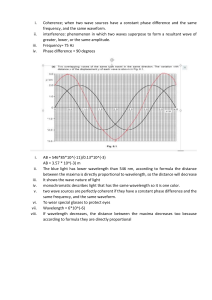
University of Gondar community school physics worksheet for grade 12 on sound and wave optics 1. Two waves being produced by two sources S1 and S 2 . Both sources have zero phase difference and have wavelength . The destructive interference of both the waves will occur of point P if 11 3 B) C) 2 D) S1 P − S 2 P has the value: A) 5 4 2 2. In general, sound is conducted fastest through A) gases. B) liquids. C) solids. D) a vacuum 3. As the temperature of the air increases, what happens to the velocity of sound? (Assume that all other factors remain constant.) A) It increases. B) It decreases. C) It does not change. D) It increases when atmospheric pressure is high and decreases when the pressure is low. 4. Compared to the velocity of a 400 Hz sound, the velocity of a 200 Hz sound through air is A) twice as great. B) the same. C) one-half as great. D) none of the above 5. The intensity of a point source at a distance d from the source is I. What is the intensity at a distance 2d from the source? A) 4I B) 2I C) I/2 D) I/4 6. You double your distance from a sound source that is radiating equally in all directions. What happens to the intensity level of the sound? It drops by A) 2 dB. B) 3 dB. C) 6 dB. D) 8 dB. 7. You move slowly toward a speaker emitting a pure tone. What characteristic of the sound increases? A) frequency B) amplitude C) wavelength D) period 8. You shout at a cliff, and hear the echo in 4.00 s. The temperature is 00C. How far away is the cliff? A) 662 m B) 680 m C) 1320 m D) 1760 m 9. What is the intensity level of a sound with intensity 10-3 W/m2? A) 30 dB B) 60 dB C) 90 dB D) 96 dB 10. The intensity level is 65 dB at a distance 5.00 m from a barking dog. What would be the intensity level if two identical dogs very close to each other are barking? A) 65 dB B) 68 dB C) 130 dB D) 136 dB 11. At a distance of 15 m from a sound source the intensity level is 60 dB. What is the intensity level (in dB) at a point 2.0 m from the source? Assume that the source radiates equally in all directions. A) 55.7 dB B) 57.5 dB C) 75.5 dB D) 77.5 dB 12. A sound source (normal frequency of 1000 Hz) approaches a stationary observer at one-half the speed of sound. The observer hears a frequency of A) 2000 Hz. B) 500 Hz. C) 1500 Hz. D) 200 Hz 13. A girl on the beach watching water waves sees 4 waves pass by in 2 seconds, each with a wavelength of 0.5 m. The speed of the waves is A) 0.25 m/s B) 0.5 m/s C) 1 m/s D) 2 m/s 14. If a 1kHz sound source moves at a speed of 50.0 m/s toward a listener who moves at a speed of 30.0 m/s in a direction away from the source, what is the apparent frequency heard by the listener? (The speed of sound is 343 m/s.) A) 796 Hz B) 949 Hz C) 1 000 Hz D) 1070 Hz 15. An oscillating system is used to create succession of waves on a water surface. The rate of wave generation is one every 0.33 seconds. What is the period of these waves? A.0.3s B.2.0s C.1.0s D.3.0s 16. If the amplitude of a sine wave is doubled, the intensity A) remains the same B) increases by a factor of 2 C) increases by a factor of 4 D) increases by a factor of 16 17. A two-slit interference pattern is formed using monochromatic laser light that has a wavelength of 640 nm. At the second maximum from the central maximum, what is the path-length difference between the light comings from each of the slits? A) 640 nm B) 320 nm C) 960 nm D) 1280 nm 18. Newton postulated his corpuscular theory on the basis of A) Newton’s rings B) Colors of thin films C) Rectilinear propagation of light D) Dispersion of white light 19. Two waves are known to be coherent if they have A) Same amplitude B) Same wavelength C) Same amplitude and wavelength D) Constant phase difference and same wavelength 20. In figure, a wave front AB moving in air is incident on a plane glass surface xy. Its position CD after refraction through a glass slab is shown also along with normals drawn at A and D. the refractive index of glass with respect to air sin sin will be equal to A) B) ' sin sin ' BD AB C) D) CD AC 21. A two-slit interference pattern is formed using two different monochromatic lasers, one green and one red. Which color light has its first maximum closer to the central maximum? A) green B) red C) Both maxima are at the same location. D) no maxima 22. A line representing a wave front for a wave should be drawn: A) from the source to the receiver. C) along one of the crests of the wave. B) from one crest to the preceding crest. D) in the direction the wave is moving. 23. Light from a small region of an ordinary incandescent bulb is passed through a yellow filter and then serves as the source for a Young’s double-slit experiment. Which of the following changes would cause the interference pattern to be more closely spaced? A) Use slits that are closer together B) Use a light source of lower intensity C) Use a light source of higher intensity D) Use a blue filter instead of a yellow filter 24. When a plane wave front is incident on a double convex lens, the refracted wave front is A) a plane wave front. C) a spherical wave front which is diverging. B) a cylindrical wave front. D) a spherical wave front which is converging. 25. A ray of light having wavelength 720 nm enters in a glass slab of refractive index 1.5. The wavelength of the ray within the glass will be A) 360 nm B) 480 nm C) 720 nm D) l080 nm 26. When a soap bubble is in air, it exhibits different colors under sunlight. The absence of a particular color in a region is due to A) Double refraction. B) Straight line propagation of light. C) Destructive interference of light of that color in that region. D) Constructive interference of light of that color in that region 27. A soap bubble (n = 1.33) floating in air has the shape of a spherical shell with a wall thickness of 120 nm. What is the wavelength of the visible light that is most strongly reflected? A) 612 nm B) 560 nm C) 638 nm D) 588 nm 28. In the Young’s double slit experiment for which colour the fringe width is least A) Red B) Green C) Blue D) Yellow 29. In an experiment to measure the wavelength of light using a double slit, it is found that the fringes are too close together to easily count them. To spread out the fringe pattern, one could: A) decrease the slit separation B) increase the width of each slit C) increase the slit separation D) decrease the width of each slit 30. In Young’s double - slit experiment interference pattern which one of the following activities move the successive bright fringes farther apart? A) Decreasing the wavelength of the light. B) Decreasing the distance between the viewing screen and the double slit. C) increasing the slit spacing. D) Decreasing the slit spacing. 31. What happens if the monochromatic light used in Young’s double slit experiment is replaced by white light? A) No fringes are observed. B) All bright fringes become white. C) All bright fringes have colors between violent and red. D) Only the central fringe is white, all other fringes are colored. 32. A light source simultaneously emits light of two wavelengths, 480 nm and 560 nm, respectively. The source is used in a double-slit interference experiment where the slit spacing is a 0.040 mm, and the distance between double slits and the screen is 1.2 m. What is the separation between the second-order bright fringes of the two wavelengths as they appear on the screen? A) 0.16 cm B) 0.32 cm C) 0.48 cm D) 0.64 cm 33. A thin film of thickness t and index of refraction 1.33 coats a glass with index of refraction 1.50 as shown in figure below. Which of the following thicknesses t will not reflect light with wavelength 640 nm in air? A) 160 nm B) 240 nm C) 360 nm D) 480 nm 34. White light is incident normally on a thin soap film having an index of refraction of 1.34. It reflects with an interference maximum at 684 nm and an interference minimum at 570 nm with no minima between those two values. The film has air on both sides of it. What is the thickness of the soap film, assumed uniform? A) 766 nm B) 627 nm C) 638 nm D) 894 nm 35. Monochromatic light of wavelength 500 nm is incident normally on a grating. If the third-order maximum of the diffraction pattern is observed at 320, how many total number of maxima can be seen? A) 5 B) 7 C) 10 D) 11 36. Light of wavelength 500 nm illuminates a soap film ( n = 1.33). What is the minimum thickness of film that will give an interference when the light is incident normally on it? A) 24 nm B) 94 nm C) 188 nm D) 376 nm 37. If the shift of wavelength of light emitted by a star is towards violet, then this shows that star is A) Stationary B) Moving towards earth C) Moving away from earth D) Information is incomplete 38. A single slit forms a diffraction pattern, with the first minimum at an angle of 300 from central maximum, when monochromatic light of 630 nm wavelength is used. The same slit, illuminated by a new monochromatic light source, produces a diffraction pattern with the second minimum at a 530 angle from the central maximum. What is the wavelength of this new light? A) 504 nm B) 450 nm C) 475 nm D) 500 nm 39. The reason there are two slits, rather than one, in a Young’s experiment is: A) to increase the intensity B) one slit is for frequency, the other for wavelength C) to create a path length difference D) two slits in parallel offer less resistance 40. Light from a small region of an ordinary incandescent bulb is passed through a yellow filter and then serves as the source for a Young’s double-slit experiment. Which of the following changes would cause the interference pattern to be more closely spaced? A) Use slits that are closer together B) Use a light source of lower intensity C) Use a light source of higher intensity D) Use a blue filter instead of a yellow filter 41. Radio waves are readily diffracted around buildings whereas light waves are negligibly diffracted around buildings. This is because radio waves: A) are plane polarized B) have much longer wavelengths than light waves C) have much shorter wavelengths than light waves D) are nearly monochromatic (single frequency) 42. A slit of width 0.010 mm has light of frequency 5 x 1014 Hz passing through it onto a screen 60 cm away. How wide is the central maximum? (c = 3 x 108 m/s) A) 0.12 cm B) 7.2 cm C) 1.8 cm D) 3.6 cm 43. When monochromatic light illuminates a grating with 8000 lines per centimeter, its second order maximum is at 530. What is the wavelength of the light? A) 336 nm B) 363 nm C) 452 nm D) 500 nm 44. If Young’s interference experiment is performed using two separate identical sources of light instead of using two slits illuminated by a single source . A) interference fringes will be brighter B) no fringes will be obtain C) interference fringes will be darker D) number of interference fringes will increase 45. The diffraction pattern due to circular aperture consists of A) a bright central disc surrounded by alternate dark and bright concentric rings B) a dark central disc surrounded by alternate dark and bright concentric rings C) a bright central disc only D) a bright central disc surrounded by alternate dark and bright concentric rings with equal spacing between the rings. 46. The number of rulings (N) in grating is made larger, then A) the principal and secondary (all) maxima will become sharp and intense B) the principal and secondary (all) maxima will become faint and wide C) the principal maxima will become intense and sharp, while secondary maxima become weaker D) the principal maxima become weaker while secondary maxima become sharp and intense. 47. Newton’s idea that a light beam consists of tiny particles did NOT correctly predict A) that light beams travel in straight lines. B) that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. C) the law of refraction. D) that the speed of light in substances with high refractive indices is lower than that in air. 48. A glass (n = 1.6) lens is coated with a thin film (n = 1.3) to reduce reflection of certain incident light. If λ is the wavelength of the light in the film, the least film thickness is: A. less than λ/4 B. λ/4 C. λ/2 D. λ 49. Three experiments involving a thin film (in air) are shown. If t denotes the film thickness and λ denotes the wavelength of the light in the film, which experiments will produce constructive interference as seen by the observer? The incident light is nearly normal to the surface. A) I only B) II only C) III only D) I and III only E) II and III only