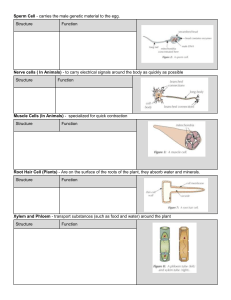
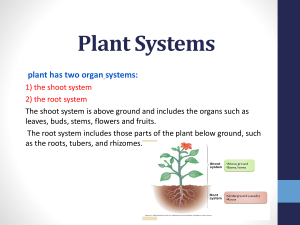
TITLE: Movement through plants 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. What is transpiration? In which type of cell does most photosynthesis take place? What is the function of the roots? Where are the heart pacemaker cells located? What are statins? How can faulty heart valves affect somebody's health? Which three organelles are found only in plant cells? Explain, in terms of the properties of water, why xylem vessels can be hollow. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. What is transpiration? The movement of water up a plant. In which type of cell does most photosynthesis take place? Palisade mesophyll cells. What is the function of the roots? To take in water by osmosis and mineral ions by active transport. Where are the heart pacemaker cells located? Right atrium. What are statins? Drugs that lower bad cholesterol in the blood. How can faulty heart valves affect somebody's health? Blood can flow in the wrong direction. Could lead to a lack of oxygenated blood, so people may feel tired. Which three organelles are found only in plant cells? Cell wall, chloroplasts, vacuole. Explain, in terms of the properties of water, why xylem vessels can be hollow. Water molecules are cohesive, so are drawn up the xylem like a straw. Today we will focus on answering this 6-mark question • Describe the movement of materials up and down the plant. Explain how the plant is organised to allow this movement. Which materials need to move around the plant? 1. 2. What is needed for photosynthesis? What is needed for respiration? Where do the materials start? • Water • Carbon dioxide • Glucose • Oxygen Where do the materials need to go? • Water • Carbon dioxide • Glucose • Oxygen Which structures are involved? Which structures are involved? • • • • Xylem Phloem Root hair cells Leaves (stomata and spongy mesophyll) Adaptations of root hair cells Plants have root hair cells to increase the amount of water absorbed via osmosis Adaptations of xylem • In pairs, discuss adaptations of xylem vessels. Adaptations of phloem • Individually, list the adaptations of phloem vessels. How is the leaf structure adapted? 8 minutes to answer Describe the movement of materials up and down the plant. Explain how the plant is organised to allow this movement. (6 marks) Peer marking- tick each point made examples of points made in the response Ions: (P) taken up by diffusion or active transport • from an area of high to low concentration (diffusion) or an area of low to high concentration (active transport) (V) travels in the xylem (M) to the leaves or from the roots / soil Water: (P) taken up by osmosis • from an area of low to high concentration allow high concentration of water to low concentration of water allow from high water potential to low water potential ignore along a concentration gradient (V) travels in the xylem (M) to the leaves or from the roots / soil (P) transpiration stream • movement replaces water as it evaporates from leaves (V) in the xylem Sugar: (P) made during photosynthesis (V) travels in the phloem (M) to other parts of the plant or to storage organs or travels up and down Peer marking- give them a mark out of 6 Level 3 (5–6 marks): Processes used for obtaining specified materials are given. and correctly linked to the vessels that the materials are transported in or correctly linked to a description of the direction of movement of the materials. For full credit, in addition to the above descriptors at least one of the processes must be linked to the vessel that the material is transported in and the direction of the movement of the material. Level 2 (3–4 marks): At least one process for obtaining a specified material is given and is correctly linked to the vessel that the material is transported in or correctly linked to a description of the direction of movement of the material Level 1 (1–2 marks): At least one process (P) for obtaining a material is given or at least one vessel (V) and the material it carries is given or there is a description of the direction of movement (M) for at least one material 8 minutes to answer Explain how the structure of the leaf is adapted for photosynthesis. Consider: 1. Which materials are needed for photosynthesis? 2. What are the layers of the leaf? 3. How is each layer related to photosynthesis?