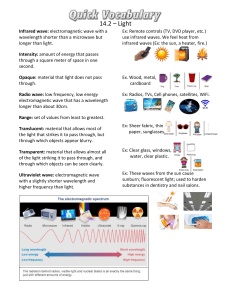
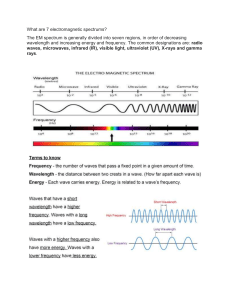
Electromagnetic Waves Name____________________ Q1. The electromagnetic spectrum is made up of waves with different wavelengths and frequencies. (a) Draw one line from each type of electromagnetic wave to a use of that type of wave. Electromagnetic wave Use Cooking food Radio waves Detecting broken bones Visible light Fibre optic communications X-rays Transmitting TV programmes (3) A student investigated how the type of surface affects the amount of infrared the surface radiates. The student used a hollow metal cube. Four of the surfaces of the cube were different. This is the method used. 1. Fill the cube with hot water and seal it with a lid. 2. Measure the infrared radiation emitted from each surface using an infrared detector. Page 1 of 24 The diagram below shows the equipment used. (b) Table 1 shows some of the variables in this investigation. Table 1 Variable Independent Distance between infrared detector and surface of cube Dependent Control ✓ Starting temperature of water inside cube Temperature measured by infrared detector Type of surface Identify each variable as an independent, dependent or control variable. Tick (✓) one box in each row on Table 1. One row has been completed for you. (3) Table 2 shows the results. Table 2 Type of surface Temperature in °C Shiny black 66.5 Matt white 61.0 Matt black 69.0 Shiny silver 26.0 Page 2 of 24 (c) What was the resolution of the infrared detector? Tick (✓) one box. 0.5 °C 1.0 °C 26.0 °C 66.5 °C (1) (d) What was the range of temperatures recorded? Range = _______________ °C to _______________ °C (1) Page 3 of 24 (e) Complete the chart below. You should: • plot the data from Table 2 as a bar chart • label each bar. (3) (f) Give one conclusion that can be made from the results in Table 2. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (1) Page 4 of 24 (g) Which equation links frequency (f), wavelength (λ) and wave speed (v)? Tick (✓) one box. f=v×λ v=f×λ (1) (h) A radio wave has: • a speed of 300 000 000 m/s • a wavelength of 500 m Calculate the frequency of the radio wave. Give the unit. Choose the unit from the box. hertz kilograms metres seconds ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Frequency = _______________ Unit _______________ (4) (Total 17 marks) Q2. X-rays and gamma rays are types of electromagnetic waves. X-rays are used for medical imaging. (a) Which substance will not absorb X-rays? Tick (✓) one box. Bone Metal Skin (1) Page 5 of 24 The table below shows the effect of exposure to different doses of radiation. Dose in mSv Effect on the human body 100 slightly increased risk of cancer 1000 5% increased risk of cancer 5000 high risk of death (b) During one X-ray a person receives a dose of 0.100 mSv Why is this dose unlikely to harm the person? ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (1) (c) A doctor takes an X-ray photograph of a person. When taking the X-ray photograph, the doctor stands behind a screen. Suggest why. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (1) (d) Which of the following are gamma rays used for? Tick (✓) one box. Cooking food Energy-efficient lamps Sterilising medical equipment (1) Page 6 of 24 (e) Why are gamma rays and X-rays harmful to humans? Tick (✓) one box. They are ionising They are radioactive They travel at the speed of light (1) (f) Electromagnetic waves are also used in communications. Describe how microwaves and visible light are used in communications. Microwaves ________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Visible light _________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (4) (Total 9 marks) Q3. Infrared and microwaves are two types of electromagnetic radiation. (a) State one example of the use of each type of radiation for communication. Infrared: ______________________ Microwaves: ___________________ (2) (b) Some of the properties of infrared and microwaves are the same. State two of these properties. 1. _________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 2. _________________________________________________________________ Page 7 of 24 ___________________________________________________________________ (2) (Total 4 marks) Q4. A solar water bag can be used to heat water for an outdoor swimming pool. A student wanted to find out if the colour of the solar water bag affects the temperature increase of the water inside the bag. The diagram below shows some of the equipment used. This is the method used. 1. 2. 3. 4. Fill each bag with water. Place the four bags on the ground outside. After three hours, measure the temperature of the water inside each bag. Repeat steps 1−3 on the next two days. (a) Suggest three changes the student should make to this method to get valid results. 1. _________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 2. _________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ 3. _________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (3) The student repeated the investigation using an improved method. The results obtained were valid. Page 8 of 24 The table below shows the results. Colour of bag (b) Temperature increase in °C Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Mean Black 44.0 31.4 43.4 39.6 Pale blue 38.5 23.6 38.1 33.4 Pale green 37.9 23.7 37.7 33.1 White 25.3 23.4 24.2 X The student used a thermometer to measure the temperature of the water inside each bag. What was the resolution of the thermometer? Resolution = _____________ °C (1) (c) Suggest one reason why the temperatures increased less on Day 2 than on Day 1 and Day 3. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (1) (d) Calculate the mean temperature increase for the white bag. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Mean temperature increase = _____________ °C (1) (e) Which colour of bag would be best to use to heat water? Give a reason for your answer. Colour ____________________________________________________________ Reason ____________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (2) (Total 8 marks) Page 9 of 24 Q5. A baby monitor has a sensor unit that transmits an image of the baby and the noises the baby makes to a monitor unit. The monitor unit then displays an image of the baby and emits the noises the baby makes. (a) Compare the properties of the waves that transmit images and noises from the monitor unit. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (4) (b) The sensor unit can detect infrared and visible light. Suggest one advantage of being able to detect infrared. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (1) (c) Write down the equation that links frequency, wave speed and wavelength. Equation ___________________________________________________________ (1) (d) The signals for the monitor unit are transmitted as electromagnetic waves with a wavelength of 0.125 m. Wave speed of electromagnetic waves = 3 × 108 m / s Page 10 of 24 Calculate the frequency of the signal. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Frequency = __________________ Hz (3) (Total 9 marks) Q6. There are different types of electromagnetic wave (a) Which type of electromagnetic wave has the shortest wavelength? ___________________________________________________________________ (1) (b) A new technology has been developed to charge small electrical devices from the radio waves in the air around us. Explain how radio waves could charge a small electrical device. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (2) The figure below shows the wavefronts of a light wave passing through air into a glass block. (c) Complete the figure to show the wavefronts as they pass out into the air. Page 11 of 24 (2) (d) Explain why there is refraction at the boundary between air and glass. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (3) (e) The period of a wave in a ripple tank was measured. The period of the wave was 420 ms The speed of the wave was 0.60 m/s Calculate the wavelength of the wave. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Page 12 of 24 ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Wavelength = ____________________ m (5) (Total 13 marks) Q7. The electromagnetic spectrum is made up of waves with different wavelengths and frequencies. (a) Give the type of electromagnetic wave with the lowest frequency. ___________________________________________________________________ (1) (b) A wave has a wavelength of 2.5 km and a velocity of 300 000 000 m/s Calculate the frequency of the wave. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Frequency = _______________ Hz (4) (c) The diagram below shows equipment that is used to investigate the emission of infrared radiation from different colours of surface. The four hollow metal cubes are each painted a different colour. The cubes can be filled with hot water before the lid is put on. Page 13 of 24 Describe a method to investigate which colour of surface emits infrared radiation at the greatest rate. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (4) (d) Which colour of surface will emit infrared radiation at the greatest rate? Tick (✓) one box. Black Blue Orange White (1) Page 14 of 24 (e) It is important to identify people at airports who may have infectious diseases, such as measles. Explain how cameras that detect the rate of infrared emission can identify people with infectious diseases such as measles. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (2) (Total 12 marks) Q8. X-rays form part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Radiographers use X-rays to produce images of bones inside the body. (a) Explain why X-rays can be used to produce images of the bones inside the body. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (2) (b) The table below shows the effect of exposure to different doses of radiation. Dose in mSv Effect on the human body 100 slightly increased risk of cancer 1000 5% increased risk of cancer 5000 high risk of death During an X-ray a person receives a dose of 0.5 mSv The radiographer takes many X-ray images each day. Explain why the radiographer stands behind a protective screen when taking an Xray image. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Page 15 of 24 ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (3) (c) Radio waves form part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The diagram below shows one use of radio waves. Explain how electrical signals in the transmitter produce a signal in the receiver. ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ (3) (Total 8 marks) Page 16 of 24 Mark schemes Q1. (a) additional line from a box on the left negates the mark for that box 3 (b) Variable Independent Dependent Control Distance between infrared detector and surface of cube Starting temperature of water inside cube ✓ Temperature measured by infrared detector ✓ ✓ Type of surface 1 1 1 do not accept more than one tick per row (c) 0.5 °C 1 (d) any one from: • 26(.0 °C to) 69(.0 °C) • 69(.0 °C to) 26(.0 °C) ignore 43(.0 °C) 1 (e) 3 bars correctly plotted allow a tolerance of +/- ½ of a small square allow any width, bars touching or not allow 1 mark for 2 bars correctly plotted 2 3 bars correctly labelled Page 17 of 24 1 (f) any one from: • matt black is the best emitter / radiator allow silver is a poor emitter / radiator • shiny silver is the worst emitter / radiator allow black is a good emitter / radiator allow an answer in terms of highest / lowest temperature allow matt white and shiny black are (almost) the same at emitting / radiating ignore any reference to absorption / reflection 1 (g) v=f×λ 1 (h) 300 000 000 = f × 500 1 f= 1 f = 600 000 1 hertz / Hz 1 [17] Q2. (a) skin 1 (b) dose is much lower than even slight increased risk of cancer dose allow much less than 100 mSv 1 (c) to reduce the dose of radiation (they are exposed to) allow reduce the risk 1 (d) sterilising medical equipment 1 (e) they are ionising 1 (f) microwaves data is transmitted / detected allow signal / information for data 1 by (mobile) phone / WiFi / satellite allow bluetooth Page 18 of 24 1 visible light example of device / system 1 description of how light is used e.g. the internet transfers information via visible light in fibre optics e.g. image produced / seen on a TV / mobile phone allow any sensible suggestion for visible light, but the two marks must be linked 1 [9] Q3. (a) use of infrared: remote controls fibre optic (communications) 1 use of microwaves: mobile/cell phones accept mobiles accept phone signals satellite (communications/TV) wi-fi Bluetooth 1 (b) any two from • same speed or travel at the speed of light (in a vacuum) • transverse accept a full description of a transverse wave • transfer energy (from one place to another) • can be reflected • can be refracted • can be diffracted • can be absorbed / transmitted • can travel through a vacuum/space • can be polarised travels in straight lines is insufficient 2 [4] Q4. (a) any three from: • same surface area of bag (exposed to sun) allow same sized bag Page 19 of 24 • same volume / mass of water allow same amount of water • use same starting temperature of water allow measure temperature at the start • • • • • place all bags out at the same time place all bags out in same area / conditions same thickness of material / bag same type of material (for each bag) use IR lamp in a lab 3 (b) 0.1 (°C) 1 (c) any one from: • more cloudy • less sunny ignore less Sun • • less sunlight cooler day 1 (d) 24.3 (°C) 1 (e) black 1 (it has the) greatest (temperature) rise allow it is the best absorber of IR (radiation) ignore best emitter of IR (radiation) 1 reason only scores if black is given [8] Q5. (a) any four from: • • • • • light waves are transverse whereas sound waves are longitudinal light waves travel faster than sound waves light waves have a higher frequency than sound waves light waves have a shorter wavelength than sound waves light waves have oscillations perpendicular (to the direction of energy transfer) whereas sound waves are parallel (to the direction of energy transfer) 4 (b) the baby can be seen in the dark 1 (c) wave speed = frequency × wavelength accept v = f λ 1 (d) 3 × 108 = f × 0.125 Page 20 of 24 1 f = 3 × 108 / 0.125 1 f = 2.4 × 109 (Hz) allow 2.4 × 109 with no working for 3 marks 1 [9] Q6. (a) gamma (waves / rays) allow correct symbol 1 (b) small device absorbs / receives the radio waves allow aerial absorbs / receives radio waves 1 which creates an alternating current of the same frequency (as the radio waves) 1 (c) direction of wave is parallel to the wave entering the block and forms a continuous line 1 wavefronts leaving glass block shown same distance apart as when entering the block 1 (d) wave(front) slows down in glass allow solid for glass allow more dense material 1 one edge of the wavefront enters the glass before the other 1 (therefore) one edge of the wave(front) slows down before the other, so the wave changes direction allow bends for changes direction 1 if no other mark awarded allow 1 mark for wave(front) changes speed and changes direction when it crosses a boundary (e) an answer of 0.25 (m) scores 5 marks T = 0.42 s 1 f = 2.38 allow a correctly calculated value using an incorrectly / not converted value of T 1 Page 21 of 24 0.60 = 2.38 × λ allow use of their value of f calculated using for this and subsequent steps 1 1 λ = 0.25 (m) allow an answer that rounds to 0.25 (m) consistent with their calculated value of f using 1 alternative method T = 0.42 s (1) distance = speed × time (1) allow s = v × t distance is wavelength and time is period of the wave (1) λ = 0.60 × 0.42 (1) λ = 0.25 (m) (1) [13] Q7. (a) radio (waves) 1 (b) 2.5 km = 2500 m 1 300 000 000 = f × 2500 this mark may score if λ is not/incorrectly converted 1 f= this mark may score if λ is not/incorrectly converted 1 f = 120 000 (Hz) or f = 1.2 × 105 (Hz) allow an answer consistent with their value of λ 1 (c) Level 2: The method would lead to the production of a valid outcome. The key steps are identified and logically sequenced. 3−4 Page 22 of 24 Level 1: The method would not necessarily lead to a valid outcome. Most steps are identified, but the plan is not fully logically sequenced. 1−2 No relevant content. 0 Indicative content Measurements • take reading of temperature using infrared detector (and record) • repeat with each cube Control variables • cubes same volume • cubes made of same metal • add same volume of (hot) water • add water at same temperature • distance of detector from surface • air temperature • thickness / type of paint • leave for same amount of time or record every minute Methods with only measurements or only control variables are limited to Level 1 (d) black 1 (e) (people with measles / infections) have raised temperature allow people with measles / infections have fever 1 (so) emit infrared (radiation) at a greater rate ignore emit more infrared (radiation) unqualified 1 [12] Q8. (a) X-rays are absorbed by bone 1 but can pass through flesh ignore skin 1 (b) taking lots of X-rays would give a large dose 1 which would increase the radiographer’s risk 1 the screen absorbs some of the X-rays allow screen reduces the risk/dose received by the radiographer 1 (c) electrical current / oscillations in the transmitter producing radio waves Page 23 of 24 1 radio waves are absorbed by the receiver inducing electrical current / oscillations in the receiver 1 at the same frequency if no other mark is awarded, allow 1 mark for radio waves transfer information/energy through the air 1 [8] Page 24 of 24