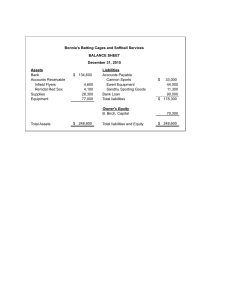
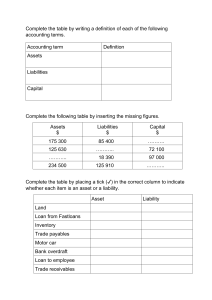
STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL POSITON Learning Outcome(s): At the end of the lesson, the learners are able to identify the elements of the SFP and described each of them and prepare the SFP using the report from and the account form with the proper classification of items as current and noncurrent Lesson Outline: 1. Statement of Financial Position 2. Elements of Statement of Financial Position 3. Steps in preparing Statement of Financial Position Statement of a financial position (SFP) is a statement that gives the financial condition of a business as of a given date. The SFP is another name for balance sheet. It is composed of there elements – assets, liabilities and capital. It provides the owner with an understanding of the financial position of the business. By looking at the SFP of the business, you will be able to answer these following questions: o o o How much are the assets it own? What is the total of its obligations to supplier and external parties? As a capitalist, what is the balance of the owners interest in the business? The financial health of a business can be diagnosed from its SFP. A proprietor needs to validate the SFP to monitor the condition of his / her business and promptly spot any erroneous report that pertains to it. Objective of a General Purpose Statement of Financial Position A general purpose statement of financial position is useful to the various users of financial statements such as the management, stockholders, regulators, creditors and customers. Basis of Classifying Assets and Liabilities For a business owner, knowing when his or her assets will be collected in cash and when his or her liabilities will be paid in cash is important. He or she needs to classify assets and liabilities into current and noncurrent. A business owners guide in classifying assets and liabilities as current and noncurrent is the length of the normal operating cycle of the business of one year. Current Asset = if the asset is not restricted in use, readily convertible to cash, or to be sold or consumed within the normal operating cycle of the business or one year, whichever is longer. Noncurrent Asset = those assets that do not qualify as current asset. Current Liabilities = are debts or obligations normally expected to be settled in the normal course of the company’s operating cycle or within one year by using current assets or creating other current Noncurrent Liabilities = are long terms debts which will be settled beyond one year. In preparing the SFP of a single proprietorship. The following steps must be applied: a. The SFP must have a heading comprising the name of the business, title of the report and date covered by the report b. Its left margin is usually subdivided into two: extreme margin for major subheadings (e.g., current assets; plant, property, and equipment, other noncurrent asset, current liabilities, non-current liabilities; and owners equity) and inner margin for specific account titles. c. At the right margin, the extreme money column is also for major subheading while the inner margin is for specific accounts. d. A double rule is placed under “total assets” and “total liabilities an owners equity. As expressed in the accounting equation, assets must equal liabilities and owner equity.