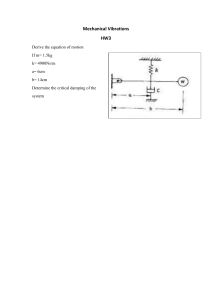
Introduction: The theory of vibrations is an important area of study in mechanical engineering, physics, and other related fields. Vibrations are the back-and-forth motions of a physical system around its equilibrium position. Understanding the theory of vibrations is essential for designing and analyzing mechanical systems such as engines, bridges, and buildings. In this research paper, we will explore the principles of the theory of vibrations, the types of vibrations, and the methods used to analyze and design mechanical systems to withstand vibrations. Principles of the Theory of Vibrations: The principles of the theory of vibrations are based on the concept of harmonic motion. Harmonic motion is the repetitive back-and-forth motion of a physical system around its equilibrium position. The amplitude of the motion is the maximum displacement of the system from its equilibrium position, and the period is the time it takes for one complete cycle of the motion. The theory of vibrations also involves the study of natural frequencies and resonance. Natural frequencies are the frequencies at which a system will vibrate when disturbed from its equilibrium position. Resonance occurs when a system is forced to vibrate at its natural frequency, resulting in large amplitude vibrations that can cause damage to the system. Types of Vibrations: There are several types of vibrations that can occur in mechanical systems, including: 1. Free vibrations: Free vibrations occur when a system is disturbed and then left to vibrate on its own. The amplitude and frequency of the vibration depend on the initial conditions of the system. 2. Forced vibrations: Forced vibrations occur when a system is subjected to a periodic external force. The amplitude and frequency of the vibration depend on the frequency and amplitude of the external force. 3. Damped vibrations: Damped vibrations occur when a system is subject to an external force and experiences resistance due to friction or other factors. The amplitude of the vibration decreases over time due to the damping. Methods of Analysis and Design: There are several methods used to analyze and design mechanical systems to withstand vibrations, including: 1. Modal analysis: Modal analysis involves determining the natural frequencies and modes of vibration of a system. This information can be used to design the system to avoid resonant frequencies. 2. Finite element analysis: Finite element analysis involves using computer models to simulate the behavior of a system under different loading conditions. This can help identify potential areas of stress and deformation. 3. Experimental testing: Experimental testing involves subjecting a physical system to vibrations and measuring the response. This can help verify computer models and identify areas of weakness in the system. Importance of Theory of Vibrations: The theory of vibrations is essential for designing and analyzing mechanical systems to withstand vibrations. Vibrations can cause damage to mechanical systems, resulting in reduced efficiency, increased maintenance costs, and even catastrophic failure. By understanding the principles of the theory of vibrations and using methods of analysis and design, it is possible to create mechanical systems that are resistant to vibrations and can operate safely and efficiently. Conclusion: The theory of vibrations is an important area of study in mechanical engineering, physics, and other related fields. Vibrations are the back-and-forth motions of a physical system around its equilibrium position, and understanding the theory of vibrations is essential for designing and analyzing mechanical systems to withstand vibrations. By understanding the principles of the theory of vibrations and using methods of analysis and design, it is possible to create mechanical systems that are resistant to vibrations and can operate safely and efficiently.