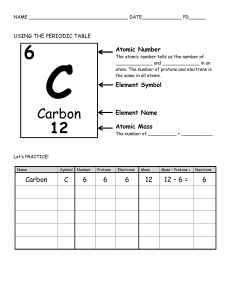
Subatomic Particles Atomic Number Number of protons in a nucleus of an atom Defines the element. Never changes … if it does, the identity of the element changes. Atomic Number Mass Number The sum of protons and neutrons in an atom. The unit of measurement is atomic mass units or amu’s. + o Mass No. = (# p) + (# n) **Mass No. is NOT found on the periodic table! NOT mass number !!! How many protons? How many neutrons? What is the mass number? Isotopes Atoms of the same element + (same # p ), but different number of no. Isotope Notation Z = mass number A = atomic number X = element symbol 107 47 Ag Name: element - Z 107 47 Example: 14 C 6 protons 8 neutrons 6 electrons 14 mass number Name: carbon-14 Ions Atoms of the same element with different number of electrons Have either a pos. (lose e ) or neg. charge (gain e ) Example +2 Ca # p+ = 20 # e- = 18 -3 P # p+ = 15 # e- = 18 Finding Particles Atomic Number = # protons Electrons: If atom is neutral (Ca): #protons = # electrons If +2 (Mg ): atom is charged Charge= # protons + # electrons Mass number (amu)= # protons + # neutrons Atomic Weight Usually, one isotope is more abundant than others. The weighted average of the isotopes of an element. Example: Chlorine has 2 isotopes: 75% …. 35Cl 25% …. 37Cl therefore: 35 amu X 0.75 = 26.25 amu 37 amu X 0.25 = _9.25 amu 35.5 amu