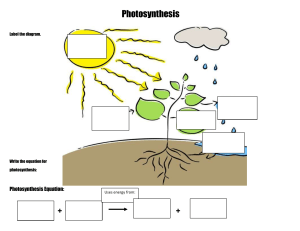
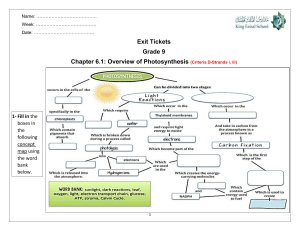
Photosynthesis Chapter: life process , Subtopic of Autotrophic. nutrition Notes Photosynthesis is a process by which plants make their own food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. It is an essential process for life on earth, as it produces the oxygen that we breathe and provides the basis for the food chain. The Process of Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis can be divided into two stages: the lightdependent reactions and the light-independent reactions. During the light-dependent reactions, light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. During the light-independent reactions (also known as the Calvin cycle), carbon dioxide is converted into glucose using the energy stored in ATP and NADPH. Factors Affecting Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis can be affected by various factors, including light intensity, temperature, and the concentration of carbon dioxide. The rate of photosynthesis increases with increasing light intensity, but only up to a certain point. The rate of photosynthesis also increases with increasing temperature, but again, only up to a certain point. The concentration of carbon dioxide also affects the rate of photosynthesis, as it is one of the raw materials needed for the process. Conclusion: Photosynthesis 1 Photosynthesis is a vital process for life on earth, as it provides the basis for the food chain and produces the oxygen that we breathe. Understanding the factors that affect photosynthesis can help us to better appreciate and protect our natural environment. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of organic compounds, primarily carbohydrates. It is the foundation of most food chains and the source of oxygen in the atmosphere. Photosynthesis occurs in two stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (also known as the Calvin cycle). During the light-dependent reactions, light energy is absorbed by pigments in chloroplasts, such as chlorophyll, and used to generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), which are used to power the lightindependent reactions. During the light-independent reactions, ATP and NADPH are used to fix carbon dioxide into organic compounds, primarily sugars. This process is also known as carbon fixation. The light-independent reactions take place in the stroma of the chloroplasts and are regulated by a number of enzymes, including Rubisco (ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase), which is considered the most abundant protein on Earth. Photosynthesis is essential to life on Earth, as it provides the energy and building blocks necessary for the growth and survival of most organisms. It also plays a critical role in the global carbon cycle, regulating the balance of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. There are a number of factors that can influence photosynthesis, including light intensity, temperature, and the availability of carbon dioxide and water. Scientists continue to study photosynthesis to better understand its mechanisms Photosynthesis 2 and potential applications, such as in the development of renewable energy sources. 📌 SUMMARY: Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of organic molecules, such as glucose. It occurs in specialized structures within cells called chloroplasts, which contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that absorbs light. The process of photosynthesis can be divided into two stages: the lightdependent reactions and the light-independent reactions. During the lightdependent reactions, light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and used to generate energy carriers such as ATP and NADPH. These energy carriers are then used in the light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle, to convert carbon dioxide into organic molecules. Photosynthesis plays a critical role in the global carbon cycle, as it removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and releases oxygen. It is also the foundation of most food chains on Earth, as it provides the energy source for primary producers such as plants, which are then consumed by other organisms. Overall, photosynthesis is a complex process that is essential for life on Earth. Understanding the mechanisms of photosynthesis has important implications for fields such as agriculture, climate science, and renewable energy Photosynthesis 3