroundings (usually in the form of heat) Ex: sodium and chlorine react so violently that flames can be seen as the ____________________ reaction ___________________________. Chemical equation—a way to describe a chemical ____________ using chemical ______________ and other ______________ Symbol Meaning → produces, forms, yields + (s) (l) (g) (aq) heat → aqueous, a substance is dissolved in water The reactants are exposed to heat light → The reactants are exposed to light Types of Reactions 1. Synthesis reaction—two or more substances combine to form only ____________________. Synthesis means “to make”. General equation (or general pattern): A + B → AB → 2 NaCl Ex: 2Na + Cl Ex: 2Ag (s) +O2 (g) Ex: calcium + oxygen → calcium oxide → 2AgO (s) What would you see in a ‘test tube’ if you were witness to a synthesis reaction? You would see two different materials combine. A _________ new material appears. 2. Decomposition reaction—___________________ breaks down into _______________________ products; “taking apart” General equation: AX →A Ex: + X BaS Ex: → Ba + S 2H2O (l) Ex: Aluminum fluoride → aluminum + fluoride → 2H2 (g) + O2 (g) In a “test tube” you would see a single material coming ________ into more than one new material. 3. Single Displacement Reaction—_______ element tries to __________ another element in a compound forming a ______________________ leaving the weaker element by itself. General equation (or pattern): A + BC Ex: → AC + B Cu (s) + AgNO3 (aq) → Ag (s) + Cu(NO3)2 (aq) 4. Double Displacement Reaction—when compounds __________ (or exchange) ions General equation (or pattern): XY + BC → XC + BY → Ex: BaS + CaO BaO + CaS Ex: zinc oxide + silver iodide → zinc iodide + silver oxide Law of Conservation of Mass Burning is an example of one the most familiar ______________ changes. When you burn a lump of coal, atmospheric oxygen combines with the coal. The _________________ or __________________ of ________________ differently is called a _________________________. The chemical reaction ____________ carbon dioxide gas, water vapor, and a small amount of ash. This change seems to involve a _______________ in the amount of ____________. A sizable piece of matter seems to have _____________ only a ___________ amount of ash. However, careful ____________________ show that the ________________ (grams) of the _____________ coal and oxygen _____________ the __________________ (grams) of the carbon dioxide, water vapor and ash _________________. Measurements of many chemical reactions lead to the ____________________________________________. This law states that matter ___________ be _____________ nor _______________. This law applies to _____________ reactions where elements on the _______ side of an _______________ must _____________ on the _________ side of the same equation. Not only must the elements be the _________ on each side, but the _____________ of _________ for each __________________ must be the __________ on each side, too. Balanced chemical equation has the same _________ and _____ of atoms on both sides of the __________. CHEMICAL REACTION represented by a CHEMICAL EQUATION CaCl + F → CaF + Cl 2 2 2 2 _______________ (grams) = ______________ (grams) Example 2KClO3 2KCl + 3O2 110g 50g + 60g 110g – 50g = 60g 5. 2H2 + O2 2H2O 4Al + 3O2 2Al2O3 150g + 10g _____g _____g + 75g 150g 2NaCl 2Na + Cl2 N2 + 3H2 2NH3 _____g 15g + 15g 75g + _____g 200g How many grams of sodium iodide (NaI) are produced by the following chemical reaction? 2Na + I 2NaI 2 37g + 52g _____g 6. Dihydrogen dioxide (H O ) decomposes into dihydrogen (H O) monoxide and dioxide (O ). How much dioxide will be produced from the grams of dihydrogen dioxide (H O ) indicated below? 2 2 2 2 3000g 2H O + � 1100g H O + ____g O 2 2 2 2 2 2 Balancing Equations Step-by-Step: Step 1: Determine number of atoms for each element. Mg + O2 → MgO Mg = 1 O=2 Mg = 1 O=1 Step 2: Pick an element that is not equal on both sides of the equation. Mg + O2 → MgO Mg = 1 O=2 Mg = 1 O=1 Since the O atoms are not equal, target those first. Step 3: Add a coefficient in front of the formula with that element and adjust your counts. Mg + O2 → 2 MgO Mg = 1 Mg = 1 2 Adding a 2 in front of MgO will change the number of atoms on the product side of the equation. Step 4: Continue adding coefficients to get the same number of atoms of each element on each side. 2 Mg + O2 → 2 MgO Mg = 1 2 Mg = 1 2 O=2 O=12 Now we need to increase the number of Mg atoms we have on the reactant side. Adding a 2 in front of Mg will give us 2 atoms of Mg and balance the equation. Practice: Is it balanced or unbalanced? 1. __NaCl + __BeF2 → __NaF + __BeCl2 Reactants Products Na Na Cl Cl Be Be F F 3. __CH4 + __O2 → __CO2 + __H2O Reactants 2. __Mg + __Mn2O3 → __MgO + __Mn Reactants 4. Mg Mg Mn Mn O O __FeCl3 + __Be3(PO4)2 → __BeCl2 + __FePO4 Reactants Products Products Products C C Fe Fe H H Cl Cl O O Be Be P P O O Conservation of Mass—the mass of the ____________ always ________ the mass of the ___________. Matter is neither created nor ____________. Atoms are ___________________ but never lost or destroyed. Oxygen + Mercury 0.7 g 9.3 g → Mercury (II) Oxide 10.0 g Balanced chemical equation has the same _________ and _____ of atoms on both sides of the __________.






